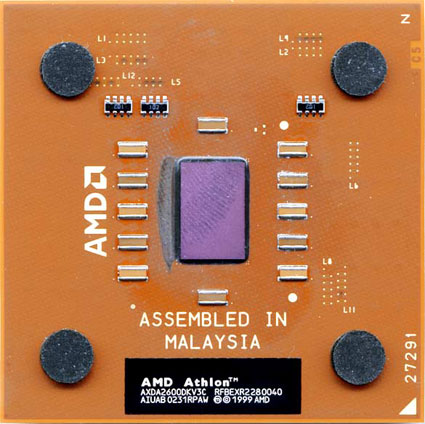
Both Processors need specific hardware in the form of motherboards to be installed and function correctly. Although both of these manufacturers are in competition the processors that they produce are slightly different even though they may be competing for the same market. AMD processors are slightly cheaper to buy per MHZ than the Intel processors. This is not at a cost to speed (dependant on tests uses)
A processor is measured by the speed, which it runs; this is calculated in MHZ (megahertz). This is the number of calculations that the CPU can work out in a second. If we have an Intel Pentium 2, 450 MHZ processor this means that it can calculate 400 million instructions per second.
There are various
classes and generation of processors. A very brief chronology of processors
is:
· 8086
· 286
· 386
· 486
· Pentium (or AMD equivalent in speed)
· Pentium 2 (or AMD equivalent in speed)
· Pentium 3 (AMD Athlon processor)
· Pentium 4 (AMD Athlon XP processor)
Peter
Khoury Productions for EPC Online. This site is best viewed with Internet
Explorer 6 or better and at a resolution of 800 x 600 Copyright EPC Online
LTD all rights reserved.
Last modified Tuesday, June 18, 2003 8:56 PM