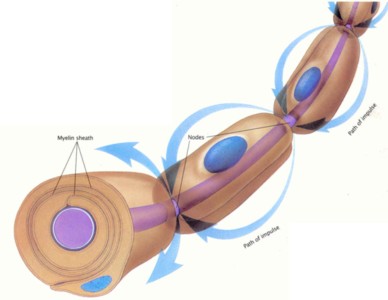
 Neurons are the cells that make up the nervous system.
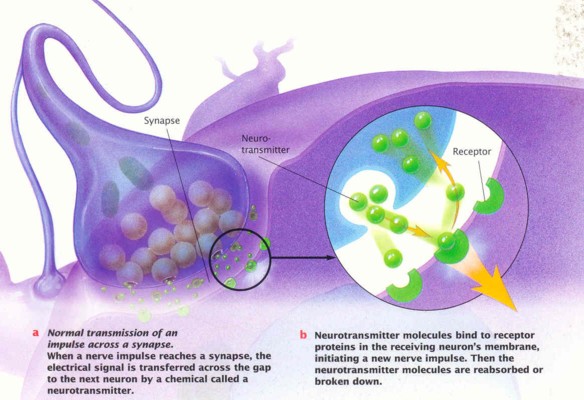
Neurons are the cells that make up the nervous system.Neurons carry an electrical signal to and from the brain. They work similarly like the electrical wires in a house. What creates the electrical current are neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters carry chemicals which will carry a message from neuron to neuron until the message gets to the brain. It works like dominoes passing that message along.
Click for Anatomy of Nerves & the Brain
1. Central Nervous System = Brain and Spinal Cord
2. Peripheral Nervous System = Nerves for feeling, sensing, and moving
1. Cerebrum = language, personality, memory, thoughts, and vision.
2. Cerebellum = balance, posture, and coordination.
3. Brain stem = breathing, swallowing, heart, digestive organs. It also controls consciousness, awareness, and sleep.
They are linked together by a tract. A tract = a bundle of nerves.
The left brain functions in language and speech. It also controls the glands and muscles on the right side of the body.
The right brain functions in math and music. It controls the glands and muscles on the left side.
This is the highway of nerves transmitting information to and from the brain. This controls the sensations of your senses (sensory neurons) and controls the movement of skeletal muscle (motor neurons).
Reflexes are quick reponses to painful stimuli. Reflexes are unique because the body moves away from the stimulus without you thinking about it. That is because the message doesn't go to the brain. The neuron passes the message to the spinal cord and automatically tells the muscle to move away.
Controls the muscles, organs, and glands that work automatically without you thinking about it. Many of your organs that move without you thinking about it are associated with the autonomic nervous system. Some examples are the intestines, stomach, heart.
Click for Brain Comparisons of Different Species
The ears control sound input as well as balance.
The ear can be divided into 3 main parts:
1. Outer ear = auricle and the tympanic membrane (eardrum) The first 1/3 has hair and ceruminous glands that secrete wax.
2. Middle ear = ossicles which are bones that vibrate from sound to relay the message to the oval window.
3. Inner ear = bony labyrinth with a water-like fluid called perilymph. These connect to the cochlear nerve which relay messages to the brain.
cornea = window of the eye and is transparent
conjuctiva = lines the eye with mucus
iris = colored part of the eye
lacrimal gland = forms tears and keeps the eyes moist
fovea centralis & malua lutea = acute image formation and color vision.
choroid = middle layer of the eye that prevents light from scattering
pupil = center of the iris which is a muscle that controls the amount of light that enters the eye
retina = innermost layer of the eye which has the rods and cones
optic disk = blind spot does not have rods or cones
Liquid that is held before the lens is the aqueous humor. Liquid behind the lens is the vitreous humor.
The muscles of the eye are the most active muscles in your body. They contract on average 100,000 times a day.
Your eyes have rods and cones which are extremely sensitive to light.
Cones = See color. People who are colorblind lack cones in their eyes.
