Fishing Terminology
Last updated on
October 17, 2015
AND
STILL GROWING
Ever wonder what it is that people are talking about using terms you are not familiar with while they are talking about fishing?
Learn all the Fishing lingo here.
If there is a word you can not find, contact us and we will inform you and post it here on this page.
If you should find an error with one of our definitions - PLEASE inform us so that we may correct it! Thank you!

![]()
Aberdeen
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See
more detailed information here
Aboard
On
a boat.
AC
Plug
A.C.
Plug A
brand name of a large trout-imitating, jointed topwater lure made of wood.
Action
(1) The act of dragging a fly across the current and giving it an unnatural drift.
(2) When fish are biting - Getting a nibble
(3)
An elusive, but important characteristic of fishing rods. Rods are
said to have fast or slow action. Fast action rods are generally
stiffer overall, but bend more at the tip, generating higher line
speeds longer casts, especially into the wind. Slow action rods,
appear to flex their entire length, giving the sense of a more
compliant feel.
Describes
the elapse time from when the rod is flexed to when it returns to
its straight configuration. Also refers to the strength of the rod,
light, medium and heavy, with light being a limber rod and heavy a
stout rod.
Adams
or
Adams
Special A
general, widely used dry fly pattern to imitate an adult mayfly.
The Adams is a great multipurpose dry fly and it is commonly used as a searching fly. By simply changing its size, the Adams can imitate a variety of mayfly duns.
Although it is very rare, occasionally trout will sip adult midges floating on the surface. A small adams effectively imitates adult midges.
Adipose Fin On some fish species its the fatty fin located between the dorsal and tail fin.

Adult
The
final phase of an insect's life cycle, most often occurring above
water for aquatic insects.
Air
bladder A gas-filled sac in the upper part of the
body cavity of many bony fishes. It is located just beneath the
vertebral column; its principal function is to offset the weight of
the heavier tissue such as bone.
Affluent (Stream)
A stream or river that flows into a larger one; a Tributary.
|
Alabama
Rig The Alabama/Umbrella/Yumbrella rigs are artificial lure/baits that involve many separate lures/baits attached via wires to a fishing line. Consequently, these rigs are not a single artificial bait/lure, rather a collection of multiple artificial lures/baits each capable of catching a fish. In the water, the rigs simulate a small school of bait fish and YouTube videos show anglers catching two and even three largemouth bass on an Alabama/Umbrella/Yumbrella rig at the same time. |
|
The rig pictured here is different than using a single lure with multiple treble hooks that is designed to catch just one fish. Instead, the Alabama/Umbrella/Yumbrella rigs are artificial lure/baits that involve many separate lures/baits attached via wires to a fishing line. Consequently, these rigs are not a single artificial bait/lure, rather a collection of multiple artificial lures/baits each capable of catching a fish.
In the water, the rigs simulate a small school of bait fish and YouTube videos show anglers catching two and even three largemouth bass on an Alabama/Umbrella/Yumbrella rig at the same time.
This rig is not legal in Minnesota waters.
Albright
knot A common knot used for tying the backing
to fly line.
Alevin
A
newly hatched salmon or trout
Algae
Simple plant organisms.
Alphabet
lures
Wide-body crankbaits that were originally fashioned from wood.
Modern examples include Bomber Model A and the Cotton Cordell Big O.


Read All There is to Know about Fishing Lures at Our Lures Page
Anadromous
-- Fish that hatch rear in fresh water, migrate to the ocean (salt
water) to grow and mature, and migrate back to fresh water to spawn
and reproduce.
Anal
Fin Fin located on the bottom and near the back of the fish.

ANCHOR
A heavy metal object that keeps boats from drifting.
Anchor
buoy
Usually a red plastic ball of at least 24 inches in diameter, with a
large ring attached. Hook the ring on the anchor rope and heave the
buoy overboard. Drive the boat upwind or upcurrent. Presto! The
anchor is pulled up quickly to the buoy using horsepower instead of
human power.

anchovy
or anchovies A
species of 4- to 8-inch baitfish found in the ocean that is also a
popular bait used for striped bass at places like Lake Powell, Lake
Mead, Lake Mohave and Lake Pleasant but can be used for catfish as well.
ANGLER
Anyone
who fishes using a pole
or a rod
and reel.
angleworm
Any live earthworm placed on a fishing hook.
Angling
a form of fishing. It is often used synonymously with the terms
sport fishing and recreational fishing, although subtle semantic
distinctions exist among the three terms. Specifically, angling is
the practice of catching fish by means of an "angle"
(hook). The hook is usually attached by a line to a fishing rod.
Frequently, the rod is outfitted with a fishing reel that functions
as a mechanism for storing, retrieving and paying out the line. The
hook can be dressed with lures or bait.
|
Anti Reverse Anti-Reverse – System that prevents reels (typically bait casters) from spinning in reverse and causing tangles. Anti-reverse-mode reels utilize a slip clutch that allows the handle to remain stationary while the fish takes line. Their two biggest advantages are bloodless knuckles and fewer broken tippets. This all means, when you stop reeling, the reel handle should not be able to move backwards at all. |
|
Some reels do not have the instant anti reverse feature & there is plenty of "play" in the reel handle. This is bad news and is usually found in "cheaper" fishing reels.
If you do not have instant anti reverse on your reel, then each time you set the hook, the handle will slam back until it stops, "shocking" the gears in your reel. Eventually, your reel will start to deteriorate and then finally, it will break on you.
Antron
A synthetic yarn material made of long sparkly fibers used for
many aspects of fly tying including wrapped bodies, spent wings, and
trailing shucks. Is also used for dubbing material.
Arbor
The center part of a fly reel where line and backing
(first) is wound.
The size of the spool of a fly reel. "Large arbor" reels have large-diameter spools, which helps prevent a fly line from curling.

Learn all about The Fly reel and Other Fishing Reels at Our Reels Page
Arbor
knot A knot used for tying backing
to the arbor of the fly reel.
|
Armor Armor, in hydrology and geography is the association of surface pebbles, rocks or boulders with stream beds or beaches. Most commonly hydrological armor occurs naturally; however, a man-made form is usually called riprap, when shorelines or stream banks are fortified for erosion protection with large boulders or sizable manufactured concrete objects. When armor is associated with beaches in the form of pebbles to medium sized stones grading from two to 200 millimeters across, the resulting landform is often termed a shingle beach. Hydrological modeling indicates that stream armor typically persists in a flood stage environment. |
|
Imitation or substitute for natural bait or fish forage and includes, but is not limited to spinners, spoons, poppers, plugs, jigs and plastic, rubber or other artificial imitations of natural bait.
Learn all about Artificial Fish Bait at Our Artificial Bait Page
Artificial
Lure
See Lure
Artificial
Reef
Any material sunk offshore for the express purpose of attracting
fish. Old boats, concrete culverts, metal pipe, the list is endless.
Most states now require a permit before dumping because non-practical
material was being used, objects that rusted quickly, polluted or
were a hazard to shrimpnets.
Attractant
Liquid, solid or power form of scent applied to fishing lures for
increased productivity.
Attractor
Attractor
patterns A
style or variety of bright, bold flies that is effective in
eliciting strikes, but has few apparent characteristics of a natural
food item. Often an attractor is flashy and bigger than life.
Attractor patterns often provoke a fish's tendency to strike.
Auger
Used for ice fishing to drill holes through the ice. Augers come in
gas powered or manual back power.
Aught
The digit 0; zero. Usually used in reference to fish hook size.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Back
leads A small device used to force your line down to
the bottom. It is a small lead weight that is tethered to a
stick pushed into your bank.
The lead has a small open clip at the top on which you push over
your line. The weight is then dropped down under the water, pulling
the line down with it. When a fish strikes, the line
pulls up and out of the open clip.
Back
cast The casting of line
in a direction opposite to the direction the fly
is intended to go. The backward counterpart of the forward cast which
acts to create a bending action on the fly
rod, setting up the conditions to generate the forward cast and
present the fly.
Backing
Thin, strong string that is attached to a fly
reel to fill up the spool
before attaching the fly line.
The
first segment of line on a reel, usually braided and used to build
up the arbor
and to offer additional distance for a strong fish to pull out line.
An unusually strong fish will take you "into your backing".
Backing
down
Driving a boat backwards (in reverse) while pursuing a fish.
Backing
Line Nylon or Dacron line tied between the fly line and the reel
to act as additional line if a longer length than the flyline is
required to play a fish.
Backlash
When
fishing line gets tangled on a reel.
Backwater
Shallow area of a river that is sometimes isolated, often being
located behind a sand bar or other obstruction in the river. Large
backwaters tat are isolated may be referred to as oxbows.
Baetis
A
small grey mayfly. see
Mayfly
Bag
Limit
The number of fish that may be kept by an Angler legally.
Bail
Metal, semi-circular arm on an open-face spinning reel that engages
the line after a cast.
Bait
usually refers to something natural or live that is used to attract
fish to bite. The terms bait and lure may be used interchangeably.
Bait is the food you put on your hook to make fish want to bite it. Any substance used to attract fish. Traditionally, nightcrawlers, insects, and smaller fish have been used for this purpose. There is also artificial bait to attract fish.
Because of the risk of transmitting whirling disease, trout and salmon should not be used as bait.
Bait Bucket
A
bucket used to hold bait.
|
Baitcaster |
|
Most common style of reel used in bass fishing, typically round or oval shaped and somewhat open construction. Also known as level wind reels.
Fishing with a revolving-spool reel and baitcasting rod; reel mounted on topside of rod.
The spool turns during casting, unlike the spool of a spinning or spincasting reel.
Baitfish
a
small fish (minnow or shiner) that is a source of food for a
larger fish: used for fishing bait.
Bait
Fishing Is a style of Fishing which uses a live or dead
organism (worm, cricket, etc,) attached on a Fish Hook. It is a
simple way of presenting a Fishing Bait in an area of water where the
fish are likely to be feeding. For more information, see our section
on Bait Fishing.
Baitholder
Hook or Bait Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See
more detailed information here
Baitwell
A special well or live well in a boat to hold bait.
Balao
Pronounced "bally-hoo," this is the popular offshore bait
used for trolling, most often for billfish.
The bait of choice for sailfish for many years. A pricey bait when
used for other saltwater species.
Ball
bearings Small
metal balls added to the mechanical mechanism of high-quality reels
to make the retrieve smoother. Normally the more ball bearings a reel
has the higher quality.
Ballyhoo
A
small shiny fish used for bait.
see
Balao
Balsa
Type of wood several lures
are manufactured from. This wood is very light, yet highly buoyant.
Gives the lure great action. Examples include Bagley's Balsa B, and
Rapala Minnows.
Bank
The
raised ground next to a body of water. The sloping area
between the water’s edge and level ground. Roots and vegetation
stabilize the banks, filter sediments, and reduce soil erosion.
The
banks of a river may be gently sloping to the water, with a flat
beach; or, there may be a steep drop, or even a cliff. An
"undercut" bank is usually on the outside part of a river
bend. With an undercut bank, water is actually "cutting"
away soil underneath the bank. Water may go several feet under the
bank, even below where you are standing. Fish, muskrats, and other
animals use undercuts as shelter.
Bar
Long, shallow ridge in a body of water.
Barb
1.
a plant hair or bristle ending in a hook
2.
any of the side branches of the shaft of a feather
3.
a raised burr on a hook to keep fish from getting off.
The barb is shaped such that after the hook goes into the fish's mouth, it won't easily come back out. Many catch and release anglers pinch barbs with pliers or file them down for easy hook removal.

Barbel
A slender tactile process or fleshy projection located around the head.
Barbless
a type of hook which
does not have a barb on
the pointed end. Barbless hooks are easier to set in the jaw of the
fish and make it easier to release
a fish unharmed. Many streams and rivers don't allow hooks with barbs
to be used.
Barbless
Hook a type of hook
which does not have a barb
on the pointed end. Barbless hooks are easier to set in the jaw of
the fish and make it easier to release
a fish unharmed. Many streams and rivers don't allow hooks with barbs
to be used.
Barbules
A small barb
or pointed projection, especially one of the small projections
fringing the edges of the barbs of feathers
Barrel knot A
knot used to tie two pieces of tippet
together -- also known as a blood
knot.
|
|
Bass
Assassin A
brand of soft-plastic jerkbait.
Bass Boat
A
fast boat made for fishing on fresh water.
Bateau
A
small flat-bottomed boat, squared off on each end.
Bay
An inlet of the sea or ocean, usually smaller than a gulf.
Major
indentation in the shoreline of a lake or reservoir
Beacon
A
signal light used to help guide boats and airplanes.
Beads
1. Glass, or plastic beads added to a Carolina Rig to enhance the noise, and protect the knot.
2.
See Knot Protector Bead
Bead
Head A Bead Head fly uses a metal bead to simulate the
thorax on a nymph
or wet fly and
to add weight to the fly.
Typically gold or silver is used, but any color can be used. Often a
bright color such as red can stimulate a fish into biting.
Usually
but not always a fly with a bead immediately behind the hook eye.
Beads come in many materials, from brass to nickel brass to ceramic.
Some beads help a fly sink, but others are floaters.
Bead
headed midges A type of fly used for fly-fishing. See above
Beds
Circular areas in the lake bottom that bass
clear out in which to lay their eggs during the spawn. "The bass
are on the beds" refers to the fish actively spawning.
Bell
sinkers
Sinkers shaped like
a bell, which are normally used on a Carolina
Rig.
Also known as casting sinkers.

Belly
The middle section of a fly line.
A
tapered fly line has several components, with a fairly sharply
tapered tip (at the fly end). The middle portion of the line is
called the belly.
Belly
Boat A trademark for a brand of rubber inner tube boat
used for fishing in quiet water.
Belly
Strip
A strip of belly meat from a baitfish.
Cut and trimmed in a streamlined fashion, it can be trolled behind
the boat, where it flutters in a fashion enticing to gamefish.
Benthic
Bottom-dwelling.
Berley
bait scattered on water to attract fish
Billfish
Any of several species of pelagic fish, including sailfish,
spearfish, blue, black or white marlin, and swordfish.
Bimini Twist A specific series of knots and twists in a leader which acts as a springy shock absorber in the line, usually used when fishing for large salt water fish.
It has a loop and a double line section making it especially strong.
Biomass
The aggregate amount of living matter or a specific species
within a specific habitat, or the total number of a specific species
in a specific habitat.
Biot
The short thick barbs
from the leading edge of the first flight feather typically from a
goose or a duck. Used to simulate tails, legs, antennae and other
parts. Can be found dyed in many different colors.
Birdnest
A
tangle that can occur using a level wind,a newbies nightmare. When
the line gets all tangled up inside your reel.

Also called Spaghetti
When
you cast with a Baitcaster
Reel and you don't put your thumb on the line before the lure
hits the water, all your line will get tangled and make a huge mess
that looks just like a bird's nest. Getting a birdnest is just part
of fishing with a Baitcaster, everybody gets them.
Bite
when a fish tries to take a bait (or lure). Also called a strike.
Bite
indicator A device which activates or signals when a
fish is on the line. It can be as simple as a bell placed on the line
between two fishing pole guides that rings when a fish either nibbles
or takes the bait. There are commercially made bite indicators as
well. Bite indicators are often used by those bottom-fishing for
catfish and carp.
Biting
Time when fish are being caught on hooks.
|
Blade Bait – A weighted, fish-shaped blade made with a swinging hook and designed for fishing deep. |
|
Fiber
glass and graphic fly rods (which also have fiber glass) are
produced by wrapping sheets of graphite and fiber glass around a
carefully tapered steel rod (called a mandrel). The hollow rod
that results from this process is called a blank. It has no guides,
ferrules or reel seat.
Blind
cast Casting at no particular target.
Blood
knot A
knot used to tie two pieces of tippet together
best known for its strength in tying monofilaments of different diameter and material together. It is rather difficult to tie on the water and commercially-made blood knot tiers are available to make the job easier. A blood knot is often used to make a fly leader of several different diameter monofilament segments.
also
known as a barrel knot.
Bloodworm
A
worm with red juice inside that is used for bait.
Bluebird
skies A term used to describe bright, sunny, blue
sky conditions that often make catching fish tough.
Bluefish
Blue
fish
A kind of fish caught in saltwater.
Bluegill
(Lepomis macrochirus)
The Bluegill is a species of freshwater fish sometimes referred to as bream, brim, or copper nose. It is a member of the sunfish family Centrarchidae of the order Perciformes.
An
edible North American fish, with a deep body and bluish cheeks and
gill covers.
Boat
A
small vessel that is moved by oars, sails or engine.
Boathouse
A
building to keep boats
Bobber
maintains bait at given depth, indicates bites. Also
known as a float.
A small piece of cork or light wood or plastic attached to a fishing line to show when a fish is biting.


Bobber Stop
stops the line from sliding through the bobber at the depth you set them.
Bobbin
A tool for holding a spool of thread while fly tying which allows
the thread to be dispensed with a controlled tension.
Bomber
Bomber
Long "A"
A
brand name of crankbait.
Bonk
To kill a fish.
Boondoggle
Drifting your boat at or about the same speed as the current so one cast
runs the entire length of the run.
Boot
Opposite
of chromer. An old salmon or Steelhead. Well past edible, although
often seen in the hands of a beek, claiming "this ones for the smoker".
Bottom
bouncing
a spin fishing technique where the spinner is cast up river from the
shore, and then allowed to bounce on the river bottom until it has
moved downstream.
Bottom
Feeder
See Bottom fish
Bottom
fish or Bottom
feeder A
bottom-feeding fish, such as a catfish or carp. Refers to a fish
that feeds predominantly on the bottom, not just one that is
sometimes caught on the bottom, such as a largemouth bass or trout.
Bottom
fishing
Fishing with the hook on the bottom
Bottom Rig
The
hooks, weights and things fastened together for bottom
fishing.
Bow
The
forward (front) part of a boat.
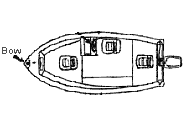
Bow fishing
Using a bow and arrow, typically with a reel attached to the bow, to
harvest fish.
Bow Rail
The
front railing on a boat.
Brackish
Water that is mostly fresh, with some salt. The far ends of tidal
creeks are mostly brackish, supporting sometimes fresh and saltwater fish.
Braided
channel
Usually found on freestone rivers, braided channels are
ever-changing smaller channels that together constitute the course of
the entire river.
Braided
fishing line Braided fishing lines are tough, strong and limp.
They excel in some fishing situations and are the best choice for
others. Braids should be used for their good qualities when appropriate.
Brook trout are native to Southeastern Canada and the United States north of Georgia.
Brook trout feed on aquatic and terrestrial insects, occasionally supplementing this diet with crayfish. Large brook trout may eat small fish.

