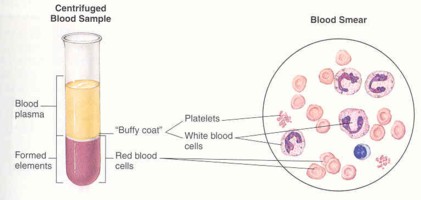
 Blood is a connective tissue made up of several components. Plasma is a clear, protein-rich liquid which makes up 55% of blood.
Plasma includes albumins (Thicken blood), globulins ( antibodies), and fibrinogen (blood clots).
Blood is a connective tissue made up of several components. Plasma is a clear, protein-rich liquid which makes up 55% of blood.
Plasma includes albumins (Thicken blood), globulins ( antibodies), and fibrinogen (blood clots).
The other 45% is red blood cells (rbc) or erythrocytes, white blood cells (wbc) or leukocytes, and platelets or thrombocytes.
Hematocrit is a percentage of the number of cells in the blood. Doctors look at the volume of RBCs as compared to everything else in the blood.
Blood serum is plasma without fibrinogen, so it can be used for its antibodies.
The average person has about 4 -6 Liters of blood or 7 - 9% of their body weight.
There are 2 kinds of connective tissue is blood. Myeloid tissue (pertains to bone marrow) and lymphatic tissue (make lymphocytes and monocytes) Lymphocytes are cells that rid the body of wastes and swelling. Monocytes are cells of the immune system.

 Red blood cells = carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. It also takes away carbon dioxide from the cells and returns it to the lungs. Carbon dioxide is toxic to the body and can poison your body if there is a build-up. This is what makes blood appear red.
Red blood cells = carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. It also takes away carbon dioxide from the cells and returns it to the lungs. Carbon dioxide is toxic to the body and can poison your body if there is a build-up. This is what makes blood appear red.
Red blood cells are unique because it is the only cell in your body that does not have a nucleus. Therefore, there is no DNA in a rbc.
Each rbc lives for only 4 months and is filtered out of the body via the spleen. Bone marrow makes new rbc. Every second 2 million new rbc are made.
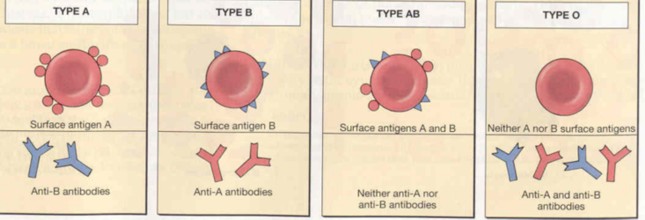
Red blood cells may have surface antigens which are distinguished by blood types A, B, AB, or O.
Blood type O does not have the surface antigens and can be donated to any person who needs a blood transfusion.
Blood type A can only accept type A or type O blood.
Blood type B can only accept type B or type O blood.
Blood type AB can only accept type AB or type O blood.
White blood cell = defend the body from invaders such as bacteria and insect bites. When fighting off intruders, pus builds up and swells in an area.
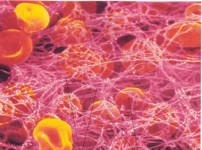
Platelets = Work to repair damage to blood vessels. They secrete fibrin which clots the blood to stop the cut from bleeding. Prothrombin, a clotting factor triggers thrombin which triggers fibrinogen to make the fibrin threads.
Neutrophil = phagocytes invaders. About 60 - 70% of all WBCs.
Eosinophil = attacks parasites such as worms by injecting enzymes that kill them. Makes up about 1.5% of WBCs.
Basophil = Responds to swelling (inflammation) by releasing histamines that cause blood to rush to an injury site.
B-lymphocyte = Formed in bone marrow, it creates new antibodies by recognizing antigens.
T-lymphocyte = Also formed in bone marrow and migrate to the thymus gland. It also has specific anitgens that recognize disease causing agents and attacks them when introduced into the body
Monocyte = phagocytes invaders. Makes up about 5% of WBCs.
Disorders of the Circulatory System
Anemia = Low number of RBCs and not enough oxygen gets to cells throughout the body.
Leukemia = Too many WBCs which take the place of RBCs.