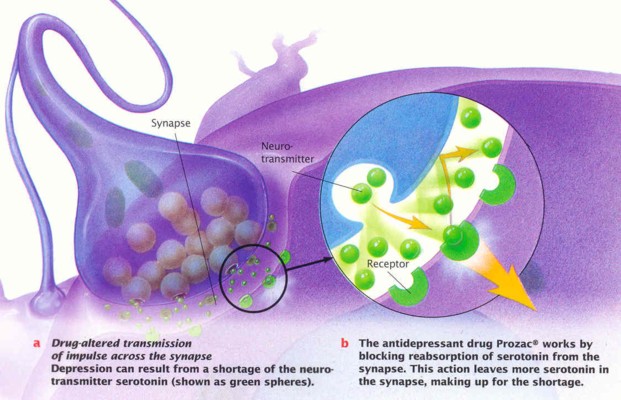
Interesting Links to How Drugs Affect the Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into 2 parts:

The brain is divided into 3 main parts: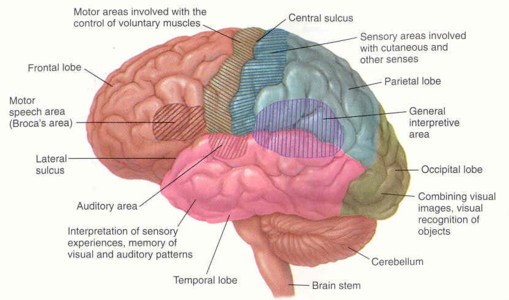 The brain has 2 hemispheres: Left Brain and Right Brain.
The brain has 2 hemispheres: Left Brain and Right Brain. You also have a structure called the Hypothalmus. It controls blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, hunger, thirst, urination, sexual drives, and emotions.
You also have a structure called the Hypothalmus. It controls blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, hunger, thirst, urination, sexual drives, and emotions.
The Peripheral Nervous System
Reflexes
Autonomic Nervous System
The Senses
 The inner ear has an eardrum which has 3 tiny bones which act as receptors. Sound vibrations shake the bones which relays the information to the brain. The brain the interprets the sound according to the frequency the bones are shaking.
The inner ear has an eardrum which has 3 tiny bones which act as receptors. Sound vibrations shake the bones which relays the information to the brain. The brain the interprets the sound according to the frequency the bones are shaking.
In the inner ear are 3 semicircular canals which have tiny hairs in a liquid which act as receptors for balance. If you tilt your head, the liquid moves by gravity and tilts the hairs. The hairs send a message to the brain that the head is tilted.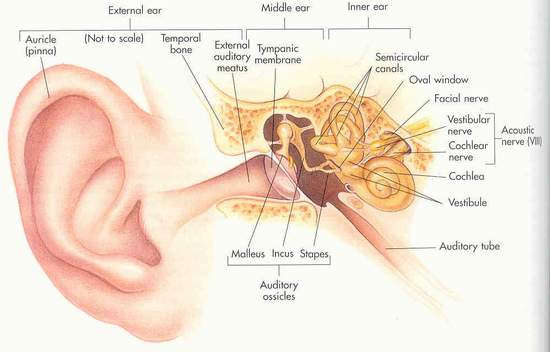
Light receptors are in the retina of the eye.
The pupil can open (dilate) and close (constrict) according to the amount of light present.
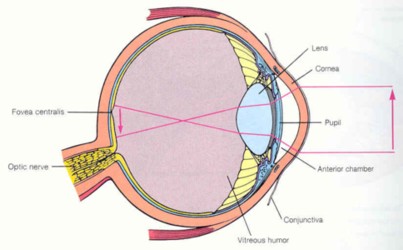
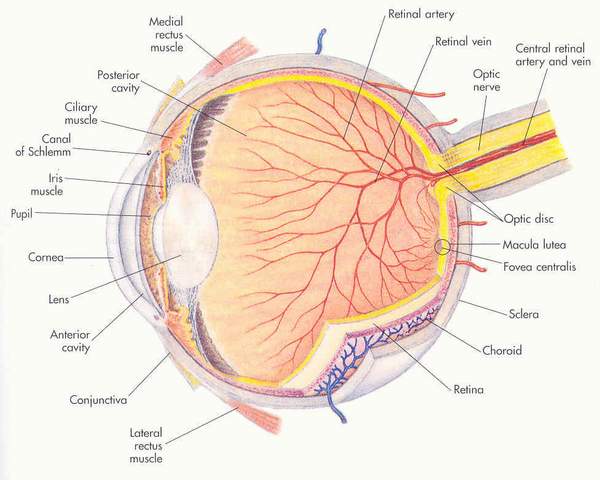
sclera = whites of the eye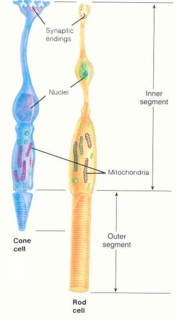

Rods = See black, white and shades of grey.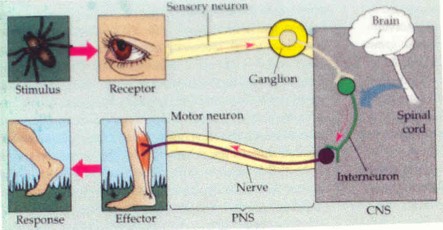
 Olfactory = sense of smell.
Olfactory = sense of smell.
The receptors are on the top of the nasal cavity. The nose is moist inside to detect scent.
Click to go to IQ Tests