Brushline
The inside or the outside edge of a stretch of brush.
Brush
pile Usually refers to a mass of small- to medium-sized
tree limbs lying in the water. Brush piles may be only one of two
feet across, or they may be extremely large; they may be visible or
submerged. They can be created by Mother Nature or be man made. They
typically attract fish, and fishermen.
Buccal
Pertaining to the cheeks or the cavity of the mouth.
Buck
Male fish
Bucketmouth -
Largemouth Bass (see
bass)-
A black bass, body green-shaded with a broad, continuous dark stripe
along each side, belly white to yellowish, dorsal fin almost
completely separated between spiny and soft portion and lower jaw
extends past the gold-colored eye. Also called bigmouth bass, green
trout, green bass
Bucktail
An
imitation bait
with feather or hair and a hook.
A
streamer fly tied to imitate a fish. This fly usually features a
long segment of hair, laid back from the eye to the bend of the hook.
That hair often is from a deer's tail.
Buffer
a vegetated area of grass, shrubs, or trees designed to capture and
filter runoff from surrounding land uses.
Bullet
Same as a chromer - A bright, fresh fish
Bullet
Head Tool A tool with a plate with several holes which can
be pushed over the eye of a hook to arrange material in a bullet
pattern. The material is first tied in facing forwards beyond the eye
symmetrically around the shank, and then pushed backwards by the tool
to form the distinctive bullet shape.
Bullet
Sinker A cone shaped piece of lead, zinc or steel of
varying weights that slides up and down the line.
Bumping
Refers to the act of making a lure hit an object, such as a log,
tree or rock, in a controlled manner (either intentionally or
unintentionally), which can get the attention of a fish and result in
a strike.
Bump-troll
Keeping a trolled bait
mostly in one spot, by pointing the boat into the current/wind and
"bumping" the engines in and out of gear, to hold position.
Buoy
A
floating marker
Buoyancy
The tendency of a body to float or rise when submerged in a fluid.
Butt
Cap
This
is at the bottom of the handle on a fishing rod: sometimes made of
rubber, sometimes of cork. This is the end you might press into your
stomach if you're fighting a good fish.
buttguide
Butt
Guide This
is the guide closest to the
handle end of your rod. Its
located on the thickest part of the rod (butt), that's why it's
referred to as the butt guide.
Butt
Seat
A seat that is shaped in a sort of half moon design, which anglers
often use to lean against while fishing. Also known as
"Bike" seats.
This small bottom cushion is popular among fishermen who fish long hours.


Buzzbait
– a
type of topwater lure. These "safety pin" wire lures for
surface fishing have a propeller blade on one wire and a weighted
body, skirt and hook on the other.

Buzzbait
Buzzing Retrieving
a spinnerbait or buzzbait along the water's surface to create a
splash effect to resemble a wounded baitfish.
Bycatch
Non-targeted sea life caught by commercial fishermen. Tuna longlines
have a bycatch of turtles or mahi-mahi, for instance. Shrimp nets
have a bycatch of at least a hundred species of fish and crab,
discarded overboard.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Caddis
Caddis
fly Also known as a "sedge," they are
characterized by a tent-like wing or wept-back wings. An aquatic
insect of major importance, along with the mayfly and stonefly, for
the trout fly-fisherman. the Caddis Fly is also an insect that goes
through a complete metamorphosis much like a butterfly. Caddis have
four stages of development, from egg to larva to pupa to adult.
A
caddis worm is the larva of a caddis fly.
Caddis
Worm the larva of a caddis fly.
Canal
A man made waterway used for navigation.
Cajun
Line See Zebco
Camouflage
A
way to hide things and make them hard to see.
Cane
Pole A pole of natural cane, often made from Calcutta or
Tonkin bamboo, used for fishing. No reel is used; the line is tied to
the pole. Extremely effective for fishing small, narrow streams or
creeks. Those fishing with such a rig are said to be cane-poling.
Canoe
A
long boat pointed at both ends that is easy to paddle.
Cape
The skin off a rooster chicken's neck, which yields several hundred
good fly-tying feathers from a quality cape.
Captive
brood stock Fish raised and spawned in captivity.
Carnivorous
Feeding on animal tissues.
Carolina
rig A
rigging method designed to present a soft plastic lure
along the contour of the bottom. This rig consists of a main line
with a heavy sinker, bead, then swivel. The swivel has a leader
(1-6ft) to which a plastic lure is tied. Best lures include lizards,
centipedes and French fries.

Carp
A
kind of freshwater fish.
Cartilaginous
fish A major group of fish including sharks and rays.
Cartop
or cartopper Refers to a boat small enough to be carried
on the top of a car and hand-launched, especially at fisheries with
limited or no boat launching facilities.
Cast
a
technique using a rod
to throw your line,
hook and bait
to the intended target.
Casting
a
technique using a rod
to throw your line,
hook and bait
into the water.
Casting
Arc The distance the rod is passed through from the
beginning of the backcast
to the end of the forward cast. The longer the cast, the longer
the arc should be, since it helps you in making the cast
Casting
Plane The angle(s) above or below horizontal the rod tip
actually follows during the casting sequence.
Casting Spoon
A spoon-shaped metal or hard plastic lure that wobbles to attract fish.


They
can be fitted with a fixed (solid) hook or swinging hook, that has a
single, double or treble points.
Cast
net A
circular net thrown by hand. The outer perimeter is lined with lead
weights. Great for catching shrimp and baitfish.
Catadromous
Refers to fish that migrate from fresh water to salt water to spawn
or reproduce such as the American eel.
Catch-and-release
Term
that refers to releasing the fish you catch so that they can live to
fight another day, and thus insuring a productive fishery.
The ethic of returning fish to the water unharmed.
This
is probably the most important thing when fishing.
It
is the policy of returning every fish you are not going to eat or
use. Just because you may not like the fish you have caught, it
doesn't mean that you should kill it !
I
find the needless death of this wonderful resource a great waste of life
![]() A
conservation motion that happens most often right before the local
Fish and Game officer pulls over a boat that has caught over it's limit.
A
conservation motion that happens most often right before the local
Fish and Game officer pulls over a boat that has caught over it's limit.
Catfish
A
kind of fish with whiskers.
|
Cattail or reed mace, any plant of the genus Typha, perennial herbs found in almost all open marshes. Cattails are common plants in many freshwater wetlands. These grass-like plants grow six to eight feet tall. Each one has a fuzzy brown tip called a spike. Cattails are found in water a few feet deep. About half their stem is underwater. Cattails grow close together, forming great hiding places for many animals. And cattails themselves are important sources of food. |
|
Bluegills
are one of many kinds of fish that like to hide among the shadows of
the cattail stems.
Caudal fin Caudal is an anatomical term meaning "the back". The caudal fin is the tail fin or tail of a fish.

Centipede
Four-inch straight plastic worm used for Carolina
rigs.
cfs
Abbreviation for "cubic feet per second," the term is a
means of measuring the flow of a stream. A small stream might carry
40 cfs and offer good trout fishing, while a large river like the
Colorado might reach 30,000 cfs in the Grand Canyon during flood stage.
Channel
The bed of a stream or river. This can also refer to a submerged
stream or river channel in a reservoir.
Channel
Marker-
Used to mark the safe edges of a channel.
Char
A species of fish that is related to trout, that prefers cold water
and is found many places in the world, including both east and west
United States. Examples of char are brook trout,
lake trout, arctic char and Dolly Varden.
Charter Boat
A
boat you pay to go out on.
Chenille
A yarn-like material for wrapping bodies which is in the form of a
pipe cleaner (with thread in place of the stiff wire). Can be found
in many colors and materials, and is a critical component of the
Wooly Worm and Wooly Buggers patterns.
Chine
The "running edge" of a boat. The chine is the edge made
by the joining of the bottom and the sides of a boat.
Chinook
The Chinook salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha, is the largest species
in the Pacific (Oncorhynchus) salmon family. Other commonly used
names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, spring
salmon and Tyee salmon. Chinook are anadromous fish native to the
north Pacific Ocean and the river systems of western North America
ranging from California to Alaska. They are also native to Asian
rivers ranging from northern Japan to the Palyavaam River in the
Siberian far east, although only the Kamchatka Peninsula supports
relatively persistent native populations. They have been introduced
to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and the Great
Lakes. A large Chinook is a prized and sought-after catch for a
sporting angler. The flesh of the salmon is also highly valued for
its dietary nutritional content, which includes high levels of
important omega-3 fatty acids.
Chironomid
Scientific name for the members of the Diptera family of insects
commonly known as Midges. In the pupae stage they typically appear to
be small aquatic worms.
Choked:
Busted of a fish or did something dumb to lose your fish
Chromer:
A bright, fresh fish - Also known as a Bullet
Chub
Chub
is a common fish name. It pertains to any one of a number of
ray-finned fish in several families and genera. A class or
subclass of the bony fishes.
Chugger
Topwater lure that
"chugs" when retrieved, similar but smaller than a popper.
Example, Storm Chug Bug.
A
Chugger has a dished-out, concave or cupped head designed to make a
splash when pulled sharply. The act of systematically working the
lure across the surface is called "chugging."
Chum
Chopped
up fish, shellfish or even animal parts (for sharks), dropped
overboard to attract gamefish; putting some bait in the water to draw
fish to your area. A lot of anglers will use bread as a way of chumming.
Chum
bag
A mesh bag left hanging overboard, filled with chum.
Trollers sometimes drag the bag alongside the boat. Smaller bags can
be trolled deep while attached to downrigger balls.
CHUMMING
– A fishing technique by which bait or scent is released into
the water to attract fish to take a lure or baited hook. Chum
consists of live, dead, ground-up or prepared baits and scents and is
used in fresh and saltwater.
Chunk
Plastic
or pork trailer commonly used on jigs.
Cigar
minnows A
yellow-tailed member of the scad family, sold most often as frozen bait
in five-pound boxes, caught along the Florida Panhandle. Widely
regarded for their firm texture and appeal to offshore fish. Cigar
minnows can also be caught on tiny fly hooks, called Sabiki Rigs.
Cinch
Knot (also known as Clinch Knot) A knot used to tie the
tippet to the eye of the fly. A modified version of this, the
Improved Cinch Knot, is probably the most used knot for this purpose.
See
how to tie a cinch knot
along
with other necessary fishing knots
by
clicking here
Circle
hook
A circular hook up to 16/0 size, very safe to handle. The fish hooks
itself with this one, and the harder they pull, the more firmly the
hook imbeds itself. Ideal for releasing fish, since the circle hook
is seldom swallowed.

This functionally-shaped fishhook results in more fish being hooked. Fishermen are learning that the Circle Sea is catching 60% more fish than conventional J shaped hooks, including a 95% lip hook rate so the fish cannot escape. The Circle Sea hook is scientifically proven to reduce fish mortality. Hook set is not required. This hook has greater holding power, more hookups, fewer drop-offs and it holds bait better. Ideal for all freshwater and saltwater fish species.
The trick is to let the fish take the bait, resist the temptation set the hook yourself, let the fish take it, eventually the rod will double and the fish will set them self. If you try and set the hook, the hook will not work properly and you will actually pull the hook right out of the fishes mouth. If you get too excited and set the hook you would pull the bait right out of the fishes mouth. You must resist as the reel screams out line . . . the fish would hook itself.
Cisco
Any
of several whitefishes found primarily in the Great Lakes region.
Clacker
A
metal device added to certain brand Buzzbait in order to make
additional noise.
Cleaning
preparing your catch for eating.
Clevis
The swivel device to which a spinner blade is attached and which
allows the blade to rotate.
Click
drag A mechanical system on many inexpensive fly reels used to
slow down or resist the pulling efforts of a fish, so as to slow the
fish down and tire it to the point where it can be landed. Basically
a clicking sound is created by a triangular steel ratchet snaps over
the teeth of the gear in the reel spool. The term singing reels
refers to the high frequency clicking associated with a big fish
pulling out line.
Clicker
cork A
thin Styrofoam cork, 3 inches long, mounted on an 8-inch wire.
Yanking on it produces a clicking sound that imitates shrimp snapping
their tails underwater. These corks are great for suspending a
plastic shrimptail jig above a grass bottom, and below troublesome
floating grass.
Clinch
knot
One of 4-5 very useful knots. Very simple to tie, yet very strong. also
known as CINCH KNOT
|
Closed-Face Spinning Reel Same as a spin-casting reel A fixed-spool reel with the spool enclosed by a housing and the bail arm replaced by a small pick-up pin. Originally designed for spinning, they are popular for light float fishing, especially trotting. The Closed face reel has a stationary spool set on the underside of the rod. A curved bar, or bail, acts as a guide on the outer lip of the spool. As the reel handle is turned, the bail also turns, winding line neatly onto the spool.
|
|
Click
here for detailed information on
Closed
Face Spinning Reel
Clouser
minnow
A streamer pattern that imitates baitfish,
popular for many different species of fish, named after originator
Bob Clouser.
Clown
A
color typically used mostly in hard jerkbait like Rogues. Consists of
chrome body, with chartreuse back, and red head or face.
Coarse
Fishing a term used in the United Kingdom and
Ireland for angling for coarse fish, which are those types of
freshwater fish other than game fish (trout, salmon and char). The
sport and the techniques used are particularly popular in the United
Kingdom and mainland Europe. A recreational sport that arose in
England and Europe as a ‘gentleman’s pursuit’, where
cyprinids including roach (Rutilus rutilus), rudd (Scardinius
erythrophthalmus), chub (Leuciscus cephalus) and dace (Leuciscus
leuciscus) are caught and released.
Coastal
pelagic An
offshore fish that migrates along the coastline, but isn't a true,
ocean-going pelagic. Examples are Kingfish, Spanish mackerel, Cobia.
Coffee
Grinder:
a spincast reel See
Spincast reel here
Cold
Front A
weather condition accompanied by high, clear skies, and a sudden
drop in temperature.
Coldwater
Fishery
Refers to waters typically in the higher elevations that can be
predominately trout fisheries.
Colorado
Blade
design used in spinnerbaits. Gives out a strong vibration. Blades
are circular shaped.
Combo
A combo is a matched rod and a reel set, configured for a specific
type of fishing. See Rod and Reel
Commercial
Fishing Fishing to sell the catch of fish for the market.
Commercial
Fishing
Boat
Used for fishing to earn a living.
Conservation
the wise use of natural resources.
Cork
Keeps
a hook from sinking. Bobbles when a fish nibbles.
Cosmic
Clock The sun's seasonal effect on water and weather
conditions relating to barometric pressure, wind, and cloud cover.
Cove
An indentation along a shoreline. A very small indentation a few
feet or so across is often referred to as a "pocket cove."
A
small sheltered inlet or bay.
Cover
Cover consists of weeds, trees, branches, tulles, buck brush,
stick-ups, rocks and man-made objects like docks, tires, etc.
Cowbells
A flashing, multi-bladed lure that resembles a small school of bait
fish that is commonly used to troll for trout.
Crankbait
plastic or wooden lure
with a diving bill, that dives downward when retrieved or "cranked."

Crappie
(kraw pee) A kind of fish that is fun to catch and good to
eat. Freckle.
Crawfish
Craw
fish
See Crayfish
Crawldad
Crawldad
See Crayfish
Crayfish
Cray
fish Small fresh water crustaceans similar to lobsters
only smaller. A favorite food of bass.
Also describes a reddish color used in all sorts of lures.
Creek
a
small to medium sized natural stream of water that is smaller than a river.
Creek
bed (or streambed) — the bottom of the creek (or any water
channel), which is usually composed of a mixture of gravel, sand, and silt.
Creek
Channel (or stream channel) - the area of the riparian corridor
that contains flowing water (either intermittently or continually).
Creel
A
small basket with a carry-strap to keep fish in.
Creel
Limit The number of fish an angler
can keep as set by local or state regulations. It can vary from water
to water, so be sure to check the fishing regulations.
Cricket Can
Keeps
crickets alive to use for bait.
Crickhopper
A brand of plastic lure resembling a grasshopper commonly used for
trout and sometimes, for smallmouth bass
Crimp
sleeve A
metal tube, thin as two wire leaders together. When attaching wire
or very heavy mono leader to a hook, one should use the crimp sleeve.
A special, plier-like tool crimps the sleeve tight.
Croaker
or "hardhead" are popular saltwater fish of the
mid-Atlantic and Gulf Coast of the USA.
From
the Sciaenidae Family. Commonly called drums, croakers, or hardheads
for the repetitive throbbing or drumming sounds they make.
Cross
chop
Wind-driven waves and ocean swell colliding from two directions.
Also caused by waves bouncing off a seawall and going back out,
colliding with incoming waves.
Crustaceans
Lobsters, spiny lobsters, crabs, prawns, shrimps, crayfish.
Crystal
Flash The trade name for a synthetic stringy material used in
many streamer patterns to add flash and color.
Ctenoid
Scales Ctenoid (toothed) scales are like cycloid
scales, with small teeth along their outer edges. They are usually
found on fishes with spiny fin rays, such as the perch-like fishes.
The scales have a rough texture with a toothed outer or posterior
edge featuring tiny teeth called ctenii. These scales contain almost
no bone, being composed of a surface layer containing hydroxyapatite
and calcium carbonate and a deeper layer composed mostly of collagen.
The enamel of the other scale types is reduced to superficial ridges
and ctenii.
Ctenoid scales can be further subdivided into three types:
Crenate scales, where the margin of the scale bears indentations and projections.
Spinoid scales, where the scale bears spines that are continuous with the scale itself.
True ctenoid scales, where the spines on the scale are distinct structures.
Both
cycloid and ctenoid scales are overlapping, making them more
flexible than cosmoid and ganoid scales. Unlike ganoid scales, they
grow in size through additions to the margin. The scales of some
species exhibit bands of uneven seasonal growth called annuli
(singluar annulus). These bands can be used to age the fish. Most
ray-finned fishes have ctenoid scales. Some species of flatfishes
have ctenoid scales on the eyed side and cycloid scales on the blind
side, while other species have ctenoid scales in males and cycloid
scales in females.
Cul-du-Canard
Feather In
French, literally, "the butt of the duck," which is where
these fine, downy, useful fly-tying feathers can be found.
Short
wispy feathers taken from near the preen gland of a duck. Typically
there are few of these feathers found per duck. These feathers add a
significant amount of float to a fly due to the fact that they are
soaked with natural preen oil. Use of floatant on these feathers will
negate their floating qualities, actually causing the fly to lose flotation.
Culling
Refers
to releasing a smaller fish when you have a limit and have now
caught a larger fish that will weed out one of the smaller ones.
"This big fish will cull that small . . . ;" is a phrase
heard on The Bassmasters TV show often.
Culprit
worm Although
there are several similar worms, Culprit is the manufacturer of the
original ribbon tail plastic worm, thus it is often referred to as a
"Culprit "style worm.![]()
Culvert
An underground water channel, usually placed under a road or
structure to allow for development of land. Culverts take the form of
concrete box-like structures or large-diameter storm drain pipes.
Curly
Tail A trademark for a brand of curved-tail
soft-plastic lures.
Curly-tailed
Grub A curved-tail soft plastic bait often fitted on a jighead.
Curve
cast A casting technique that allows an angler
to cast a fly around an obstacle. It is also used to minimize the
influence of water current or wind on the fly or the fly line.
Cut
A narrow body of water cutting through land. For instance, a boat
cut gouged through a barrier island, for boater access.
Cut
bait
Fish cut into chunks to fit the hook.
Cuttbow
a
rainbow/cutthroat hybrid, the cuttbow has both the rainbow's stripe
and a cutthroat's "slash" under its jaw.
Cutthroat
trout A
native to many Rocky Mountain rivers, the cutthroat has a crimson
"slash" under its jaw and black spots concentrated near the tail.
Cutting
board Plywood
surrounded by a lip of wood, sealed and painted. Or just an old
piece of plywood. Used for cutting bait,
and preventing knife cuts on expensive boat gunnels.
Cycloid
Scales Cycloid (circular) scales have a smooth
texture and are uniform, with a smooth outer edge or margin. They are
most common on fish with soft fin rays, such as salmon and carp.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Dabbing
Working a lure up and down in the same spot a dozen or more
times in a bush, or beside a tree or other structure.
Daily
Limit The number of fish that may be legally taken during a
calendar day. A fish when landed and not immediately released
becomes part of the bag limit of the person originally hooking the
fish even if the fish is donated to another person. If you receive
fish from another angler,
those fish also become part of your daily limit.
Dam
Used
to hold water back. It usually makes a lake.
Damselfly
A small member of the dragonfly family.
Dapping
A relatively ancient technique of presenting a fly on the surface of
the water where the fly is connected to a short piece of line on a
long rod. The fly is then touched on the surface of the water,
immediately over a place where a fish might lie.
Dardevle
A trademark for a brand of spoons typically used for trout and
northern pike fishing.
Dead
drift A
drift that imitates the natural action of an insect by floating
directly downstream with the current.
DEC
D.E.C.
Department of Environmental Conservation.
Deer
Hair Body hair from deer which is used in many fly patterns to
supply body and floatation.
Deer
Hair
Bug
A floating fly-rodding lure made from hollow deer hair and used
principally for bass and panfish.
Depth Finder
Measures
how deep the water is under a boat.
A sonar device, either a flasher unit or LCR recorder, used to read the bottom structure, determine depth, and in some cases actually spot the fish.
also called a fishfinder.
Depth Recorder See Depth Finder
Depth
Sounder See
Depth Finder
Deep-drop
Bottom fishing
in deep water, from 500 to 1,100 feet and sometimes deeper. Usually,
a sash (window) weight is required to reach bottom. Circle
hooks
are a necessity.
Delta
Sediment deposited at the mouth of a major river, pushing shallow
water offshore, as in the Mississippi Delta.
Demersal
Fish living at or near the bottom, although sometime in mid-water i.e.
cod, haddock, hake, pollock, and all forms of flatfish.
Deposition
settlement of materials from moving water onto the channel bed,
banks, and floodplains. Deposition occurs when flowing water is
unable to transport the material.
Die
off
Die-off
Refers to having many fish die at the same time, quite often
baitfish; also referred to as a fish kill.
Dillies
See Dilly's
Dilly's
A
type of small earthworm popular for catching sunfish and trout.
Dink
Bass not long enough to meet state fisheries regulations or
tournament standards. Typically less than 14 inches
Dip
Bait
A smelly paste-type bait primarily used for catfish.
Dip Net
A
net with a handle. Used to get fish into a boat.
Disgorger
Device for removing hooks deeply embedded in the throat of fish.
Disk
drag A mechanical system on more expensive fly reels whereby
resistance is created to the line as a fish pulls it out. This
resistance is intended to slow the fish and tire it. The resistance
proper is created by applying pressure between two disks. Different
from the click drag, the disk drag is smoother and less likely to
create a sudden force that will break the line.
Disturbance
pattern Fly fishing term for creating a fish attracting
disturbance by working the fly.
DNR
D.N.R.
Department of Natural Resources
Dobsonfly
A large aquatic insect, the larva of which is the popular
hellgrammite bait.
Dobber
(also called float) a small red and white ball that sink when a fish
has grabbed the hook
Dock
1.
an enclosed area of water in a port for the loading, unloading, and
repair of ships
2.
a platform built out from the shore into the water and supported by
piles; provides access to ships and boats
Dock
lines
Ropes used to secure the boat.
Dodgers
a type of Lure
Doe
Hen
Steelies/Salmon
Doll
Fly A trademark for a brand of chenille-bodied,
hackle-wrapped jig.
Do-nothing
rig Western,
clear water technique generally applied in deep water and on light
line. Consists of main line with a small brass sinker, then a bead,
and light wire hook. baits
are usually small 4-inch worms. The rig is dropped to desired depth
and then just slightly jiggled or left to "do nothing."
Doodlesock
or Doodlesocking A method of cane-pole or
long-pole fishing in which a lure or bait is repeatedly dipped and
dragged through likely fish structures. Used in largemouth bass and
crappie fishing. Very effective when fish are holding tight to cover.
Doormat
Large flounder, roughly the length and weight of a doormat.
Dorsal
Fin Dorsal meaning top. This is the large fin
on top of the fish's back.