AIDs = caused by the HIV virus, this disease attacks T-cells. Without the T cells, the body is defenseless against bacterial or viral invaders.

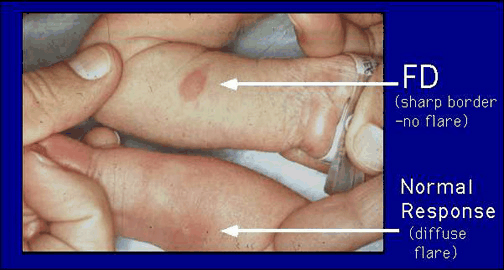
Allergies = Hypersensitivity to allergens cause the histamine to dilate blood vessels causing swelling and the mucus membranes become watery to fluch out the allergen.
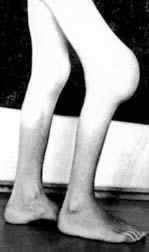 Hemophilia = The body lacks platelets. If blood cannot clot, a person may die from a small cut on the skin.
Hemophilia = The body lacks platelets. If blood cannot clot, a person may die from a small cut on the skin.
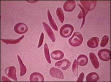 Sickle Cell Anemia = Many RBCs are shaped like sickles that can get hooked together and clog up the blood vessels. Poor circulation and edema (swelling) often occur.
Sickle Cell Anemia = Many RBCs are shaped like sickles that can get hooked together and clog up the blood vessels. Poor circulation and edema (swelling) often occur.
Polycythemia = Too many RBCs and blood becomes too thick to flow properly.
Thrombus = clotted blood that flows throughout the body. It may get stuck and clog up blood vessels. May lead toa stroke or cardiac arrest.
A blood transfusion is a short-term fix for someone in need of more blood or to replace lost blood.
Bone marrow transplant takes myeloid tissue from a donor to give to the donee so that the proper blood cells can be formed.
Vein = Allows blood to flow back to the heart. These vessels have semilunar (halfmoon) valves to allow blood to flow against gravity.
Each artery and vein consists of 3 layers:
1. Tunica adventitia = Outer layer of connective tissue
2. Tunica media = Middle layer of smooth muscle and elastic tissue
3. Tunica intima = endothelial layer
Click here to go to the virtual heart
Mother's blood goes to the placenta and at the placenta nutrients, wastes, and gases are exchanged with the arteries and veins of the umbilical cord. A mother who is Rh negative may run the risk of having some of her blood cells cross into the umbilical cord and attack the fetus' blood. Miscarriage can result.
Aneurysm = The walls of the artery weakens and dilates which can form a thrombus (blood clot).
Arterioscelrosis = Hardening of the artery walls from a build up of calcium. When an artery becomes blocked, ischemia can result. This condition is the death of cells/tissue from not getting enough nutrients.
Artheroscelrosis = Arteries blocked by fat deposits and cholesterol.
Varicose veins = The valves of the veins are weakened and dilate. These are visible on the surface of the skin.
Hemmorhoids = Varicose veins of the veins in the rectal area.
