
The skin is the largest organ of the body and accounts for about 20 pounds or 16% of the body's weight. It is the body's first line of defense to bacteria, chemicals, and other foreign invaders.
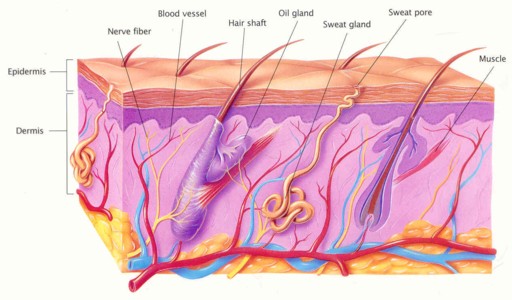
The integumentary system includes skin and its appendages:
1. nails
2. hair
3. sweat and apocrine glands
4. nerve endings to feel pain, temperature, pressure, and touch
More on the Integumentary System
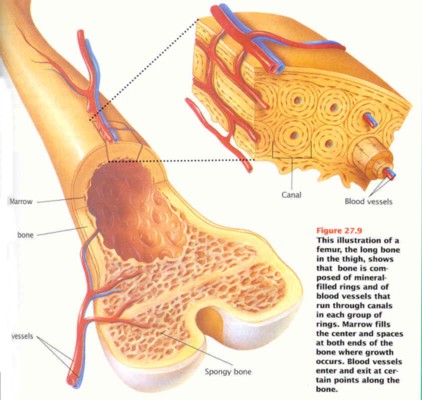
The human body consists of 206 bones which are used to:
 1. Support the body
1. Support the body
2. Movement
3. Protects the organs in the trunk of the body
4. Produce red and white blood cells (in bone marrow)
This system also includes ligaments which hold bones together. (If bones touched each other they would fuse together) Cartilage is also associated with this system.
The body has 3 types of muscles for specific functions:
1. Smooth muscle = involuntary muscles
2. Skeletal muscle = voluntary muscles
3. Cardiac muscle = heart muscle
 Muscles do more than move the body, it also regulates body temperature by creating heat.
Muscles do more than move the body, it also regulates body temperature by creating heat.
This system includes the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system:
1. Central nervous system = brain & spinal cord
2. Peripheral nervous system = all nerves expanding throughout the body.
The primary functions of the nervous system are:
1. Communicate body functions from the brain to involuntary and voluntary organs.
2. Control and coordinate body functions incuding glands and hormones
3. Recognize outside stimuli (sight, sound, touch, taste, feel)
Similarly to the nervous system, the endocrine system functions to communicate, integrate, and control different parts of the body. The body has several glands such as the:
1. Adrenal glands
2. Hypothalamus
3. Pineal gland
4. Pituatary gland
5. Thyroid
6. Parathyroid
7. Thymus
8. Pancreas
9. Ovaries (female) ot Testes (male)
This system circulates oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the body and rids the body of toxic wastes and carbon dioxide. It is composed of:
 1. Heart
1. Heart
2. Arteries
3. Capillaries
4. Veins
5. blood
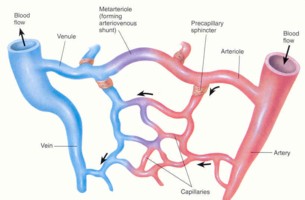
More on the Circulatory System
This system moves fluids and certain large molecules around the body. It is very important in reducing swelling in parts of the body.
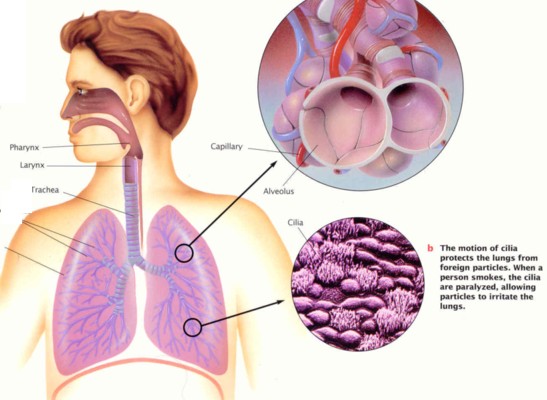 The main function of this system is to absorb oxygen and exchange it with carbon dioxide. Its components include:
The main function of this system is to absorb oxygen and exchange it with carbon dioxide. Its components include:
1. Pharnyx
2. Larnyx
3. Trachea
4. Bronchi
5. Lungs
6. Alveoli
More on the Respiratory System
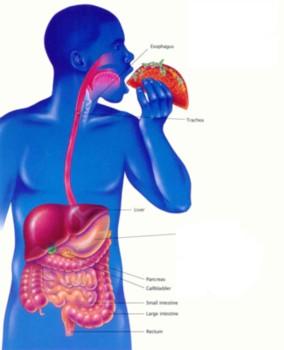
Several organs and glands are involved in this system which begins with the mouth and ends with the anus.
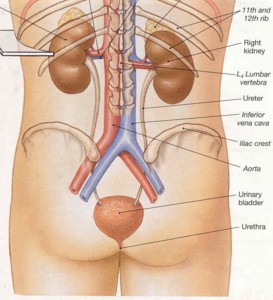
This system filters out wastes from the blood. Blood runs through the kidneys and are cleaned out. The wastes then pass through the ureters and are stored inside of the bladder will it will later be excreted through the urethra.
This system includes the organs that secrete hormones, create gametes (sex cells like sperm and eggs), and the structures that are used for conception and developing offspring.
More on the Reproductive System
Organ transplants are another option for people who need to replace vital organs such as the heart, liver, kidney, bone marrow, or pancreas. Of course, these organs are donated from people who recently died and declared to family members that their dying wish would be to donate their organs.
Why is knowledge about cell surface markers important for successful organ transplants?
Embryonic stem cell research is vital to learning how to make new organs which will match a person's cell surface markers. This will reduce the chance of the body rejecting the new organ that has been transplanted.
Grafting is a procedure that takes tissue from a person and transplants it to another part of their own body. This is especially used for burn victims and women with breast cancer.
Genetic Enigineers are currently trying to combine human DNA with pig DNA. Their purpose is to create a species of pig that can be used for heart transplants.