Double
haul A
casting technique
where the angler
pumps the fly line with the non-casting hand on the forward and
backward segments of the cast.
The pumping motion accelerates the line and gives the cast
additional length. Double hauling is an essential technique for long casting.
Double Hook two hooks made together; built into one.
Some states make double and treble hooks illegal and also regulate the number of hooks that can be attached to one line. Get familiar with your State Fishing Laws by clicking here
Double-tapered
fly line A
fly line that is thicker on both ends and thinner in the middle.
Double-tapered fly lines can be switched around as one end becomes worn.
Doughball A doughball is just what it sounds like, a little ball of dough.
A
ball of bait made from bread or specially prepared dough used for
bait-fishing. Commonly used for carp.
Downcurrent
term referring to direction
Downlake
term referring to direction
Downrigger
Used to slow troll most commonly for Kingfish and grouper. Standard
equipment on the Kingfish
tournament boats.
Downrigger
ball Cannonball-shaped
device with a fin, used to keep a trolled bait
far beneath the boat.
Downriver
term referring to direction. Something that is moving down-river
is moving towards the mouth of a river,
from a point further up the river. Something that is down-river is
towards the mouth of a river.
Downshore
term referring to direction
Downstream
term referring to direction
Downstream
drift The
act of allowing the fly to drift past the fisherman and rise to the
surface on the river below him, particularly on a nymph drift.
Drag This
is the mechanism that allows you to set how much resistance a fish
feels when it pulls on the line. The tighter you set the drag, the
more resistance the fish feels. You want to set the resistance tight
enough that it tires out your fish, but not so tight that the line
gets over stressed or breaks
It
limits how fast a fish can strip line from the reel.
When
you tighten the drag on your reel it makes the line harder for the
fish to pull out and makes them get tired faster. But you have to be
careful not to make it too tight or the fish can pull so hard your
line breaks.
2.
When a fly line catches on a current, making the fly drift in an
unnatural fashion.
Dredging
Retrieving a Crankbait so that it continually digs or dredges up the
bottom. This causes reflex strikes from fish.
Dressed
See Dressed Fish
Dressed
Fish A fish which has been cleaned by removing the entrails.
Dressed fish also may be filleted and/or have their head, gills and
scales removed.
Dressed
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed
information here
Drift
anchor
Used most commonly in windy areas, by fishermen who drift all day.
This anchor is more of an underwater kite that slows the boat's drift
in order to thoroughly fish a productive area.
Drift
boat Also
known as a Mackenzie river dory, it's a river fishing craft ranging
between 14 and 18 feet long with a flat bottom, upswept prow and
rigid hull.
Drift
Boating Technique used to fish by drifting with the current,
sometimes in a drift boat.
Drift
fishing
Drifting along with the wind and tide, casting
repeatedly. Anglers
working the grass flats off Florida, for instance, make one drift
after another all day. Catch a few fish, and toss a buoy, to make an
accurate drift through the same area. If Saturday crowds threaten to
overwhelm the buoyed area, use a GPS to mark the spot for return.
Drift
sock A
large sock shaped like airport wind socks. This is dropped over the
side of the boat to help control the boat in rough water.
Drip
bag Very
similar to an IV drip bag used by doctors, this device releases a
constant drip of pogey oil over the side, attracting fish.
Drop
Off
Drop-Off
A sudden increase in depth, associated with a flat, point, gulley
washes, small creek channels, land points, and the general lay of the land.
![]() When your wife leaves you with the kid(s) and you take them to the
babysitter to go fishing.
When your wife leaves you with the kid(s) and you take them to the
babysitter to go fishing.
Dropper
a separate line tied onto the main line near the hook. It is used to
attach a weight to a separate line or to fish two hooks.
The secondary fly tied on the leader somewhere between the lead fly and the fly line.
A practice of fishing two flies at the same time, often one on the surface and a second underwater. This increases the chances of getting a successful fly in front of a fish.
Drop
Shot Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more
detailed information here
Drop
Shot Rig Japanese
designed technique in which the main line is tied to a sinker. The lure
is tied to a leader which is tied above the sinker. This allows the
lure to sit a the exact depth of suspended fish.
A
tackle rigging technique employing a hook tied to the line from
four-inches to four-feet above the sinker. The hook is attached using
a Palomar knot and the weight is attached to the tag line from the
knot. The hook is set at a 90-degree angle to the line, typically
with the hook point pointing upward toward the pole. Typical drop
shot baits are small, usually 4-inches or less.
Dry
fly A
pattern designed to imitate an adult insect, floating on top of the water.

Dry flies can also imitate mice, frogs, and snakes. A dry fly is often tied on a light hook so it can float easily.
Dry
flies can be tied to imitate insects on the water, such as Pale
Morning Duns, or to attract fish to rise without
imitating any one specific insect, such as a Royal
Wulff or Adams
dry fly. Traditional dry flies have a few basic parts,
tail, body, wing, hackle, and head. Floatation of the fly can be
achieved in a variety of ways. Traditional dry flies use the surface
tension of water to float. The fly will ride on the hackle and tail,
and in some cases the hook point will not break through the surface.
Closed-cell foam can be used in the construction or sometimes a CDC
feathers, to hold molecules of air. Some dry flies have to be oiled
with special dry fly floatant before presentation to further enhance
the floatation.
Dry
fly technique
Fishing technique with dry flies is what makes fly fishing so easily distinguishable. In order for the dry fly to float unobstructed, it has to be dried after it is pulled out of the water for another round of presentation. This is accomplished by several rapid strokes or whips of the airborne fly line, called "false casting", in the air.
Another method is squishing the dry fly in amadou to suck out the absorbed water in the dry fly.
Dry flies can be fished upstream or downstream. Casting upstream generally keeps the angler out of the view of the fish while casting downstream may be easier to get at productive holes.
Dubbing
A wrapping to thicken the body of a fly, made by rubbing ground-up
muskrat fur, rabbit fur or other substance onto a waxed thread.
A
primary body ingredient in both dry flies and nymphs, dubbing is a
chopped-up fibrous material pinched and twisted onto the thread for
wrapping onto the fly. Also refers to the process of applying the
dubbing material.
Dubbing
Rake Tool used to tease out dubbing on a fly to give it an
enlarged appearance.
Dun
1.
a greyish or greyish blue (dull) color often seen in the wings of
mayfly adults
2.
an aquatic insect in a life stage just as it has emerged from the
water and can fly.
Duncan's
loop A monofilament knot used most often to tie a tippet to the
eye of a hook. Also called a uni-knot
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Eagle Claw a brand name of fishing hooks
In the late 1920’s Drew McGill and Stan Wright formed the Wright & McGill Co., for the tying of high grade fishing flies. Drew was on the upper Colorado River pursuing his favorite sport, fly fishing that magnificent stream. It all happened when he stopped to light his pipe and take a short rest. The morning’s fishing had not been as good as it could have been, for it seemed that even though the rainbows and native Trout were rising, they were difficult to hook. While thinking of this and the ways that he could improve his fishing techniques, he watched the lazy circles of two large eagles. As he sat quietly enjoying this wilderness scene, one of the eagles slowly spiraled downward and landed beyond him in the top of a dead cottonwood; the tips of the bird’s talons lightly gripping a weathered bare limb. His thoughts turned to the penetrating power of those lethal claws, and then to the penetrating power of the fishhooks he was using.
As the powerful bird took to the air, Drew took his fly and holding it by the tiny leader pulled it across the leather of his fishing creel. The point scraped along the leather, but did not penetrate. Using his fishing pliers, he changed the shape of the hook by slightly curving the point. He tried the fly again and found that, this time it would penetrate. He quickly modified several flies and was back on the stream. The results were encouraging, and he eagerly tested shapes and sizes until driven from the stream by an afternoon thunderstorm.
Returning to the fly factory in Denver, Drew started working to produce a fishhook design with greater penetrating power. A hook that would exert this power in the direct line of pull of the leader. From this research came a fishhook that had sweeping curves and sharper points. It was forged for strength and was double offset for greater hooking qualities. The hook’s point was in direct line of pull and shaped like the talons of that mighty bird.
The rest is history.
This design quickly swept the country, for it offered
the first improvement in fishhooks in hundreds of years. When Drew
and Stan sat down to name their new product, what else could it have
been except Eagle Claw? That’s how it all happened, and
that’s the story of the bird that built a fishhook business.
Earthworm
A
skinny worm that wiggles and makes good bait.
|
Eddy or Eddies A calm spot next to a fast current, or in the case of a "back eddy," where the current switches direction. Have you ever seen a river where some of the water looks like it is moving the wrong way? This is an eddy. Eddies are spots on the river, usually at the edges, where some of the water moves back upstream. This countercurrent usually moves slower than the main current, and if you watch closely, you'll see the water is actually moving in a big circle and eventually continues downstream. |
|
Electro
fishing A term used to describe using electrical current to
temporarily stun fish, typically during fish surveys.
Electronics
Commonly
refers to the depth finders, and fish locaters used by anglers.
Electro
shocking A term used to describe using electrical current
to temporarily stun fish, typically during fish surveys.
Elk
Hair Body hair from elk which is used in many fly patterns to
supply body and floatation.
Emergence
The process during which fry leave their gravel spawning nest and
enter the water column.
Emerger
1.
An aquatic insect in the transition period from hatching off the
bottom of the river to flying away from the surface of the water as
an adult insect.
Often will have an attached trailing shuck which feeding fish may key upon.
2.
A fly designed to imitate a waterborne insect as it is leaving it's
nymph stage and emerging into a flying insect.
Entrails.
the internal organs, especially the intestines; viscera
E.P.A.
EPA
Environmental Protection Agency.
Esox Esox is a genus of freshwater fish, the only living genus in the family Esocidae — the esocids which were endemic to North America, Europe and Eurasia during the Paleogene through present.
The type species is E. lucius, the northern pike. The species of this genus are known as pike and pickerel, and in heraldry they are usually called lucy.
The big pike species are native to the Palearctic and Nearctic ecozones, ranging across northern North America and from Western Europe to Siberia in Eurasia. They have been found in many urban lakes in Western Europe, reported to be in the Rostrum (Lucerne) and the Serpentine, (London).
Pike
can grow to a maximum recorded length of 6 ft, reaching a maximum
recorded weight of 77 lb.
Estaz
Trade
name for a chenille which uses colored fine plastic strips for the barbules.
Can be found at many craft shops and yarn stores
Estuary
Area where salt water (such as the bay) and fresh water (such as
creeks) join, usually influenced by tides. Sheltered water, often
with grass bottom or grassy shorelines, where juvenile fish have
shelter, food and a chance to grow.
Evening
hatch When
many insects choose to emerge from under the water.
Eye
1. could refer to eyelets on a fishing rod - See Eyelet
2. could refer to a part of the fishing hook. The eye is where you tie the hook onto your fishing line. See how to tie a hook onto your line here

Eyelet
The eyelets, line guides or rings on a rod through which fishing line
is passed.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
FAD's
Fish Attracting Devices were first used centuries ago. Any large,
floating object like a tree that attracts pelagic fish. Some are
anchored; others are allowed to drift.
False
cast
False
casting
Casting
the fly line forward and back in the air as a means to lengthen the
amount of line that extends out from the rod, to dry the fly or to
modify the path of the line. In a false cast, the fly is not allowed
to drop onto the water.
Casting
ever-increasing segments of line, or casting the same amount of line,
keeping the line aloft in the air without touching the water.
Fan
cast
To cast in a manner
that resembles the arms of a clock. Thus the angler
is attempting to cover as much ground as possible.
Farm
Pond
Small man made body of water.
Fathom
Six feet of depth. Many nautical charts are marked in fathoms, not feet.
FAS abbreviation
for Fishing Access Site
Federation
of Fly Fishers A
non-profit organization dedicated to teaching the sport of fly
fishing and the improvement of fisheries.
Feeder
Stream A feeder Stream is a smaller one that leads
to a more important one, usually a river. When the river warms up in
July and August, many of the trout species congregate in the mouths
of feeder streams where the water is cooler.
Felt
soles Most
wading shoes for fly fishing are soled with thick felt for good
traction on slick rocks.
Ferrule
The joint where different sections of a fishing rod fit together.
1. A ring or cap, typically a metal one, that strengthens the end of a handle, stick, or tube and prevents it from splitting or wearing
2. A metal band strengthening or forming a joint
Click
Here for MORE detailed information on FERRULE
Fiberglass
Material
used to make Crankbait rods. Glass makes the rod less sensitive and
more flexible, and reduces the chance of pulling a Crankbait
from a fish's mouth.
Fillet
A piece of fish with the bones removed, cut out for human consumption.
Fin
The external membranous projecting part of a fish used in propelling
or guiding the body.
Folds of skin supported by cartilaginous tissue in elasmobranches and by bony rays in bony fishes. Used for locomotion, display, and sometimes specialized functions such as fertilization.