Heart Attacks = Parts of the heart muscle die because blood does not reach it. Build up of cholesterol and fatty deposits clog the blood vessels and prevent blood from reaching the heart. This is called Atherosclerosis.
High blood pressure = Hypertension. This condition results when the heart must pump harder and faster in order to spread blood throughout the body. Obesity is linked with hypertension.
* Chest pain. Sometimes mistaken for heart burn
* Numbness in left arm.
* Dizziness, sweating, nausea, shortness of breath.
* Sudden weakness on one side of the body.
* Sudden confusion.
* Sudden difficulty with speech or comprehension.
* Severe headache.
* Dizziness, stumbling.
The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes found in various parts of the body for making WBCs and filtering lymph. The thymus for making T cells, and the spleen for attacking bacteria and filtering old RBCs.
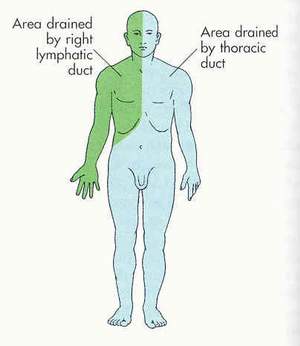
Lymph empties back into the circulatory system via the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct in the neck region. Lymph enters the left and right subclavian veins.
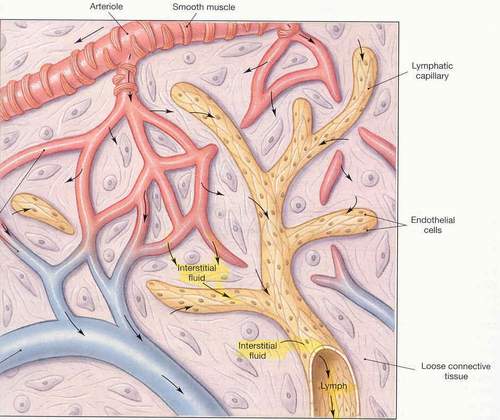
Blood usually removes wastes throughout the body. But what about substances that are not absorbed by the blood vessels. That is where lymph vessels come in. Lymph removes excess fluid like pus and excess proteins. Lymph goes back to the blood to be cleaned out by the liver and kidneys.
Lymph capillaries absorb wastes. The afferent vessel takes lymph to the node. The efferent vessel exits the node.
Lymphedema occurs when the lymph vessels are blocked by worms or parasites. Lymph cannot drain into the circulatory system and elephantitis can occur.
Hodgkin's disease = Enlargement of the lymph nodes, anemia, weakness, fever, weight loss.
Lymphoma = Cancer of the lymph tissue
Cancer = lumps are often found by rubbing where the lymph nodes are located. A hard lump can mean the spread of various types of cancer.
Parts of the Circulatory System
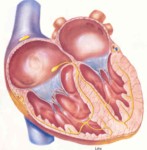 Heart = pumps blood
Heart = pumps blood
Artery = blood vessels which allows blood to flow away from the heart.
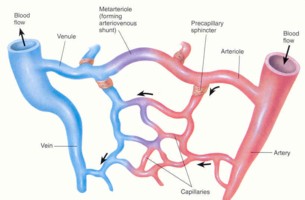
Capillary = Tiny blood vessels to allow nutrient & oxygen exchange from cells to blood.
When blood returns to the heart from the stomach, spleen, pancreas, and intestines it goes to the liver first. It is detoxified and led to the right atrium via the inferior vena cava.
Disorders of the arteries
Heart Disease

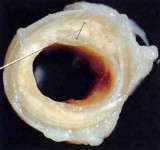
Symptoms of a Heart Attack


Symptoms of a Stroke
Live Healthy!!!
Regular exercise and eating healthy foods are the best ways to take care of your heart. Avoid smoking and drugs too.
The Lymphatic System
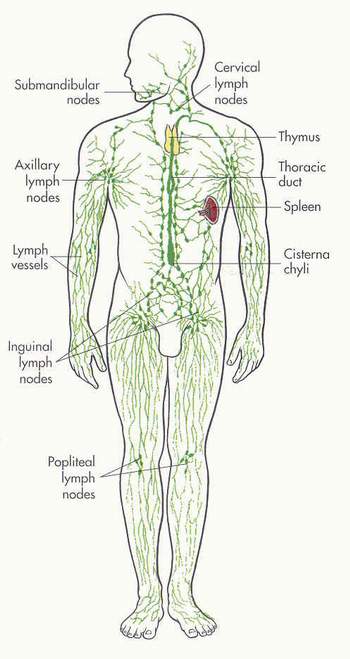

Diseases of the Lymph System