What is CPU?
The CPU is the brains of the computer. Sometimes referred to simply as the processor or central processor, the CPU is where most calculations take place. In terms of computing power, the CPU is the most important element of a computer system.
On large machines, CPUs require one or more printed circuit boards. On personal computers and small workstations, the CPU is housed in a single chip called a microprocessor.
Advance knowlegde of CPU:
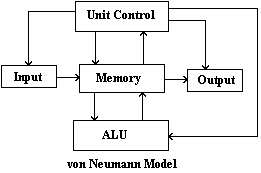
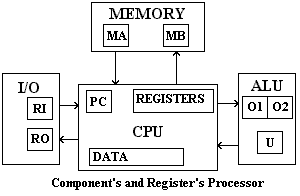
CPU consists of several components: memory, input/output, registers ,aritmetic logic unit,, control units
Memory:
In writing and reading memory address is loaded with address of data to push into or pull from memory. In reading data is stored into Memory Buffer. In writing is pushed into Memory Buffer and after is stored in memory. Read enable and Write enable are processor signal to perform reading or writing.
Input/Output:
Every Input/Output task is carried out by specific programs. Generally CPU does not comunicate directly with other devices. It comunicate with registers and bus that comunicate with devices. We have two registers and I/O tasks are only MOVE from a register to another.
Registers:
Registers are device where save data. They are like main memory: the main difference is that registers are located phisicaly in the CPU and so they are more fast then memory located outside CPU chip. A register can be caractherized by a number: the bit number that can be stored.
ALU-Aritmetic logic unit:
Under processor's order, it can perform aritmetic and logic operations on data given by processor. Generally it is included in the same processor chip. Data to perform are stored in two input register (O1, O2 figure), and the operation result is stored in output register (U).
Control unit:
The control unit, which extracts instructions from memory and decodes and executes them, calling on the ALU when necessary.
|