See
either: Adipose Fin Anal
Fin Caudal Fin
Dorsal Fin Pectoral
Fin or Ventral Fin
Finesse
Commonly
refers to slowing down and using smaller lures,
line, and rods. Also a style of small lures used for this technique.
Fingerling
Refers to a young fish in its first or second year of life - about a
finger long, usually 2 inches or so in length.
Fire
tiger Color
scheme that involves a lure
with green back, chartreuse sides, orange belly and black vertical
lines on the sides.
FISH
A
creature that lives in water and has fins and gills.
Literally, a vertebrate (animal with a backbone) that has gills and lives in water, but generally used more broadly to include any harvestable animal living in water. Fishes refers to more than one type of fish; finfish refers to sharks, some rays and bony fishes, and scalefish refers to fish bearing scales
Fisherman One
who engages in fishing for sport or occupation, or for food. Also
referred to as Angler
Fishery
A term used for a lake, river or stream where people can catch fish,
or even a particular kind of fish, such as a bass or trout fishery.
Fishfinder
A fishfinder or sounder (Australia) is an instrument used to locate
fish underwater by detecting reflected pulses of sound energy, as in
SONAR. A modern fishfinder displays measurements of reflected sound
on a graphical display, allowing an operator to interpret information
to locate schools of fish, underwater debris, and the bottom of body
of water. Fishfinder instruments are used both by sport and
commercial fishermen. Modern electronics allow a high degree of
integration between the fishfinder system, marine radar, compass and
GPS navigation systems.
See also Depth
Finder
Fish
Hair Synthetic hair used in tying streamers and salt water flies.
Fish
Hook see Hook
Fishing
a term applied to any activity which aims to capture fish or
shellfish for subsistence, scientific, commercial or recreational
purposes. An enormously diverse range of approaches can be taken to
this, from a large, open-water trawler, to a simple lobster trap, to
a dry fly.
Fishing
Access Site (FAS) An area adjacent to a
stream or lake which has been acquired by FWP to allow anglers
access to a water body. Fishing access sites are funded in part by
fishing license fees.
Fishing
Boat a boat for fishing; often has a well
to keep the catch alive. See also Jon
Boat
FISHING
HOLE
A
place known to be good for fishing.
Fishing
Hook see Hook
FISHING
LICENSE
A
permit to fish. You must have a permit if you are over the age of 18.
Fishing line Specialized "string" used for fishing. It connects fishing reel to the hook
Nylon
monofilament line is the most popular. Other lines are made of
different materials, including braided fibers and wire.
FLY
LINE is a specialized line made of a plastic coating on a core, and
often made tapered (changing diameter) to make fly casting easier.
See More Detailed Information on Fishing Line Here
Fishing Pole
A pole with a hook
and line used to
catch fish.
a rod of wood or steel or fiberglass that is used in fishing to extend the fishing line [syn: fishing rod]
Fishing
Reel A
fishing reel is a device used in recreational and sport fishing for
the deployment and retrieval of fishing
line using a spool mounted on an axle. They are most
often used in conjunction with a fishing
rod, though some specialized reels are mounted directly
on to boats.
Reels come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but there are now three basic configurations of reel in common use - overhead, underhand, and threadline (eggbeater).
A multiplier reel allows for longer range casting.
Fishing
Regulations
Laws that are made to protect fish, and govern how many fish can be
caught and under what conditions
Fishing
Rod A
rod of wood, steel, or fiberglass used with a line for catching fish.
A length of fishing line is threaded along a long, flexible rod or pole; one end terminates in a barbed hook for catching the fish, while most of the rest of the line is wound around a reel at the base of the pole. The pulley-like arrangement of the reel allows the fish to be "reeled in" once caught. The use of a fishing rod is known as angling. Fishing rods vary in length and strain capabilities. Usually fishing rods will vary in size between 6 and 16 feet (2 and 5 m). This length advantage increase the amount of force which the fish exerts on the fisherman's arms.
|
Types of Fishing Rods |
Also
called fishing pole.
But
its not a pole
Fishing
Tackle All
the things used to go fishing.
Pole
Rod
Reel
Fishing Line
Bait
& Lures
Live
and Natural Bait
Artificial
Bait and Lures
Plugs
Poppers
Spoons
Spinners
Jig
Crankbaits
Hooks
Sinkers
Bobber
Swivels
Tacklebox
See Our Basic Fishing Equipment Page for more detailed information
Fish
pass
A cut dredged through a barrier island, created to allow better fish
traffic and tidal flushing.
Fixed Spool Reel As the name suggests the spool is fixed in position and the bale arm rotates around the spool when the handle is turned and this lays the line in an even manner up and down the spool core. The spool moving up and down a central rod system creates this evenness. This action occurs simultaneously when the reel handle is turned.
See
Spinning Reel
Flashabou
Commercial name for a colorful synthetic filament material used in
fly tying for adding flash to streamers as well as other patterns.
Flasher
a type of Lure
Flake
a term used in Australia to indicate the flesh of any of several
species of small shark, particularly Gummy Shark. The term probably
arose in the late 1920s when the large-scale commercial shark fishery
off the coast of Victoria was established. (Until this time, shark
was generally an incidental catch rather than a targeted species.)
Flake rapidly became popular. It has a mild flavor, a soft texture that nevertheless remains well-defined after cooking, and a clean white appearance. These qualities, combined with the ready supply and a low price, saw flake become by far the most common type of fish to be served in Australian fish and chip shops.
Flake remains popular, but it is no longer especially cheap. By the mid to late years of the 20th century, Australia's growing population and more efficient harvesting methods had led to an alarming decline in shark stocks, and the fishery is now regulated in the hope of preventing any further deterioration.
Although the primary shark species sold as flake is the Gummy Shark, there are several others, as listed below.
|
During the late 1960s it became apparent that larger individuals of several shark species were contaminated with high levels of heavy metals, particularly mercury, and a public outcry eventually led to a ban on the sale of large School Sharks in 1972, which remained in effect until 1985.
Flat
Flats
Very
shallow water, where water is still and easy to wade, usually with a
sand bottom. This water is so thin, anglers
equipped with polarized glasses can visually spot and cast
to various fish, such as bonefish, Redfish and tarpon.
A bottom that does not change more than a couple feet in depth. The flat can be near the shore or far away from it.
A flat might be called a shallow pool. Flats may or may not be productive, depending on bottom type. Smooth, sandy flats are almost worthless as trout habitat, except at the edges or near woody debris. Gravel flats are better, but flats that are filled with aquatic vegetation are perhaps the best. Open channels that often form between the weeds are perfect holding spots for trout, but beware: trout on flats are incredibly wary and can see the area above the water perfectly. Fishing for trout in flats is a place where presentations must be artful, tippets must be long and fine, and trouters must make every effort to conceal themselves from their quarry.
A topo map shows the contour lines very far apart.
Flatfish
Fish with a flattened body form that live on or in the bottom of waters.
Flier
The flier (Centrarchus macropterus) is a sunfish (family
Centrarchidae) native to muddy-bottomed swamps, ponds, weedy lakes,
and riverine backwaters across the American South, from southern
Illinois east to the Potomac River basin and south to Texas.
Flies
Artificial imitations of the aquatic and terrestrial insects found
in and near trout streams. Flies are tied of many and various
materials, such as feathers, fur, thread, tinsel, and even space-age
materials. Patterns imitating minnows, baitfish
and other fish and crustacean species are also called "flies."
Flipping
The technique of placing a lure in a given spot precisely, and
quietly, with as little disturbance of the water as possible using an
underhand cast while controlling the line with your hand. Normally
used in dirty water and in thick cover.
Flipping
stick
A heavy 7 ½-foot rod designed specifically for flipping.
Normally these rods telescope down to a smaller size.
Float maintains
bait at given depth, indicates bites.
Also
called a "bobber",
these suspend hooked baits off of the bottom, and signal hits by
"bobbing" when a fish takes the bait.
Float
Fishing Any fishing from a boat or wade fishing when fishing
access is gained by boat.
Float
Outfitting The operation of any boat for the commercial purpose
of float fishing by a fishing outfitter or fishing guide.
Float
tube A
one-man fishing floatation device for lake and slow river fishing
that looks like an inner tube covered with a cloth mesh liner, seat,
and back rest.
Using floats help you catch fish that swim near the surface of the water
Similar
to an inner tube in size and shape, a float tube is an inflated ring
covered with a fabric structure with a seat and pockets for an angler
to fish ponds and lakes. Also known as a "belly boat."
Floatant
Material applied to flies and leaders in order to cause them to
float on the surface of the water. Typically sold in liquid or paste
form, although dry shake crystals have recently been found on the market.
A
coating designed to keep a dry fly from becoming waterlogged.
Floss
Material for tying flies.
Floater
same
as float
Floating
worm
Plastic worm used to catch spawning bass
that actually floats on top of the water. Common colors include pink,
yellow, and sherbet.
Floodplain
any lowland that borders a stream and is inundated periodically by
its waters.
Florida
Rig
A worm sinker that has a metal cork screw in the base so that the angler
can screw in the worm. This keeps the sinker and worm together and
reduces tangles.
Very
similar to the Texas rig, the only
difference is the weight is secured by "screwing" it into
the bait.
Flossing
Using really long leaders to float thru lots of stacked up fish,
trying to hook the fish on the outside of the jaw
Flounder
a group of flatfish species. They are demersal fish found at the
bottom of coastal lagoons and estuaries of the Northern Atlantic and
Pacific Oceans.
Fluorocarbon
New style of line that is often invisible below the water's surface.
Flutterbait
Any type of bait that is cast and then allowed to "flutter"
down, resembles a dying bait fish. Typically used in bass fishing.
Fluvial
Migrating between main rivers and tributaries. Of or pertaining to
streams or rivers.
Fly
An artificial
lure hand tied with "stuff" on hooks.
An
imitation of a fish food item, traditionally very light and made of
hair, feathers and thread tied to a hook. Modern flies have many
synthetic materials and often include lead to help them sink.
Fly Angler
Anyone who fly
fishes using pole
or rod
and reel.
Fly
Casting The process of casting
a flyline out onto the water.
Fly
Drag Refers to the wake made by the fly when being
retrieved or when the fly has reached its maximum drift on a stream.
Fly
Fishing A technique for fishing where the weight of the line is
used to cast a very light weight fly that would not be heavy enough
to be cast with a conventional spinning or casting rod.
Casting small, very light-weight artificial flies that simulate insects and other fish food requires weighted fishing line from very flexible rods and hand-controlled reels. The casting is different from other kinds of fishing because the weighted line is usually extended through a series of both forward and backward casting motions.
Fly
Fishing Rod Fly Fishing rods are long, thin, flexible rods
sometimes made of bamboo, but more recently from man-made materials.
Fly rods tend to have large diameter eyes (or guides) spaced along
the rod to help control the movement of relatively thick fly line. To
aid in the freedom of movement required to skillfully cast
with a fly rod, there is usually little to no butt (handle) extending
below the fishing reel. Although fly rods are mainly used for casting
from fixed positions, they can also be used for trolling for fish.
Fly
Line A weighted line which is cast
out onto the water to deliver the fly to the desired location. Can be
found in many densities and tapers.
|
Floating Line A flyline design to float on the surface of the water along its entire length. Typically used for dry fly fishing and shallow water nymphing. Sinking Line A flyline design to sink below the surface of the water for getting a wet fly or streamer down deeper. Can be found with different sink rates for different fishing styles. Sinking-Tip Line A hybrid flyline design which is floating for most of its length except for a short section of sinking line at the end. |
Fly
lure "Blue Winged Olive", a classic dry fly for trout.
A fly lure or Fly, in terms of sport fishing and fly fishing, is an artificial lure tied with thread, feathers, and hair.
Fly tying is becoming common practice in fly fishing. Many fly fishers tie their own flies, either following patterns in books, natural insect examples, or using their own imagination. The technique involves attaching small pieces of feathers, animal fur and other materials on a hook in order to make it attractive to fish. This is made by wrapping thread tightly around the hook and tying on the desired materials.
There
are four main categories of flies:
|
1
Dry fly |
Fly
Pattern Recipe used for tying a specific fly.
Fly
Reel
|
A reel used to store line, provide smooth tension, or drag, and to counterbalance the weight of the fly rod during the casting process. Can be found in many different weights and with different drag mechanisms. A special fishing reel with fairly simple mechanics (compared to spinning or bait casting reels) designed to hold large diameter fly line. A fly reel is relatively light and attaches below the handle on a fly rod. More sophisticated (and expensive) fly reels have a drag system that creates resistance to the rapid pulling off of line by a fish. |
|
The
special fishing rod constructed so as to cast a fly line. Fly rods
are generally longer and thinner than spinning or casting rods. The
special design involves careful attention to the way the fly rod
bends because that bending action
determines how well it can help cast a fly line. Fly rods were
originally split cane bamboo. In the last 60 years, other materials,
especially fiberglass and fiberglass with embedded graphite fibers
are used. Fly rods are rated in their stiffness to match fly lines of
different weights. (a number 6 fly rod should be used with a number
six fly line).
Fly
Tying The process of building fishing flies using thread
and various materials.
Flying
bridge A
permanent, raised steering cabin or platform on the bigger fishing
boats. On the big offshore charter boats, the captain stays up on the
flying bridge all day, while the deckhands below scurry about,
catching the fish.
Flying
gaff A
detachable gaff, designed for big fish. The steel hook is attached
to a strong rope. The pole is used to jerk the hook into the fish,
detaches, and the fish is suddenly attached to the boat by a rope.
Football
head Design
refers to the shape of certain jigs that resemble a football mounted
side ways. Normally used in very rocky locations.
Forage
Small baitfish, crayfish and other creatures that bass or other
predator fish eat. Term may also be used in the sense of bass
actively looking for food (foraging).
Foul
hook To hook a fish other than in the mouth where it
should take bait or lure
Free
Spool A reel that allows line to feed freely to the fish
or current, or the method of feeding line without drag or resistance
to fish or current.
Freestone
River
A
creek or river that gets most of its water flow from rainfall or
snow/glacier melt. Freestone streams are most common in mountainous
regions. The name freestone refers to the fact that typical freestone
streams have a bottom of stones or gravel.
Freestone
Stream
A creek or river that gets most of its water flow from rainfall or
snow/glacier melt. Freestone streams are most common in mountainous
regions. The name freestone refers to the fact that typical freestone
streams have a bottom of stones or gravel.
French
fry
Soft-plastic worm about 4 inches long. Resembles a crinkle-cut
French fry. Used often on Carolina
Rigs .
Freshwater
In a broad sense 'freshwater' is used for all continental aquatic
systems such as rivers and lakes. In a technical sense it refers to
bodies of water that do not have salt.
Freshwater Fish
Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in
fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salinity of less than 0.05%
Frog
Soft,
tough plastic lure
that swims on top of the water. Often used in thick, scummy areas.
Front
Weather system that causes changes in temperature, cloud cover,
precipitation, wind and barometric pressure.
Fry
The first stage of a fish after hatching from an egg.
A
stage of development in young salmon or trout. During this stage the
fry is usually less than one year old, has absorbed its yolk sac, is
rearing in the stream, and is between the alevin
and parr stage of development.
FWS
F.W.S.
Fish
and Wildlife Service.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]

Gaff
A steel hook of varying sizes, mounted on a pole or stick, used for
snagging worn-out fish that have been played to boatside by fishermen.
Use of gaffs is permitted only to help land a fish that was lawfully hooked.
Gaiters
Commonly a neoprene anklet or legging put over the top of wading
shoes and to keep gravel from getting into the shoe and abrading the
stocking foot of the wader. These are also called gravel guards.
Gamakatsu
A brand name of hooks.
Game
Fish Game
fish are fish pursued for sport by recreational anglers. They can be
freshwater or saltwater fish. Game fish can be eaten after being
caught, though increasingly anglers practice catch and release to
improve fish populations.
The species of fish pursued by anglers varies with geography. Some fish are sought for their value as food while others are pursued for their fighting abilities or for the difficulty of pursuit.
Big game fish are bony saltwater fish such as tuna, tarpon, and billfish (sailfish, marlin and swordfish).
In North America, anglers fish also for common snook, redfish, salmon, trout, bass, pike, catfish, walleye and muskellunge. The smallest fish are called panfish, because they can fit in a normal cooking pan. Examples are crappies, perch, rock bass, bluegill and sunfish. Panfish are often hunted by younger anglers.
In
the United Kingdom, "game fish" refers to Salmonids (other
than grayling) – that is, salmon, trout
and char. Other
freshwater fish are called coarse fish.
Game
Warden A
person in uniform (water police) who checks on fishing laws. Do you
have a permit?
Ganoid
Scales Ganoid scales are found in the
sturgeons, paddlefishes, gars, bowfin, and bichirs. They are derived
from cosmoid scales, with a layer of dentine in the place of cosmine,
and a layer of inorganic bone salt called ganoine in place of
vitrodentine. Most are diamond-shaped and connected by peg-and-socket
joints. They are usually thick and do not overlap. In sturgeons, the
scales are greatly enlarged into armour plates along the sides and
back, while in the bowfin the scales are greatly reduced in thickness
to resemble cycloid scales.
Gap
The gap is the size of the bend in a fish hook from the shank to its point.

GAR
A
long freshwater fish; not good to eat.
Gear
Any tools used to catch fish, such as rod and reel, hook and line,
nets, traps, spears and baits.
Gear
ratio
Retrieve speed of reel determines how much line is reeled in one
revolution of the reel's handle.
German
brown trout
A native of the European continent, the brown trout has a golden
sheen and black and orange speckles with white rings around them.
GIG
A
spear with prongs used to catch fish.
Gill
See Gills below
Gill
Arch Bony or cartilaginous arches in the throat of fish to
which the filaments and rakers of the gills are attached. Bony fish
usually have four gill arches.
Gillnet
Gill
Net
A
commercial (not sport-fishing) net used to harvest fish. So named
because of the mesh sizes designed to catch the intended species by
the gill. Commonly used by biologists when conducting fish surveys.
Gill
Opening An opening behind the head that connects the gill
chamber to the exterior. Bony fishes have a single such opening on
each side whereas cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) have
five to seven. The gill opening of sharks and rays are called gill slits.
Gill
Plate A bony protective flap that covers the gills.
Gills
The fleshy and highly vascular organs comparable to lungs used in
aquatic respiration.
The feathery organs of fish and other aquatic creatures that extract oxygen from the water and return carbon dioxide.
Respiratory
organ of many aquatic animals; a filamentous outgrowth well supplied
with blood vessels at which gas exchange between water and blood occurs.
Gizit
A brand name of tube bait (the original).
Global
Positioning Satellite device used to accurately determine
your location with in feet. Handy for finding your way on unfamiliar lakes.
Golden
rule
Gold color aluminum measuring device used in tournaments to measure bass
in order to easily determine the length of the fish.
Gong
Show:
Also known as the "gong".
A term that refers to a spot where fisherman stack up, usually close
to the road. Lines are getting tangled and there is a disportionate
amount of anglers
wearing camo getups.
GPS
abbreviation for Global
Positioning Satellite
Grand
slam Some
notable angling
achievement, usually three popular species of fish from a certain
area. A flats grand slam would be a tarpon, permit and bonefish. A
billfish grand slam would be a sailfish, blue marlin and white marlin.
Graphite
Material
used to make rods. Good conductor thus graphite rods are sensitive.
A
common material which if formed into fibers and placed in the fiber
glass of a fly rod, makes the rod relatively stiff with little
increase in weight as compared to fiber glass alone.
Grass
Vegetation
catch-all phrase. Refers to green plants growing in the water. Bass
are attracted to the grass, which is home to prey.
Grayline
The grayline on a fish finder lets you distinguish between strong and
weak echoes. For instance, a soft, muddy or weedy bottom returns a
weaker symbol, which is shown with a narrow or no gray line. A hard
bottom returns a strong signal, which causes a wide and dark grayline.
GREAT
OUTDOORS Being out in Nature.
Green
Drake A
large, green-bodied mayfly found in many trout streams, a particular
favorite food for trout.
Greyline
See Grayline
Grinder
A
device used to grind chum
before tossing it overboard.
Grip
The cork handle of a fly rod, generally made of cork rings shaped in
several different ways, including a cigar grip, full-wells grip,
half-wells grip, superfine grip.
Ground
Fish Fish that live on or close to the bottom of the ocean.
Groundwater
the water contained in the open spaces between individual soil
particles. Below the ground surface and above the water table, water
in the soil does not fill all the open spaces. Groundwater is not the
same as surface water runoff.
Grub
A short, plastic type of worm, usually rigged with a weighed jig
hook. In saltwater fishing, "grub" covers all of the basic
plastic shrimptail brands, one of the first of which was the Boone
Tout Tail. Or, it might be a plastic minnow tail, such as the Sassy Shad.
Guadalupe
bass (Micropterus treculii) The Guadalupe
bass is a rare species of fish endemic to the U.S. state of Texas,
where it also is the official state fish. It is restricted to creeks
and rivers (including the Guadalupe River, hence the name Guadalupe
bass), and was formerly listed as vulnerable, but IUCN currently
considers the data insufficient to determine its status. Today, most
fly fishermen and anglers practice catch-and-release techniques to
improve fish populations. The Guadalupe bass is often difficult to
distinguish from the smallmouth bass or spotted bass, and the first
is known to hybridize.
Guide -
|
1. An eyelet. Metal rings, usually bent pieces of wire along the length of the fly rod to ease the release of line during casting and to distribute the stress of a fish along the entire length of the rod. |
|
2.
Person who is paid to lead others.
Gunwale (Gunnel)
The
top of the boat's sides. The rail.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Habitat
The natural environment where people, animals and plants live.
In an aquatic environment, it includes the water, topography,
structure and cover present in a lake.
An
area that provides food, water, shelter and space for wildlife.
Hackle
Any soft-stemmed feather with non-adhering barbules.
The
series of extended fibers right behind the eye of a fly.
The
hackle is what allows a dry fly to float.
Typically used to refer to hen or rooster chicken feathers.
|
Hen Hackle Hackle feathers from a hen chicken characterized by soft, wide feathers. Since these feathers readily soak up water, they are usually used on nymphs and streamers. Jungle Cock A type of hackle with prominent singular white dot patterns often used to suggest eyes. Neck Feathers Feathers from the neck of the chicken which are shorter and tend to have a wider selection of sizes on a single skin. Saddle Feathers from the back of the chicken which are longer and have thinner stems. Best choice for most dry flies. Herl Feathers used for tying with long individual barbules each having short dense fibers. Typically from Peacock and Ostrich. |
Handline
A fishing line used without a rod or reel; a line held in the hand.
Harbor
Part of a body of water protected and deep enough to furnish anchorage.
Harpoon
A barbed spear used in hunting large fish
Hatch
Generally refers to a stage of aquatic insect change when there is a
transformation from a swimming to a fly stage and from an underwater
to a surface stage. Insects in the early part of this transition are
also referred to as emergers.
Hatch
box A device used to incubate relatively small numbers of
fish eggs. The hatch box is usually located adjacent to a stream,
which supplies the box with water.
Haul
A pull on the fly line with the non-casting hand to increase the
line speed and get greater distance. This is done effectively during
line pickup. An action associated with fly casting whereby the line
speed is increased with an extra pull during line pickup, or back
casting.
Also see double haul.
Hawg:
A really big fish - Slang Term
Headboat
A government fisheries term for partyboat. Basically a fishing boat
for hire that carries more than six people. The average is more like
30 anglers,
and sometimes more than 100. With that many lines, you mostly fish
straight down with heavy tackle for bottom
fish.
Headwaters
uppermost reaches of a stream.
Hellgrammite
The larvae of the dobsonfly.
Helm
A
tiller or wheel used to steer a boat
Helmsman
Person who steers a boat.
Hen
Female
fish
Hit see
strike
Hitch
A
loop around an object then back around itself.
High-sticking
Holding
the rod high to keep the line taut in a nymphing drift.
Hog
line:
Boats or bankies stretched across a river in a line
Hone
To sharpen hooks or knives with a stone.
Honey
Hole A slang term describing a specific hole, spot, or
area containing big fish or lots of catchable fish.
|
Hook A curved piece of metal; Pointed wire hook used to catch fish (hopefully). A hook can be barbed or barbless. It is usually attached to a fishing line, which in turn is most often supported by a fishing rod. In general the hook is concealed within the bait or trailed closely behind or within the lure. The most dangerous part of fishing equipment. At least one of these is tied to the end of the line, or is attached to a lure. There are more brands, types and sizes than anyone could ever use, but all anglers have dozens of them. Some can be sharpened, some can't. But they all get dull, or bent, and have to be replaced more frequently than razor blades.
The punch administered by said fisherman's wife after he spends their life savings (see also, Right Hook, Left Hook). |
The size of the hook refers to the gap between the point and the shank. The length of the shank is referred to as 1XL for one extra long, or 2XL for two extra long and so forth. Assuming that the hook we are discussing is of regular length, and the hook is between size 2 and 28: the higher the number the smaller the hook, the lower the number the larger the hook, and hook sizes are represented by an even number. After size two, we use both odd and even numbers, and after size one we add a slash and a zero after the hook size like 1/0 or 2/0, and the higher the number the larger the hook. So the hooks run in size from smallest to largest like this: 28, 26, 24, etc . . . ., 8, 4, 2, 1/0, 2/0, 3/0, etc . . . For general trout fishing you will probably use sizes 6 through 20 the most. For panfish, sizes 10 through 16 are most common, however these are usually a little heavier and more wind resistant than trout flies. For bass you will use sizes 2/0 through 8 and these flies are even heavier and more wind resistant than most.
Hook
and Line referring to a Fishing
Pole, Fishing
Rod or Fishing
Reel
Hookset
(setting the hook or striking)
Hookset
is a motion made with a fishing rod in order to "set" a
fish hook into the mouth of a fish once it has bitten a fishing lure
or bait. That is, in order to secure the fish on the hook, a sharp
motion is performed to push the barb of the hook into the fish's
mouth, preferably in the corner. If this motion were not performed,
while it is possible for a fish to set itself, the likelihood of
successfully landing the fish is slim since, without the barb of the
hook secured, the fish could simply shake the hook out of its mouth.
The motion is usually a sharp, sweeping motion of the rod, either
upwards or to the side, depending on the orientation of the rod at
the moment the fish bites. Some fishermen will sometimes perform
several hooksets in quick succession to ensure that the fish is
securely hooked, especially on fish with tough mouths such as some
saltwater species, while in contrast, anglers using circle hooks
needn't set the hook at all, since the hook's unique design allows it
to set itself when the angler reels in.
Hook
size To a degree hooks are standardized based upon the gap (or
gape) which is defined as the distance between the hook shank and the
hook point.
Smaller numbers refer to larger hooks, consistent with the origin of hooks made from steel wire stock. Hooks for fly fishing range from a very small #24 (gap of 2 mm) to very large #2 (hook gap of 10 mm).
Hoop
Net A net trap designed to capture fish moving
within a body of water. Hoop nets are permitted for use in certain
locations in the Eastern Fishing District. A permit is required for
fishing with a hoop net.
Hopkins
Spoons
A brand name of spoon with a hammered appearance.
Hoppers
A good-sized live shrimp sold at the marinas, usually a white shrimp.
Horse
To force a fish in too fast . . . . "he really horsed that one".
Hula
grub Soft
plastic curly-tailed grub, with a soft skirt type feature at the
head of the grub.
Hump
Section of the lake bottom that rises vertically toward the surface,
or is shallower than the area around it. A submerged island would be
considered a hump. Humps can often hold fish.
Husky
Jerk A
classic jerkbait by Rapala
Hydrilla an aquatic plant. As it is native to the cool and warm waters of the Old World in Asia, Europe, Africa and Australia, with a sparse, scattered distribution; in Europe, it is reported from Ireland, Great Britain, Germany, and the Baltic States, and in Australia from Northern Territory, Queensland, and New South Wales - Hydrilla is now naturalized and invasive in the United States following release in the 1960s from aquariums into waterways in Florida. It is now established in the southeast from Connecticut to Texas, and also in California
The
stems grow up to 3 - 6' long. The leaves are arranged in whorls of
two to eight around the stem, each leaf 1/4 - 1/2 " long, with
serrations or small spines along the leaf margins; the leaf midrib is
often reddish when fresh.
Hydrology The science dealing with the distribution, properties and circulation of water on land, in the soil, and in the atmosphere.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Ice
Fishing The act of fishing through holes cut in the ice. Usually
from a shelter or hut.
Ichthyology
The science or study of fish.
IGFA
I.G.F.A.
International Game Fish Association
Improved
clinch knot The
suggested knot for tying a fly to the leader or tippet.
Inboard
(1)
Within a boat.
(2)
A boat with a built-in engine.
Incoming
tide Water
pushing inshore, generally caused by the moon's gravity pull. A
strong wind blowing out to sea can
somewhat
negate an incoming tide, however.
Indiana
blade
Refers to a teardrop shaped blade used on spinnerbaits.
Indicator
species
A species of plants or animals that suffers when pollution or
environmental stress begins, thus indicating environmental degradation.
Inlet
A natural pass between ocean and bay. Unjettied inlets are more
hazardous to boat traffic, because of shifting sandbars that can be a hazard.
Most inlets are now jettied with granite rocks, to protect against erosion and to save dredging costs.
In-line
Commonly refers to in-line spinners where the blade, body, and hook
are all in a straight line. Example is a typical Mepp's spinner.
In-line
spinner A spinner where the hook is on the same shaft, or
line, as the spinner all in a straight line , such as a Mepps,
Rooster Tail, Panther Martin or Vibrex spinner.
Inshore
A
nebulous term that means perhaps within sight of land. "Let's
head inshore" means moving the boat from offshore back towards land.
Inshore
Fishing Fishing carried on near the shore.
Intermittent
stream (or seasonal stream) a stream that flows only
when there is sufficient stormwater runoff. Most creeks in East Bay
watersheds are intermittent. Compare perennial
stream.
Imbricate
Imbricated
Lying lapped over each other in regular order (like scales of a fish
or shingles on a roof).
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Jack
A
kind of saltwater fish; fun to catch and good to eat.
Jack
plate
Device attached to the transom of a bass
boat that allows the outboard motor to be mounted farther
back and higher that originally. Improves performance. Example, Rite
Hite Jackplate. Also used for shallow-running flats boats. This
device jacks the motor straight up and down, without tilting the
lower unit, even while running.
Jacobson
downdrift Feeding
slack into the line as the fly emerges downstream to imitate an
emerging insect.
|
Jerkbait There are two types: soft and hard. The soft style is similar to a baitfish profile and rigged with a large worm hook. Example: Slug-Go. Hard jerkbaits resemble more of a minnow baitfish. Examples are a Rapala or Smithwick Rogue. Both style lures are fished by twitching or jerking the lure forward, hence the name. |
|
The rocks attract many species of coastal fish.
Jewfish
A
large saltwater fish; very good to eat. Grouper.
Jig
A
kind of fishing lure
used for jigging.
Sometimes called "bucktails"
Jig
and pig
or
Jig
n Pig
Combination
of a leadhead jig fitted with a pork trailer. Popular for flippin'
and pitchin' fish-holding structure, such as submerged bushes and trees.
Jig Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed information here
Jig
Fishing see Jig above
Jigging
Working
a jig. That means
popping the rod tip up and cranking in some line with the reel,
making the jig dart through the water. Very attractive to most fish species.
Fishing
with short little jerks on the line.
Jigging
Rod Jigging rods are very thick spincasting
rods which are used to bounce heavy metal lures
on or near the ocean bottom. Very heavy bait
and line is used in ocean jigging in order to reach the ocean floor
through strong currents. To counter act this, jigging rods need to be
stiffer and with a larger diameter than spinning rods used for casting
or in fresh water applications. Bottom
fish such as halibut and cod require a jigging rod.
Jigging as a technique is also practiced in fresh water, however as a rule, normal spincasting rods can be used for this.
Jigging
spoon Refers
to a spoon that is typically "jigged" or bounced off the
bottom with a slight up-and-down motion of the rod or rod tip so the
spoon resembles a dying shad or other baitfish.
Jitterbug
Old
wooden-body topwater lure
with large metal lip. Makes a gurgle-type commotion when retrieved.
Jon Boat A small flat-bottomed, square-fronted, shallow-draft boat that is popular with duck hunters and many anglers alike.
Nobody
knows why a Jon boat is called a Jon boat. The origins of the
nickname are actually unknown. What is certain is that the term has
been used since the early 20th century to refer to various types of
boats. Today, "Jon boat" is used specifically to refer to a
flat-bottomed boat used for fishing, usually in relatively small,
calm waters. It's usually between 8 and 20 feet long, and is also
typically fitted with bench seats inside - anywhere from two to three
basic board seats that stretch across the width of the boat. Because
a Jon boat doesn't have the V-shaped hull of other fishing boats, it
doesn't "cut through" water in the same way and isn't
really designed for use in rough conditions
Johnboat
John
boat See correct name Jon Boat
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Kahle
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed
information here
KastMaster A
brand name of spoon.
Keel
The
underwater backbone on the bottom of a boat.
Keel
guard Handy
device that is glued to the keel of a bass
boat, so that it can be beached without damage to the
bottom of the boat.
Keeper
1. Any fish large enough to keep for eating.
Legal size bass. Example: In Missouri bass must be 15 inches long in order to be a keeper.
2.
A loop of thin wire built into the shaft of the fly rod (near the
grip) the fly can be attached while still connected to the tippet and
line. This allows the fly fisher freedom to walk and climb without
concern about hooking trees, grass or himself.
Keeper
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed
information here
Kelp
A kind of seaweed. Fish like to swim under it.
Kelt
A spawned out Steelhead on the way back to the Ocean, also known as a
dropback, downriver
Kicker
Larger, heavier bass
that really helps out the total weight of a tournament angler's
catch. Example; "I had a limit of 2-pounders, but was lucky and
caught a 5 pound kicker."
Kidney Spoon
A fishing lure with an
oval shape.
King Mackerel
A kind of saltwater fish; good to eat. Kingfish.
Kingfisher
A kind of bird (waterfowl) seen around water.
Kite
rig Fishing
a bait with a kite.
Fishing kites are different from land kites, usually flat and square.
The live bait skips around on the surface, without the telltale line
being visible. Used mostly on sailfish, but effective on other species.
Knot Protector Bead The bead protects the knot from the sliding sinker. it is placed between the knot and the sinker
I would not suggest using a bead to protect your knot. The beads edges around the hole on both sides can become sharp and cut or fray your line at the knot causing it to become weak.
I would recommend using silicone airline tubing or the "Owner" soft beads, either of the 2 will protect your knot with no worries.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Lace
Hollow fine plastic tubing wrapped around a hook shank to supply a
segmented body.
Lagoon
Found
mostly in the Pacific, lagoons are shallow, protected areas usually
ringed by coral reef.
Lake Lakes are inland bodies of freshwater ranging in size from less than one acre to several thousands of acres. Simply stated, lakes are the bodies of water that fill depressions in the earth's surface.
|
What's The Difference Between A Lake, A Pond and A Reservoir? The main difference between lakes and ponds is size, but ponds are also usually artificially created and are not natural. Lakes are deeper and larger bodies of water that can influence local climate if large enough. Ponds are much smaller than lakes and usually have the same temperature from top to bottom, whereas lakes can have dramatically different temperatures from the surface to the bottom waters. Also, rather than affecting local climate, ponds are usually greatly affected by local conditions. Reservoirs are lakes, often man-made, that control water flow for hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and/or municipal water supplies. |
Lake
Bed
The bottom of a lake.
Lake
Trout Lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) is a
freshwater char living mainly in lakes in
northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, lake
char (or charr), touladi, and grey trout. Lake trout are prized both
as game fish and as food fish.
Lake
Zones Designation that includes four categories:
shallow water, open water, deep water and basin.
Land
bringing the fish to the land or to a net for capture.
Landing
Net a bag-shaped fishnet on a long handle to take a captured
fish from the water
Largemouth Bass (Micropterus
salmoides) A black bass, body green-shaded with a broad,
continuous dark stripe along each side, belly white to yellowish,
dorsal fin almost completely separated between spiny and soft portion
and lower jaw extends past the gold-colored eye.
Also
called bigmouth bass, Green Trout, Green Bass, Bucketmouth.
Puts up a big fight and is good to eat.
Larva
The
second, or "worm" phase of an insect's life cycle.
Sub
surface stage of development of an aquatic insect.
Lateral
Line The lateral line system allows the detection of
movement and vibrations in the water surrounding an animal, providing
spatial awareness and the ability to navigate in space. This plays an
essential role in orientation, predatory behavior, and social schooling.
The
lateral line is a system of sense organs found in aquatic
vertebrates, mainly fish, used to detect movement and vibration in
the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified
epithelial cells, known as hair cells, which respond to displacement
caused by motion and transduce these signals into electrical impulses
via excitatory synapses. Lateral lines serve an important role in
schooling behavior, predation, and orientation. For example, fish can
use their lateral line system to follow the vortices produced by
fleeing prey. They are usually visible as faint lines running
lengthwise down each side, from the vicinity of the gill covers to
the base of the tail. In some species, the receptive organs of the
lateral line have been modified to function as electroreceptors,
which are organs used to detect electrical impulses, and as such
these systems remain closely linked.
Lead
A
heavy metal weight.
Leader
the piece of line attached to the hook.
Section of line used between the flyline and the tippet. Often purchased as a tapered section, but can be assembled by tying successively smaller diameter sections of monofilament.
A strong wire or string used between a lure and the fishing line.
1. The piece of clear, tapered monofilament line attached to the fly line, usually between six and 15 feet long.
2. In bass fishing, a short piece of line attached to a swivel when making a Carolina Rig.
Leaders provide extra strength or abrasion resistance from the rough mouth and teeth of fish (pike, barracuda, sharks), scales (sharks), gill covers (tarpon and snook), blows from tails (tuna).
Lead
fly The
primary fly tied on the end of a fly line.
Leadhead
Bare Leadhead jig that is normally used to rig a grub body onto. A
term for a jig where lead is molded to the hook shaft.
Leading
the act of keeping the rod tip and strike indicator downstream of
the drifting nymph.
Leech
A bloodsucking worm that trout love to eat.
Lees
Ferry The popular 16-mile stretch of tail-water fishery
along the Colorado River tucked between the Glen Canyon Dam and the
Grand Canyon in northern Arizona. It is renowned for its large, wild trout.
Legally
Taken Any fish caught using legal methods and not immediately released alive.
Leptoid
Scales Leptoid scales are found on higher-order bony
fish, the teleosts (the more derived clade of ray-finned fishes). As
the fish grow, scales are added in concentric layers. The scales are
arranged so as to overlap in a head-to-tail configuration, like roof
tiles, allowing a smoother flow of water over the body and thereby
reducing drag.[citation needed] Leptoid scales come in two forms:
Lew’s
See Zebco
Lever
drag
The serious offshore reels designed for ocean fish now use a very
smooth lever drag, as opposed to the older star drag.
Lie
Areas in a river or lake where fish hang out, commonly well-located
because they are out of the main current, present cover from
predators or provide a good source of insects and other food.
Light
Cahill A dry fly pattern.
|
Lilly |
|
Limerick
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed
information here
Limit
Legal
limit of bass, or
other fish.
Line
![]() Something
you give your co-workers when they ask on Monday how your fishing
went the past weekend.
Something
you give your co-workers when they ask on Monday how your fishing
went the past weekend.
Line
dressing An old term carried over from the days of silk fly
lines referring to the oily substances applied to clean and increase
buoyancy. Modern fly lines generally only need to be cleaned with
warmwater and soap. Line weight: The weight of the first 30 feet of a
fly line, used as a way to standardize fly lines in matching them to
fly rods of differing stiffness. Line weighting is not a linear
numbering system; the first 30 feet of a #6 weight line 160 grains
while the first 30 feet of a #3 weight line is 100 grains.
Line
Guides The eyelets or rings on a rod through which fishing
line is passed. See Guide
Line
Hand The hand used to handle and manipulate the fly line
during the casting sequence and the retrieve. The line hand
works in conjunction with, and in proximity to, the rod hand
Line
memory When
a fly line, leader, or tippet stays in the same position in which is
has been bent, tied, spooled, or coiled.
Line
Speed How fast a fly line travels as a result of the casting
stroke and rod action
Line
weight The
relative weight of a fly line. A "1 weight" rod throws a
thin, light line, while a "10 weight" rod throws a very
heavy, thicker line.
Lipless
Crankbait
Shad-shaped Crankbait
that has no visible diving lip. The line attaches to the top of the lure.
Artificial
baits designed to resemble a swimming baitfish.
Such plugs vibrate and/or wobble during retrieve; some have built-in rattles.
Also
called swimming baits.
Example;
Rat-L-Trap
Lipping
A method of landing fish, especially bass, by placing a thumb into
its mouth to bend the lip down slightly, temporarily paralyzing the
fish to get it into the boat or unhook and release it.
Lit
up Pelagic
fish such as the marlins, sailfish and wahoo have a tendency to
"light up" with neon, powder blue colors when excited or hooked.
Live
Bait A natural bait, as opposed to an artificial
lure, such as a minnow, grasshopper or worm, mealworms,
red worms, night crawlers, leeches, maggots, crayfish, reptiles,
amphibians and insects
Can also be dead or sections of a real fish.
Live
Bait Hook A
name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed information here
Live
bottom Rocky
bottom, sometimes very flat, where sponges and corals can find
something solid to grow on. This attracts various bottom
fish, such as grouper.
Livewell
Compartment in a boat designed to keep fish alive.
Lizard
Soft
plastic lures similar
to a salamander. Used for Carolina
Rigs , and fishing shallow water in the spring.
Load
Loading
Loading
the Rod
Stored energy in a rod resulting from forcing a bend into the rod.
A term used to describe the effect of the weight of the line and the momentum of the cast upon the rod. A loaded rod is bent or loaded more with a greater casting force and a heavier line.
The
weight of the in-flight fly line and the motion of both the back and
forward cast cause the rod to load or bend. The bend or load
enables the rod to store the energy necessary to make the cast when
the rod is abruptly stopped.
Locators
Common
nickname for depthfinders since they will often display images of
fish as they pass over them.
Long
line fishing is a commercial fishing technique that uses
hundreds or even thousands of baited hooks hanging from a single
line. Swordfish, tuna and Patagonian toothfish are commonly caught by
this method. It is also practiced on a smaller scale in New Zealand,
where a twenty five hook maximum is prescribed by law. Long-line
fishing is controversial because the lines can lead to significant
bycatch, often of endangered species such as sea turtles and albatrosses.
Longliner
As
seen in the movie, The Perfect Storm, longliners are commercial
fishing boats with a huge spool of heavy monofilament line on their
back deck, up to 40 miles long. Used mostly for targeting tuna and swordfish.
Loop
The
candy-cane pattern made by a fly line as it is cast.
The tighter the loop, the more accurate and powerful the cast.
A
general term used to describe the "U" shape of the fly
line as it unrolls during both the back and forward casts. Soft action
rod produce open loops and gentle presentations; fast rods produce
tighter loops and greater distance.
Loop
Connection A method of setting up a flyline/leader rig
using loops tied in each section which can be interlocked for easy changing.
Loose
Action Plug
A
lure with wide slow movements from side to side. Can be the
lure of choice when fish are sluggish in colder water, such as during
winter or early spring.
Lotic
Flowing or actively moving water including rivers and streams.
Lowholed:
When someone steps in front of you as you move down a drift, or sets
up their boat in front of you or your boat.
Lunker
A slang term used to describe a very large bass.
Also
known as Hawg or monster.
a
large specimen of a species of fish.
Lunker
Lure Original
designer of the Buzzbait. Many anglers
still refer to all Buzzbaits as "Lunker Lure."
Lure
 A
man-made bait
used to fool fish.
A
man-made bait
used to fool fish.
A fishing lure is an object attached to the end of a fishing line which is designed to resemble and move like the prey of a fish. The purpose of the lure is to use movement, vibration, and color to catch the fish's attention so it bites the hook. Lures are equipped with one or more single, double, or treble hooks that are used to hook fish when they attack the lure.
Lures are usually used with a fishing rod and fishing reel. When a lure is used for casting, it is continually cast out and retrieved, the retrieve making the lure swim or produce a popping action. A skilled angler can explore many possible hiding places for fish through lure casting such as under logs and on flats.
|
There are several types of fishing lures:
A
jig |
![]() An
object that is semi-enticing to fish, but will drive an angler into
such a frenzy that he will charge his credit card to the limit before
exiting the tackle shop.
An
object that is semi-enticing to fish, but will drive an angler into
such a frenzy that he will charge his credit card to the limit before
exiting the tackle shop.
Lure
Fishing Lure
Fishing is one of the basic Fishing Disciplines. It makes use of
wood, plastic, or a metal device which can emulate or simulate
anything that the fish would likely tend to eat. For more
information, see our section on Lure Fishing.
Lure
Retrievers
Heavy
devices designed to knock loose or retrieve snagged fishing lures.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Main
stem
Mainstem
In
a particular drainage, the mainstem is the primary stream or river
into which most tributaries flow.
Mangroves
The only trees that grow in salt water. Mangroves protect tropical
coastlines from storm surges, and their extensive root system
attracts a variety of shallow water gamefish.
Marabou
Jig A weighted jig with light, fluffy feathers
attached to the body.
Marker Buoy A small plastic buoy, often fluorescent color that is tossed into the water to mark a fish holding area or a school of fish. Such buoys are popular for those fishing schooling sport-fish, such as crappie, white bass, or striped bass, in open water.
Martin
See Zebco
Matching
the hatch Choosing
the fly pattern that imitates the insects that are hatching nearby.
Mayfly
The most beautiful of aquatic insects, the mayfly is characterized
by an upswept wing and long, delicate two- or three-stranded tail.
The mayfly goes through three stages -- egg, nymph, and adult -- then
metamorphoses once again from a sub-imago adult to a spinner. It is
an important food for trout, which means it is also important for fly-anglers.
Mealworms
Small beetle larvae often used for catching crappies or sunfish.
|
Meander A meander, in general, is a bend in a sinuous watercourse or river. A meander is formed when the moving water in a stream erodes the outer banks and widens its valley. A stream of any volume may assume a meandering course, alternately eroding sediments from the outside of a bend and depositing them on the inside. The result is a snaking pattern as the stream meanders back and forth across its down-valley axis. |
|
All
rivers and streams "meander." This means they have bends
and turns, depending on the geography of the land. Land that is
fairly flat may have a straighter river, while hilly land probably
creates a river that meanders more. A "switchback" is when
a river doubles back on itself, making a "U" shape. Bends
in rivers also affect depth. The outer part of a river bend is
usually deeper, while the inner part of the bend is usually shallower.
Meat
Hole
A spot where "fisherman" gather because the fishing is so
good, even the biggest fool can get fish at the "meat hole".
Usually lots of guys ripping sides trying to snag fish.
Mend
To move the fly line upstream from the location of the fly to ensure
no unwanted drag is on the fly that may scare a fish
Throwing
an upstream curve into your fly line as it floats down the stream to
avoid having water currents pull on it and cause unnatural movement
of your fly (unnatural drift or line drag). Fish and especially trout
are exquisitely sensitive to (and turned off by) movement of a insect
that moves at a different rate or in a different direction than the current.
Mending
The act of lifting the fly line off the water and flipping it either
upstream or downstream to eliminate drag and accomplish a more
natural drift.
Mepps
Mepps
Spinners
A brand name in-line spinner.
Merging
currents A
dead spot of calm water created where two currents come together.
Midge
A
very small species of aquatic insects found in trout streams. Many
species of midges hatch into adults in the middle of winter. They
have four stages of development, from egg to larva to pupa to adult.
A
very small (non-biting), two-winged insect, related to deer flies,
mosquitoes and crane flies.
Migration
Route The path followed by bass or other fish when
moving from one area to another.
Milfoil
Surface-growing aquatic plants.
Milk
To play a fish too long
Milt
The sperm of fishes.
Mini
Jig A small leadhead jig, usually 1/16- or 1/32-ounce,
often used for catching crappie or sunfish.
Minnow
Any
of several small fish less than a specific size and not considered gamefish.
Mojo
rig Technique
similar to a Carolina Rig
except that it is rigged on a spinning rod. Thus it is a
finesse-type method. The sinkers are cylindrical or pencil-shaped to
come through rocks without snagging.
Mollusks
Oysters, scallops, mussels, snails, squid, octopuses.
Mono
Short for monofilament fishing line.
Mono
leader
Leader made of monofilament. Mono leaders are of course heavier
grade than the line on your reel. Standard mono leader for huge
marlin, for instance, is 300-pound test, while line on the reel
seldom exceeds 80-pound test.
Monofilament
The clear style fishing line most commonly used by anglers.
Fishing line with a single strand of material
Monofilament lines have been around for years and are commonly used as fishing lines. In fact, monofilament lines are the most popular type of fishing line used today because of their strength and low cost. They are made by melting and mixing polymers and feeding the end product through tiny holes, forming the line, which is then spun into spools of various thicknesses.
Discarded monofilament lines presents a serious environmental issue. The lines are extremely difficult to spot when submerged in water, making it possible for fish, birds, and other marine life to easily become entangled in them. Monofilament lines also present a risk to swimmers and scuba divers.
Moon Phases The four phases or quarters of the moon are usually what the fisherman is concerned with. Generally, the bad times in a month occur three days prior and three days after the full moon or new moon. The first-quarter and second-quarter periods are considered as the good moon times.
Moon
Times
See Moon Phases
Moronidae also known as the "temperate basses", is a family of perciform fish consisting of at least 6 freshwater, brackish water and marine species. Moronidae fish are most commonly found near the coastal regions of eastern North America including Gulf of Mexico, northern Africa and Europe.
Asian seabasses Lateolabrax spp. are sometimes placed in this family instead of their own family Lateolabracidae; this would increase the species number of this family to eight.
They are highly prized as sport fish.
Motor
Fish
When
fishing over a tiny spot that is deep, it is more practical to keep
the engine running, attempting to "hover" the boat over the
spot. For instance, the tiny rocks in the Gulf of Mexico, no bigger
than a car, are often 200 feet deep. Anchoring here is impractical
and time-consuming. Instead, you motor over the boat, while a couple
of anglers
drop their baits down.
Muds
Created
by a bottom-grubbing school of fish. For instance, a school of
bonefish rooting on the bottom will gradually muddy the water in a
large patch, easily visible on a sunny day.\
Multifilament
fishing line that is several strands woven together.
Muskellunge
See Muskie
Muskie
Muskellunge or muskie (Esox masquinongy) are large,
relatively rare freshwater fish of North America. They are the
largest member of the pike family, Esocidae. The name muskellunge
comes from the Ojibwe word maashkinoozhe, meaning "ugly
pike," by way of French masque allongé (modified from
the Ojibwe word by folk etymology), "long mask."
Mysis
A type of silvery freshwater shrimp found in cold mountain lakes and reservoirs.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Nail
Knot A knot used to tie together two lines of significantly
different diameters. See also Needle Knot
Nail
Knot Tool A tool used to simplify the process of tying Nail Knots.
Nates
Native steelhead, not of hatchery origin
Native
Something that evolved in this place over a long period of time,
usually in reference to a plant or animal. California poppies and
coast live oaks are native to this region. Eucalyptus trees, which
were imported from Australia, are not native.
Natural
Bait see Live Bait
Net
See Landing Net
Nibble
when a fish is taking small bites out
of the bait on your hook
Night
Crawler a large earthworm found on the surface of the ground at
night, often used as bait
in fishing
Nocturnal
active at night
Non-game
Fish Any wild fish not otherwise legally classified by statute
or regulation of this state.
Non-native
something that evolved somewhere else. Eucalyptus trees evolved in
Australia and were transplanted here. Non-native plants and animals
are usually introduced by humans as they move about the land. Most of
the grasses on the hillsides of the Bay Area are non-native. Vinca
(periwinkle) started as a landscaping ornamental but now crowds out
native plants on creek banks. See native
Northern Pike The northern pike is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus Esox (the pikes). They are typical of brackish and freshwaters of the northern hemisphere (i.e. holarctic in distribution).
Also
referred to as Esox lucius, known simply as a pike in Britain,
Ireland, most parts of the USA, or as jackfish in Canada or simply
"Northern" in the Upper Midwest of the USA. See Pike
Nymph
1.
A general term used to describe the subsurface forms of aquatic
insects prior to emergence.
Also used as the name of flies imitating these insect forms. see below (#2)
2. A nymph resembles an insect or stage of insect living underwater. Leeches, mayfly nymphs, caddis fly larva, and Diptera can all be imitated by nymphs.
Normally a nymph is tied on a heavier hook, sometimes with an added weight in the body or head to keep it underwater during presentation.
Nymph technique
Nymphs can be fished successfully upstream or down. A large percentage of what fish eat is found living underwater and imitated by nymphs.
To learn more about nymph fishing visit http://www.nymph-fishing.com.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]

Oarlock
A
U-shaped holder that keeps an oar in place.
Oars
A
long pole with a blade used to row or steer a boat.
Octopus
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed
information here
Offshore
Fishing
Fishing
done away from the shore.
|
Open Face Spinning Reel An Open face Spinning reel has a stationary spool set on the underside of the rod. A curved bar, or bail, acts as a guide on the outer lip of the spool. As the reel handle is turned, the bail also turns, winding line neatly onto the spool.
|
|
Click
here for detailed information on
Open
Face Spinning Reel
Organic
Baits Minnows, insects, worms, fish eggs, cut bait,
cheese, or similar substances placed on a hook and used as a lure.
Oshaughnessy
O'shaughnessy
A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed information here
Outboard Motor
A
removable engine for boats.
Outfall
the outlet of a body of water, especially in reference into a drain.
Outrigger
Long
poles to hold trolling lines out to the side.
Overhanging
Vegetation Whether it is tall grass or tree branches,
anything hanging out over a stream is worthy of notice. These
structures protect trout from their most effective predator, the
fisherman. Plus, terrestrial insects, such as ants, aphids, and
beetles, may drop into the stream from such. A carefully planned cast
that is allowed to drift beneath overhanging vegetation is always
worth a shot. Or, you can creep up on the bank and gently lower a
tiny ant imitation onto the surface of the water and feed out line to
let it drift beneath a tree. This crafty and highly enjoyable tactic
has always been enjoyable.
Oxbow
A U shaped bend in a river or stream. An abandoned meander
in a river or stream, caused by neck cutoff. Used to describe the
U-shaped bend in the river or the land within such a bend of a river.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Scientific
Names: Ephemerella inermis, E. infrequens
Other
Common Names: PMD
This small, pale-yellow mayfly of the crawler group is often referred to by its initials, PMD. Despite the name, hatches can occur in the morning, early afternoon, or evening. It's not unusual to have both morning and evening emergence on the same day.
The
hatch season begins as early as June and lasts as late as September,
depending on the stream. This is often the dominant hatch where and
when it occurs. By this time trout are feeding heavily on these Mayflies.
Palmer
A method for wrapping a hackle feather over a section of the fly's body.
Pan Fish
The
size fish that just fits inside a frying pan.
A small fish, not considered a game fish but sought after for their eating quality. Often applies to sunfish, crappie and perch.
Panther
Martins A
brand name of in-line spinner.
Parachute
style fly A dry fly with the dry fly hackle wrapped
horizontally under the hook or at the base of the wings, providing a
type of outrigger flotation.
Peacock
Ladies
A type of fly used by fly-anglers.
Peacock
Sword A feather from a peacock with bushy herl-like barbules,
commonly used for tails.
Pectoral
Fin Front steering fins on either side of a fish;
corresponds with front legs.

Pelagic
Fish Fish living in the open sea, alone or in schools, at
or near the surface i.e. herring, tuna, and their related species.
Pelvic
Fin Lower fin on either side of a fish; corresponds to
hind legs.
Pencil
Poppers A brand name topwater lure that is long and
thin. Often used for catching striped bass.
Perch
A
kind of fish, fun to catch and good to eat.
Percidae
The Percidae are a family of perciform fish found in fresh and
brackish waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The majority are
Nearctic, but there are also Palearctic species. The family contains
about 200 species in 10 genera. The darters, perches, and their
relatives are in this family; well-known species include the walleye,
sauger, ruffe, and three species of perch. However, small fishes
known as darters are also a part of this family.
This
family is characterized by a greater or lesser degree of armour
about the head, caused by the presence of teeth or spines on the
cheeks and opercles (gill covers) or their edges, and by two narrow
bands of numerous close-set teeth on the sides (palatines). Also,
many percid fishes have a heart-shaped plate of teeth on the roof of
the mouth (vomer). The shape of these fishes is usually somewhat
oblong and laterally compressed. Their scales are generally harsh and
rough to the feel, or ciliate. Percid fishes are among the most
beautiful of the freshwater fishes due to their brilliant colors
(red, brown, orange, and yellow are the most predominant tints).
Perennial
stream a stream that flows continuously throughout
the year. Compare intermittent stream.
P.F.D
PFD
Personal Floatation Device, aka, a life vest or life jacket
Pier
A
platform that goes from the land out into the water. (dock)
Pier
rats Crusty fishermen who spend many hours and days on the big
surf piers, waiting (and often sleeping out there) until the fish
begin biting. These people have the art of pier fishing down to a
science, with their own customs.
Pike
Fish of the Family Esocidae, Order Salmoniformes (salmons, pikes
and smelts).
Esox is a genus of freshwater fish, the only living genus in the family Esocidae — the esocids which were endemic to North America, Europe and Eurasia during the Paleogene through present.
The
type species is E. lucius, the northern pike. The species of this
genus are known as pike and pickerel, and in heraldry they are
usually called lucy.
Pitching
Presentation technique in which worms or jigs are dropped into cover
at close range with an underhand pendulum motion, using a 6 1/2 to 7
1/2 foot baitcasting
rod.
Placoid
Scales Placoid scales are found in the cartilaginous
fishes: sharks, rays, and chimaeras. They are also called dermal
denticles. Placoid scales are structurally homologous with vertebrate
teeth ("denticle" translates to "small tooth"),
having a central pulp cavity supplied with blood vessels, surrounded
by a conical layer of dentine, all of which sits on top of a
rectangular basal plate that rests on the dermis. The outermost layer
is composed of vitrodentine, a largely inorganic enamel-like
substance. Placoid scales cannot grow in size, but rather more scales
are added as the fish increases in size.
Similar scales can also be found under the head of the denticle herring. The amount of scale coverage is much less in rays and chimaeras.
The
skin of sharks is entirely covered by placoid scales.
Plastic Worm
A
flexible, colored, plastic worm with hooks.
You fish these real slow, pulling your pole up and down waiting for a fish
Playing
process of bringing a fish to the angler so it can be landed.
To
exhaust a hooked fish by allowing it to pull on the line.
Plug An artificial bait used to catch fish. A lure.
|
Plugs are a popular type of hard-bodied fishing lure. They are widely known by a number of other names depending on the country and region. Such names include crankbait, wobbler, minnow, shallow-diver and deep-diver. The term minnow is usually used for long, slender, lures that imitate baitfish, while the term plug is usually used for shorter, deeper-bodied lures which imitate deeper-bodied fish, frogs and other prey. Shallow-diver and deep-diver refer to the diving capabilities of the lure, which depends on the size of the lip and lure buoyancy. |
Plunge
Pools Small waterfalls will occasionally be encountered on
trout streams. Where the falling water hits soft bottom, a hole is
scoured out that may be considerably deeper than the surrounding
water. Trout love these tiny, sheltered pockets and a weighted nymph,
cast above the waterfall and allowed to travel down to the bottom of
the plunge pool, will take fish.
Pocket
water Where fast current rushes around boulders and other
obstructions, creating pockets of calmer water.
because
rapids are an area of water that is so swift, trout do not hold in
them. Within a rapid, however, fish will maintain station in scour
holes, behind rocks, and in small "pocket water"
of various types. Heavily weighted nymph rigs may be employed to
explore these areas.
Point -
1.
Where land sticks out into a body of water.
2.
In regards to a fishing hook - the point is what you use to put on
the bait, and what penetrates the mouth of the fish when it eats the
bait. It's critical to keep points sharp, so invest in a file and use
it often.
|
|
|
Polarized
sun glasses Sunglasses with iodized lenses that block incident
light (glare) and thus allow anglers
to better see beneath the surface glare of water.
Pole
see Fishing Pole
Polyphydont
a process by which teeth are continuously replaced as in most fishes
with teeth. The alternative process, termed diphyodont, is having two
successive sets of teeth like humans.
Poly
Yarn A synthetic yarn made from polypropylene. Used in fly
tying, often for parachute posts and wings on dry flies.
Pond
A body of water smaller than a lake, often artificially formed.
|
What's The Difference Between A Lake, A Pond and A Reservoir? The main difference between lakes and ponds is size, but ponds are also usually artificially created and are not natural. Lakes are deeper and larger bodies of water that can influence local climate if large enough. Ponds are much smaller than lakes and usually have the same temperature from top to bottom, whereas lakes can have dramatically different temperatures from the surface to the bottom waters. Also, rather than affecting local climate, ponds are usually greatly affected by local conditions. Reservoirs are lakes, often man-made, that control water flow for hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and/or municipal water supplies. |
Pools
are one of the most obvious features of a stream. They are popular
with beginners who become mystified by the trout they see lurking in
pools. Pools often hold suckers as well as trout. The pool provides
the two things that are generally lacking in coldwater streams: depth
and still water. The deep water of a pool provides a trout with the
ultimate in protection from predators. However, because current in
the main pool, especially near the bottom, is almost nonexistent,
food is hard to come by there. Where a riffle or run enters a pool,a
featured called "the tongue of the pool" is created. This
area is where all biological drift enters the pool, and is a prime
location for trout to lie in wait. The entire upstream end, where the
tongue is, is called the "throat". The deepest section in
the middle of the pool is called the "belly" and the
narrows at the bottom where the water speeds up as it exits the pool
is called the "tail". The tail concentrates food, and any
kind of structure located in the tail of the pool is a prime location
which will hold fish.
Pool
cue: Stiff
action
rod, undesirable
Popper
Artificial lure
with a flat head and surface. Designed to run on the surface when
retrieving or trolled which creates a lot of water surface distortion
to attract predator fishes

Popping
cork A Styrofoam cork with the top shaped to make it
gurgle when yanked. The noise is supposed to imitate sounds of fish
feeding on top, thereby attracting the attention of gamefish.
Pop
R A brand of popper topwater lure.
Port
1.
The left side of a boat when you face forward
2.
A harbor or city where ships may take on or discharge cargo.
Porthole
A small round window of a boat.
Possession
Limit The maximum limit or amount of a fish species set by
regulation that may be possessed at one time by any one person.
Post
front The period following a cold front; atmosphere
clears and becomes bright. Usually characterized by strong winds and
a significant drop in temperature. Fishing can often be slow during
such conditions, especially for bass.
Power
Bait Brand
name of commercially prepared scented baits
Power
Craw Brand
name of commercially prepared scented baits
Power
Eggs Brand
name of commercially prepared scented baits
Power
Grubs Brand
name of commercially prepared scented baits
Power
Worms Brand
name of commercially prepared scented baits
Practice
plug A practice plug is like a lure
without hooks. You tie it on your line and it lets you practice casting
in your back yard or at the park so when you do go fishing you won't
catch a bunch of trees, or your dad or other stuff that is not very good.
Predator
Catches and feeds on other animals.
Presentation
The
placement of the bait on the hook as seen by the fish.
The
placement of the fly on the water as seen by the fish.
The cast as viewed from the prospective of the fish. The angler's goal, of course, is to present the bait or fly in an irresistible way through the mechanism of a perfect cast.
Prey
Something being hunted to be eaten.
Professional
overrun Fancy nickname for backlash
or bird's nest in baitcasting
reels. Also called spaghetti.
Prop
Common term for the propeller of a trolling or outboard motor.
Prop
bait Topwater lure with a metal propeller on one or both ends.
Example; Luhr-Jensen Wood Chopper.
Pulpit
A strong guardrail around the bow or stern.
Pumpkinseed
Light brownish color used often in soft plastic lures. Very natural hue.
Pupa
Sub-surface larval stage of aquatic insect development
The
third phase of an insect's life cycle, when wings are beginning to grow.
Push
pole A long, 20-foot pole made of wood or graphite, used
for silently pushing the boat across the flats, easing within casting
ranger of various fish, such as bonefish.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]

Quantum
See Zebco
|
Quarry |
1.A place, typically a large, deep pit, from which stone or other materials are or have been extracted. 2.An animal pursued by a hunter, hound, predatory mammal, or bird of prey. |
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Rainbow
Trout A beautiful trout species characterized by a
brilliant pink stripe running lengthways down its side. The rainbow
is a silvery fish and has black spots.
Rapids Rapids are a section of a river where the water moves very fast, often over rocks.
Rapids
are areas where the water is so swift that trout do not hold in
them. Within a rapid, however, fish will maintain station in scour
holes, behind rocks, and in small "pocket water" of various
types. Heavily weighted nymph rigs may be employed to explore these areas.
Rat-L-Trap
Original type of lipless Crankbait Thus, most anglers
refer to all similar lures by this name.
Rattles
Glass or metal noisemakers added to lures in order to help bass find
the lure easier.
Reach
cast A cast used for adding extra slack in the line, or
when fishing downstream, in order to provide a more natural float.
Reaper
Soft plastic lure that resembles a leach. Popular on the west coast.
Redfish
Redfish is a common name for several species of fish. It is most
commonly applied to certain deep-sea rockfish or the reef dwelling
snappers. It is also applied to the slimeheads or roughies, and the alfonsinos.
Other
common names: Redfish, Crimson snapper, Malabar blood snapper,
Emperor red snapper, Queen snapper, Deep-water redfish, Blackfin
snapper, Southern red snapper, Lane snapper, Vermillion snapper,
Sockeye salmon, Acadian redfish, Red snapper, Red drum, Ocean perch.
and Norway redfish.
Red
reel The common baitcasting
reel used back in the 1960s was the red Ambassadeur reel.
The reel has changed colors and owners since then, but was the basic
model that jumped countless saltwater anglers
into serious fishing.
Redd
A spawning bed for trout, identifiable by a hollow of clean gravel
in a mild current.
The hollowed out nest in a streambed where a fish deposits its eggs, a behavior typical to most salmonids.
Reds
short for Redfish
Reef
An underwater ledge that sticks up from the bottom.
Reel
![]() A
weighted object that causes a rod to sink quickly when dropped overboard
A
weighted object that causes a rod to sink quickly when dropped overboard
1.
A spool to wind line on.
2.
Winding the line up.
3.
A device in which something is wound i.e. line for fishing; usually
located toward the bottom of a rod.
A
reel is the mechanical device which the line
is wound.
A
device for holding and spooling fishing line. Reels have a line
spool, brake to slow running fish, handle to retrieve line and foot
for clamping to a rod.
A reel most often is used in conjunction with a fishing rod, though some specialized reels are mounted directly on to boats.
Reels come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Reel
styles include
|
Baitcasting
(revolving spool) |
Reel
seat The section of a rod below the grip where the reel is
attached. Reel seats often are constructed of attractive wood,
including many exotic woods.
Reflex
strikes Drawing a bite from fish that have no intention of feeding.
Example; by bumping the Crankbait into the stump (where the bass was hiding) the angler triggered the fish into a reflex strike even though it had just eaten a crawfish
Release
Returning
fish, in the best possible condition after removal of the hook, to
the water from which it was taken.
Reservoir
An
artificially impounded body of water behind a man-made dam extending
upstream to the mouth of its inlet stream(s).
|
What's The Difference Between A Lake, A Pond and A Reservoir? The main difference between lakes and ponds is size, but ponds are also usually artificially created and are not natural. Lakes are deeper and larger bodies of water that can influence local climate if large enough. Ponds are much smaller than lakes and usually have the same temperature from top to bottom, whereas lakes can have dramatically different temperatures from the surface to the bottom waters. Also, rather than affecting local climate, ponds are usually greatly affected by local conditions. Reservoirs are lakes, often man-made, that control water flow for hydroelectric power generation, flood control, and/or municipal water supplies. |
(also
called "stripping" by many fly fishermen.)
stripping
in the fly line that gives the fly action
2. Also, a term used in describing fly reels, as to whether they are left hand or right hand retrieve.
Retrieving
See retrieve
Reverse cast The nymphing cast made by casting across the body on the "off" hand side of the stream. (For a right-handed fisherman, the right side of the stream. For a left-handed fisherman, the left bank.)
Also called the "Western roll cast."
Revolving
Spool Reel Another term for baitcasting
reel.
Rhino
See Zebco
Ribbon
tail Style of plastic worm that has a long ribbon type
tail that ripples when the worm is retrieved.
Ribbonfish
A long, flat, silvery fish many people mistake for an eel, easily
three feet long and sometimes up to five feet long. Long, sharp teeth
are wicked, and they'll chomp through a 40-pound mono leader. Highly
esteemed bait in the Kingfish tournaments, Ribbonfish must be rigged
with multiple hooks because of their length.
Rigging
how you hook your bait and where you put your hook, snap or swivel,
weight and float.
Riffle
A small rapid in a river. Shallower areas in the creek where water
flows quickly, often over gravel or rocks.
Riffles
are the preeminent feature of coldwater streams. They are at once a
food source, a shelter from predators, a hedge against oxygen
depletion, and a conveyor belt that brings food to the trout.
Riffles, with their broken water surface, not only hide the trout
from predators, but also hides predators (such as humans) from the
trout. Because of this, trout in riffles may be approached more
easily, and are harder to spook. Many species of insects reproduce or
grow to maturity in riffles. The constant fast current dislodges
nymphs from the rocks, freeing them into the "biological
drift", a term that refers to the constant downstream movement
of organisms in flowing water. Riffles also oxygenate the water. In
hot weather, trout may congregate in riffles, where the oxygen
content of the water is highest. Riffles may be any depth, but most
are between one and three feet deep. Within a riffle, trout may lie
in wait behind rocks, hug the bottom, or roam about. Small pockets of
deeper water in a riffle are prime feeding locations for trout, and
invariably hold good fish. Riffles also hold larger prey items, like
darters, sculpins, and crayfish, so large trout may move into riffles
periodically to feed, especially at night.
Ring
worm Brand of plastic worm that features rings or
ribs over the outside of the body. The texture is believed to feel
soft and lifelike to fish.
Riparian
Corridor
the vegetated area adjacent to (and including) the creek.
Ripper:
Hard fighting fish, makes your reel "scream"
see
screamer
Ripping
Sides:
Purposely setting the hook every ten feet during your drift with the
intent of snagging a fish by the belly/ass/fin.
Riprap a
layer, facing, or protective mound of rubble or stones randomly
placed to prevent erosion, scour, or sloughing of a structure or bank.
See Armor
Rip
tide
On the beach, this is the water that flows back offshore, after the
waves have piled so much water next to the sand. Unfortunate swimmers
have found themselves in this narrow but strong flow. Savvy surf
fishermen drop their baits in these same spots, where gamefish like
pompano and Redfish congregate.
River
A river is a body of water with current moving in one general
direction. They can vary in size, with smaller versions of rivers
being referred to as streams, creeks, or runs. The water in a river
flows into either a larger river, a bay, or ocean. Rivers themselves
are fed by smaller rivers or streams. Rivers are important habitat to
many different types of plants and wildlife.
Riverbank
A river bank is the land along the edge of a river.
Riverbasin
A river basin is the area of land from which all the water flows
into a particular river.
Riverbed
The area/channel between the banks through which a river flows. The
ground which a river flows over.
Riverboat
A boat designed for use on a river or stream.
Rivulet
A small stream or brook.
Rock
Bass also known as the rock perch, goggle-eye, red eye
The
rock bass is a native fresh water fish to the east-central North
America. This red eyed creature is a species of freshwater fish in
the sunfish family and can be distinguished
from other similar species by the six spines in the anal
fin (other sunfish have only three anal fin spines).
Rocket
launcher A rack of tubes designed to hold five or six
fishing rods in a boat.
Rod A fishing pole with eyelets for line to pass through.
A long lever, usually made of fiberglass, graphite or composite materials and used to catch fish.
Different types are available, such as rods for spinning, fly fishing, spincast, bait casting, boat fishing, offshore trolling, surf fishing, jetty/pier fishing, etc.
Most rods have a reel-holding clamp and guides through which the line runs.
See our Fishing Rod Page for more detailed information
Rod
and Reel
Rod
and Reel Combo A general term used to describe any
combination of a casting or spinning reel attached to a fishing rod.
Rod
belt A leather or (in more modern times) a plastic
belt that fits around an angler's
waist while fighting a fish. The belt socket keeps the rod butt snug,
and saves weary arm muscles and that lower back during a long fight.
Rod
Blank A rod before being fitted out with guides, grip,
reel seat and other accouterments.
Rod
Hand The hand into which the angler
entrusts the rod during either the casting sequence or the
retrieve. Some anglers prefer using one hand to hold the rod
during the cast, exchanging it to the other hand when making the
retrieve or playing a fish.
Rod
Guides see Guide
Rod
Tip
The eye at the end of a fishing pole.
Roe
Fish eggs.
Roll
Cast This is a casting technique that is used when a back
cast is not possible. The line is made to loop in front
of the angler
and if properly executed it "rolls" out to present the fly.
The
roll cast uses the surface tension (drag) resulting from the line's
contact with the water as the means to load the fly rod.
The
roll cast is useful when a
(1)
routine backcast cannot be made
(2)
to return a sinking line momentarily to the surface thereby enabling
the standard backcast.
Rough
Fish Those species of fish considered to be of either poor
fighting quality when taken on tackle or of poor eating quality, such
as carp, gar, suckers, etc. Most species in this group are more
tolerant of widely fluctuating environmental conditions than Game Fish.
Royal
Wulff Dry Fly
The
Wulff series of fly patterns were developed by Lee Wulff.
|
It presents a bushy, high floating fly, that remains visible into the evening twilight, and rides well in rough water. He designed and sold the first fly fishing vests, championed reeling with the left hand on fly reels (so the rod was in the stronger right hand), invented the first palming spool fly reels, introduced the fly-O casting practice rigs, popularized the "riffling hitch" for salmon fishing and designed |
|
Wulff patterns were the first flies to use hair for fly wings and tails. Almost all dry flies available in the winter of 1929/30 were, according to Wulff, anemic and too delicate, which he ascribed to their British tradition. The reason for very slim flies was that if a fly was too bulky the feather materials did not have the buoyancy to hold it up. A very popular pattern, for example, was the Fanwing Coachman that not only twisted the leader but also sunk at the tail due to the golden pheasant tail fibers used. Wulff also noted that dry flies with wings and tails of feathers get slimed up and are not very durable. To Wulff, the solution was obvious use bucktail (deerhair) for tails and wings. The mobility and buoyancy of elk and deer hair has made it a favorite North American fly tying material.
The first Wulff flies were tied to imitate the Isonychia (Gray Drake) and Green Drake hatches in the Catskill area of North East America. Wulff first fished these patterns with his regular fishing companion, Dan Bailey, who was then a science teacher in Brooklyn. In those early trials with these new patterns, Lee's was not disappointed. He found that the fish seemed to prefer the bulkier flies that "looked more" like the naturals than the more anemic patterns that were then popular. With respect to durability, the hairwing flies also excelled. Wulff reports he caught 51 trout on one Gray Wulff fly in an early outing, needing only to "grease up the fly for every 5-6 fish". The first patterns included the Gray Wulff, White Wulff and Royal Wulff. The Grey Wulff can be used to imitate any dark mayfly the trout are feeding on but when Lee Wulff was reportedly asked what the Royal Wulff was imitating he supposedly said, "Strawberry shortcake, something great big and juicy floating down to a large trout." It is an attractor pattern that is easily seen and high floating. It is a sweet little dessert that predatory fish find irresistible.
Later
several other Wulff patterns, including the Grizzly Wulff, Black
Wulff, Brown Wulff and Blonde Wulff were developed. Lee Wulff stated
that these flies were a general kind of fly, not a particular
pattern. When you first use Wulff flies treat with floatant and fish
on the surface. Leave the fly to drift with the current. Occasionally
accelerate it gently over short distances of a yard (meter) or more,
or else twitch it to represent a struggling insect trapped in the
surface film. They were first used in Britain in the 1950's but they
saw very little service in Ireland until after 1990.
Run
1.
(of fish) A group of fish of the same species that migrate together
up a stream to spawn, usually associated with the seasons, e.g.,
fall, spring, summer, and winter runs. Members of a run interbreed,
and may be genetically distinguishable from other individuals of the
same species.
2.
The pulling out of line a hooked fish makes in trying to escape.
3.
A smooth, deep glide of water that usually follows a riffle. Runs
are similar to riffles, but although their current may be somewhat
swift, their surface is smooth enough to allow light to penetrate.
Runs are characterized by moderate current and a smooth surface. Runs
may be deeper than riffles, but this depends on the size of the
stream. Runs that form bends may form undercut banks, as the current
erodes the underside of the streambank. Trout use runs as both
holding and feeding areas. Trout do not need to expend as much energy
fighting current in a run as in a riffle, so when food is abundant,
trout may move out of a riffle and into a run to save energy while feeding.
Runoff (surface runoff) the portion of rain that moves over the ground toward a lower elevation and does not infiltrate the soil. "Urban runoff" refers largely to water from rain, irrigation, or industrial and household discharge that typically flows into a storm drain system that empties into a body of water.
Runoff
is not the same as groundwater.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Salmonid
Any species of trout, char,
salmon, grayling, cisco, or whitefish. All salmonid fish have an adipose
fin (small, fleshy fin on the back near the tail).
Salmon
Egg Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more
detailed information here
San
Juan Worms A type of wet fly designed to look like a
small aquatic worm
Salt
Water Ocean
water. It has salt and many other minerals.
Saltwater
Fish fish that spend some or all of their lives in
salt water such as oceans or salt lakes, generally with a salinity of
more than 0.05%.
Sassy
Shad A brand of soft-plastic lure that resembles a shad.
Scale
Scales
The
skin of most fishes are covered with scales. Scales vary enormously
in size, shape, structure, and extent, ranging from strong and rigid
armour plates in fishes such as shrimpfishes and boxfishes, to
microscopic or absent in fishes such as eels and anglerfishes. The
morphology of a scale can be used to identify the species of fish it
came from.
S-cast
An "S" pattern of the fly line on the water created by
side-to-side movement of the fly rod during the forward cast. This
cast is used to put slack in the fly line and hence to reduce the
influence of the current on the fly line and thus to minimize drag.
School
A
group of fish swimming together.
School
of Fish A school of fish is a bunch of fish playing
together, kind of like all the kids in your class playing on the
playground. But unlike the kids in your playground, all the fish in a
school are going the same directions and when one turns, they all
follow-like instantly!
I don't know how they know whose turn it is to change direction, but they seem to know.
Screamer:
Hard fighting fish, makes your reel "scream"
Schmeg:
The stuff an egg fisherman gets all over his waders, rods, reels,
vest, rocks around him, trees around him, and all over the boat.
Scour
concentrated erosive action of flowing water in streams that carries
away material from the bed and banks.
Scud
1. Term used for freshwater shrimp.
2.
A small freshwater shrimp-like crustacean that is present in most
trout waters and serves as a food source for trout
Scutes
A scute is less common type of scale. Scute
comes from Latin for shield, and can take the form of:
an
external shield-like bony plate, or
Some
fish, such as pineconefish, are completely or partially covered in
scutes. River herrings and threadfins have an abdominal row of
scutes, which are scales with raised, sharp points that are used for
protection. Some jacks have a row of scutes following the lateral
line on either side.
Seam
A calm spot caused by an obstruction in a river such as a rock or log.
Seasonal
Stream See Intermittent stream
Sediment
the soil particles in the creek. The sediment can be on the bottom
of the creek or it can be suspended in the water. Water with a high
sediment load (or turbidity) looks muddy or cloudy.
Seine
A large fishing net made to hang vertically in the water by weights
at the lower edge and floats at the top
A net, usually suspended between two poles, which is pulled through the water to capture fish for bait.
Seines used for this purpose must not exceed 12 feet in length and four feet in width.
selective
harvest personal ethics that includes reduced harvest
within established legal size and creel limits.
Setline
A line or lines with or without a pole set to catch fish without the angler
being present or within immediate control. The angler's name and
phone number, or 9 or 10 digit ALS # must be attached.
Set
The Hook
Giving
a quick tug so the fish gets caught.
When
you feel a fish biting your line you need to jerk your pole real
hard, that is what setting the hook is.
This
hooks the fish real good so he won't come off.
Setting
the hook To make sure the hook penetrates the fish's
mouth, an angler
must apply an upward motion of the fly rod or some sort of quick
tension on the fly line. When fishing with artificial
lures and flies,
fish often do not hook themselves because very soon after they
"mouth" the fly, they are aware that it does not feel,
taste or smell like it should. They will spit it out! This puts a
premium on setting the hook at the right time!
Shackle
A
U-shaped metal fitting with a pin across the "U".
Shad
Natural baitfish
prey of bass. Common throughout the U.S. Any of several species of
forage fish that have a rather deep body.
Shad
Rap A brand name crankbait.
Shakespeare
The Shakespeare Company is a subsidiary of Jarden which manufactures
fishing equipment.
Shank The Shank is the section from the eye of a hook to where the bend starts. Shanks come in short, medium or long lengths, and are a major influence of how a hook is used. Short ones are often used for finesse fishing when a compact hook and minimal weight are critical to a successful presentation, like micro plastic smallmouth tactics or live bait fishing with a leech. Medium shanks are the most common and used in an array of fishing situations. Long shanks are used to match a longer profile of an artificial bait (like a spinnerbait or big plastic).
|
|
Short shanks are often used for finesse fishing when a compact hook and minimal weight are critical to a successful presentation, like micro plastic smallmouth tactics or live bait fishing with a leech. Fly fishermen prefer these for their small body flies.
Long shanks are great for live bait and larger/longer artificials like plastic baits and spinnerbaits. Sometimes there are "barbs" cut into the shank intended to keep soft baits on the hook. |
Shiner
Shiner is a common name used in North America for any of several
kinds of small, usually silvery fish, in particular a number of
cyprinids, but also e.g. the Shiner Perch (Cymatogaster aggregata).
Shoal
A submerged ridge, bank, or bar consisting of, or covered by,
unconsolidated sediments (mud, sand, gravel).
Shock
leader A short but heavy piece of monofilament, attached
to the hook, designed to take the shock of a hard strike. And the
resulting abrasion from sharp teeth or bottom scraping.
Shooting
head Part of a special fly line used for long distance casting.
The shooting head is a heavy section of line attached to a thin
running line (made of monofilament, Dacron or fine fly line).
The Shooting head has almost all of the weight of a normal line, but
obviously is it almost totally concentrated in that first 30 feet.
Shooting heads are used for making long casts in fishing saltwater,
warmwater and steelhead.
Shooting
line The process of extending the length of your fly cast be
releasing an extra length of fly line (usually held in your
non-casting hand) during the forward/presentation part of the
cast. This technique allows a fly
angler to false cast a shorter segment of line and then
only at the time of the final forward cast to bring a longer segment
of line into play.
Shore
The land along the edge of a sea, lake, or other large body of water.
Shrimping
the act of fishing for shrimp.
Silver
eels Slang for Ribbonfish, which are not really eels.
Single
action The typical fly reel wherein a single turn of the handle
causes one turn of the reel spool. This is distinguished from the
multiplier reel where a single turn of the handle causes multiple
turns of the spool and makes it easier to retrieve line.
Almost all high quality fly reels are single action.
Single
haul The technique of pumping the fly line on the forward
segment of a false cast. It is easier than double hauling, which
requires more coordination and technique.
Sinkant
A liquid applied to flies to make them sink.
Sinker
A
weight of lead or other metals designed to sink a hooked bait or lure.

A weight made from lead attached to the rig to hold it in position due to strong current or used to cast the line out further. Commonly found types are bomb sinker, bullet sinker, ball sinker and split shots.
The maximum sinker weight for casting are usually specified on the rod.
A
sinker is a weight used in fishing to force a lure
to sink more rapidly. The ordinary plain sinker is made of lead,
shaped round like a pipe-stem, and swelling out in the middle. There
are loops of brass wire on either end to attach the line. The weight
is from a quarter of an ounce for trout fishing up to a couple of
pounds or more for sea bass
and porgies.
The
swivel winker is similar to the plain one, except that
instead of loops, there are swivels on each end to attach the line.
This is a decided improvement, as it prevents the line from twisting
and tangling. In trolling, swivel sinkers are indispensable. The
slide sinker, for bottom
fishing, is a leaden tube which allows the line to slip
through it, when the fish bites. This is an excellent arrangement,
inasmuch as you feel the smallest bite, whereas in the other case the
fish must first move the sinker before you feel him. Split shot are
sometimes put on trout lines in place of a sinker. Independent
swivels are useful in some kinds of fishing to prevent the
entanglement of your line.
Sinking
Line A flyline design to sink below the surface of the
water for getting a wet fly or streamer down deeper. Can be found
with different sink rates for different fishing styles.
Sink
Tip
Sinking
Tip Line
Sinking
Tips
A
fly line that has both a floating segment (say the first 95 feet)
and a sinking section (the last 10 feet). This style of line is used
for underwater presentation of flies in fast water or in some still
water fishing situations.
A hybrid flyline design which is floating for most of its length except for a short section of sinking line at the end.
Siwash
A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed information here
Size
Limit The legal length a fish must be if it is in possession.
Slip
Sinker A lead, zinc or steel weight with a hole through
the center. Threaded on line, a slip sinker slides freely up and down.
Slot
Limit Dictates that fish within a specified minimum and
maximum size range which must be released immediately. Usually
extends life of predators or reduces number of small fish.
Slough
A long, narrow stretch of water such as a small stream or feeder
tributary off a lake or river.
Slow
Roll Spinnerbait presentation in which the lure is
retrieved slowly through and over cover and objects.
Slush
Bait Topwater plug with flat or pointed head.
Skirt
Silicone, rubber, or plastic material fashioned around a spinnerbait
or similar lure to create the body.
Skunked
Failure
to produce any fish on a given day.
To
catch zero fish or keepers.
A
bad day on the water!
Slime
Layer The layer of mucous covering fish that protects it
from fungi, parasites, and disease.
Slinky
Parachute
cord filled with buckshot, used for weight.
Slip
Bobber a float that slides freely along the angler's
fishing line.
Sloughing downward
slipping of a mass of soil, moving as a unit usually with backward
motion, down a bank. Sloughing is similar to a landslide.
Slug-Go
A brand of soft-plastic jerkbait.
Smallmouth
Bass A black bass, primarily bronze in color, who's jaw
does not extend beyond the eye and is found in clear rivers and lakes.
also called bronzebacks, brown bass, river bass, and smallies.
In freshwater ecology it refers to trees, branches, and other pieces of naturally occurring wood found sunken in rivers and streams; it is also known as coarse woody debris or snag pile.
An unforeseen or hidden obstacle.
To catch unexpectedly and quickly
To catch (a fish), especially by hooking in a place other than its mouth. See Snagging
Snagger
A
person who can't get one the fair way. see
Snagging below
Snagging
A technique of angling
in which a hook or hooks are cast,
trolled or lowered into the water and manipulated to embed the hook
or hooks into the body of the fish. You have snagged a fish if: (a)
you are fishing in a manner that the fish does not voluntarily take
the hook in its mouth, or (b) if you accidentally hook the fish in a
part of the body other than the mouth.
Snakes:
Pink
rubber worms
|
Snap – A small device similar to a dog leash snap, a metal wire clip with a swivel tied to the line and used for attachment and quick release of hooks, rigs and lures. |
|

Often
sold in bulk to be rigged on a hook by the angler.
Sonar
An acronym derived from the expression "sound navigation and
ranging." Refers to the method or equipment for determining by
underwater sound techniques the presence, location or nature of
objects in the water. Fish finders use sonar.
Spaghetti
Another term for backlash.
Also called Professional Overrun.
Spawn
The behavior of fish where females deposit eggs (also called spawn)
on various surfaces (varying with species) and the male
produces necessary milt to ultimately turn the eggs into fry.
The act of reproduction of fishes. The mixing of the sperm of a male fish and the eggs of a female fish.
Spey
A particular casting technique using special two-handed rods and
a modified roll cast. It is named after a river in Scotland where it
was developed.
Spider
Jig
A type of leadhead jig with a skirt, much like the one on a spinnerbait.
Spider
Trolling Trolling with several rods at once.
Spincaster A manner of fishing employing a push-button, closed-face spinning reel and baitcasting rod.
|
Spincast
Reel Reel featuring push button spool release. A fixed-spool reel with the spool enclosed by a housing and the bail arm replaced by a small pick-up pin. Originally designed for spinning, they are popular for light float fishing, especially trotting. The Closed face reel has a stationary spool set on the underside of the rod. A curved bar, or bail, acts as a guide on the outer lip of the spool. As the reel handle is turned, the bail also turns, winding line neatly onto the spool. |
|
|
The following are sub-sets of spincasting rods: |
1. A spent adult aquatic insect following laying its eggs on the surface of the water.
The last stage of a mayfly, based upon the fact that the wings are spread horizontally as it falls to water surface after mating. The spinner is of significance because the spinner is an easy target for feeding fish.
2. A spinner is a lure designed to make noise underwater in order to catch the fishs' attention instead of mimicking food.
Spinner blades rotate around the straight wire shaft of these weighted-body treble-hook lures.


The build of a spinner consists of a metal pin with a dish around it which will make noise when water is flowing by due to the fishing line being reeled in, almost like a fan or turbine. Below the dish metal weighs are placed in order to make the lure sink and to keep the dish from getting stuck in the hook which is placed at the end of the pin. The hook, which is a three-hooked version, as seen on the wobbler, is often camouflaged in a soft material like feathers.
also referred to as Spinnerbait or Spinner bait
Spinnerhead
The spinnerhead is the device that rotates in front of a fixed spool
and lays the line onto the spool. Spinnerheads use either round edges
(like small teeth) to pick up line, or pins that pop out of the
spinnerhead to snare the line.
Spinning
A manner of fishing employing an open-face or closed-face
spinning reel an spinning rod; reel is mounted on the underside of
the rod; rod guides are on the underside of the rod.
Spinning
Reel
Style of reel that allows easy casting of small lures. Best
described as the type of reel that mounts under the rod for best
balance. A fixed spool.
Usually used for casting and inland fishing. Unlike the multiplier, the spool does not turn unless a pulled with pressure on the line by a sizable fish. Line is reeled in by method of using a bale arm rotating around the spool which coils the line evenly.
Spinning
Rod
A
rod made to be used with a spinning
reel.
Split
Cane Rods Fly rods constructed of six pieces of split cane
bamboo, which are triangularly shaped, tapered and glued together.
Split cane rods appear to have originated in the U.S. in the middle
of the 19th century. While used by some modern anglers,
graphite/fiber glass rods offer less expensive and easier-to-care
for options.
Split Shot
Split Shot Sinker Small
weights to squeeze onto a fishing
line.
A small ball of lead of varying weights that is split open on one side and can be placed directly on the line.
Split
shotting Another method of finesse fishing. This technique
involves pinching a small lead split shot sinker a foot or more above
a small worm, then slowly dragging this on the bottom.
Spool
1. a. A cylinder of wood, plastic, cardboard, or other material on which wire, thread, or string is wound. b. The amount of wire, thread, or string wound on such a cylinder. c. Something similar to such a cylinder in shape or function.
spooled, spool·ing, spools
To
wind or be wound on or off a spool.
Spoon
see
Spoon Lure below
Spoon Lure
A
spoon lure
is an oblong, concave metal piece resembling a spoon. The spoon lure
is mainly used to attract fish by reflecting light and moving randomly.
The design of the spoon lure is simple; an oblong, concave metal piece with a shiny chrome or paint finish, and a single or treble hook on the end.

Sport
Fishing Sport fishing is a form of recreational fishing
where the primary reward is the challenge of finding and catching the
fish rather than the culinary or financial value of the fish's flesh.
The distinction is not completely rigid - in many cases, sport
fishers will also eat their captures. However, the philosophies and
tactics used for sport fishing are usually sufficiently different
from "feed fishing" to make the distinction clear enough.
Sport fishing methods vary according to the area being fished, the species being targeted, the personal strategies of the angler, and the resources available, ranging from the aristocratic art of fly fishing invented (?) in Great Britain, to the high-tech, incredibly expensive methods used to chase marlin and tuna. However, in virtually every case, the fishing is done with rod and reel rather than with nets or other aids.
In the past, sport fishers, even if they did not eat their captures, almost always killed them to bring them to shore for weighing. However, pressure from outside combined with genuine concern about fish stocks have seen many sport fishers releasing their captures alive, usually after fitting them with identifying tags and recording their details so as to aid fisheries research (known as tag-and-release).
Sport
fishing competitions give competitors (individuals if the fishing
occurs from land, usually teams where conducted from boats) a
specified time and area to where they are to catch fish from. Scores
are awarded for each fish caught, the points depending on the fish's
weight and species, and then divided by the strength of the fishing
line used (so catching fish on thinner, weaker line scores additional
points). In tag-and-release competition a flat score per fish,
divided by the line strength, is awarded for each species caught.
Spotted bass (Micropterus punctulatus), also called "Spotty", "Leeman", or "Spots" in various fishing communities, is a species of freshwater fish sunfish family (Centrarchidae) of order Perciformes. One of the black basses, it is native to the Mississippi River basin and across the Gulf States, from central Texas through the Florida panhandle. Its native range extends into the western Mid-Atlantic States and it has been introduced into western North Carolina and Virginia. It has also been introduced to southern Africa, where it has become established in some isolated waters. It is often mistaken with the similar and more common largemouth bass.
A
convenient way to distinguish between a largemouth bass and a
spotted bass is by the size of the mouth. A spotted bass will
resemble a largemouth bass in coloration but will have a smaller mouth.
Spring
creek A creek or stream that gets its water from a ground (underground)
flow or spring sources, rather than glacier/snow melt or surface run
off. Spring creeks are generally at a temperature of the average
rainfall temperature over the course of the year (the source of
most ground water) and hence usually do not warm significantly in
the summer nor freeze in the winter.
Spring creeks are typically small, clear, and challenging to fish.
Spring
runoff The time of year when the snow melts and runs into
the rivers, swelling the trout streams with a great volume of water.
Square
Bill Style
of Crankbait known for their small square diving bills. Excellent
lures to retrieve through trees, stumps, rocks.
Example: Bagley B-III or Luhr-Jensen Speed Trap.
Squall
A
sudden storm with wind and rain.
Square Knot
A
double knot. Also called a reef knot.
Standing
end Line leading back to pole or rod
Standing
Line The rest of the line that runs up toward the reel.
Standing
Water Water that is not flowing; stagnant.
Starboard
The
right side of a boat.
Still Fishing
Fishing
without moving the bait once it is cast. The method of fishing that
usually involves the use of a bobber to suspend live bait at a
certain depth.
Stimulator
Used frequently with a dropper,
it is a dry fly that doesn't
closely mimic one particular insect, but is "buggy" and
attractive to game fish.
Stinkbait
Stink bait is exactly what it sounds like: a stinky bait used to
catch fish, especially catfish. You can purchase stink bait at bait
shops or sporting goods stores, or make it yourself using items from
the grocery store. Some stink bait consists of just one or two
ingredients. Strong odors seem to draw catfish. What smells awful to
the fisherman apparently smells pretty good to the fish, so the
stinkier the bait, the better.
Steelhead
A variety of rainbow trout that spawns and lives part of its life in
freshwater streams and other parts in oceans. While native to the
Pacific Ocean, steelhead have been successfully introduced into many
large lakes and now are found in some tributaries of all of North
America's Great Lakes.
Stern
The
rear part of the boat.
Stick
Bobber
a type of bobber shaped like a stick
Stocking
The process of releasing fish into a lake or stream.
Stonefly
Family of aquatic insects commonly imitated in fly fishing. Many
species are found in western streams.
One of the major species of aquatic insects found in a trout stream. Stoneflies have three phases of development, from egg to nymph to adult, and may live underwater as long as four years before hatching to an adult winged insect. Stonefly nymphs often crawl out of the river to hatch out of their nymphal shucks on rocks.
Storm
drain system consists
of street gutters, catch basins, underground pipes, open channels,
culverts, and creeks.
Stream
A body of running water.
Stream
Bank the rising ground bordering a stream channel.
Streambed
The channel being occupied or formerly occupied by a stream. See
also creek bed
Stream
Channel see Creek Channel
Streamer
Streamer
fly A streamer fly or streamer can be used to mimic injured
fish. Streamers can be used to catch predatory fish of almost any
size. Fish will bite streamers out of aggression while protecting
spawning areas, out of curiosity, or when feeding. The big showy
Atlantic Salmon flies, bucktails (hairwing), and feather wing flies
all fall into the streamer category.
Streamer fly technique
The fishing technique with a streamer is much the same as with a spoon lure. Casting across and downstream is the traditional presentation. Retrieves can be fast or slow and erratic to imitate an injured fish.
Stream
Mouth The downstream point defined as a straight line running
from the most downstream extremity on one stream bank
to the most downstream extremity on the other stream bank or a point
defined and marked by FWP (Fish, Wildlife and Parks)
Strike
Any "hit"; the action by a fish taking a lure or bait.
This term also refers to the movement of the rod a fly angler makes to set the hook.
Strike
Indicator A term used interchangeably with very small
brightly colored floats or a stimulator. Basically strike indicators
help the angler know when a strike has occurred.
A
strike indicator is anything that can be attached to the leader to
let the waiting angler know that the drift of a sunken fly (or nearly
invisible small dry fly) has been intercepted by a feeding fish.
Therefore, the defining characteristics of an indicator are that it
should float and it should be visible to the angler.
Stringer
A method of keeping fish alive after they have been caught. A string
or small nylon rope is threaded through the mouth and gills of a fish
and is then tied off to the boat or dock allowing the fish to remain
overboard in the water but preventing them from swimming away. With
the advent of livewells and other more modern methods of keeping
fish, stringers have become nearly obsolete, but can still be quite
handy when fishing from the bank of a pond.
The
term "stringer" is also used by anglers to indicate the
size of their catch for the day (10 pound stringer = 10 pound fish).
Striped
Bass (Morone saxatilis), also called Atlantic
striped bass, striper, linesider, rock, pimpfish, or rockfish) is the
state fish of Maryland, Rhode Island, South Carolina, and the state
saltwater (marine) fish of New York, New Jersey, Virginia, and New
Hampshire. They are also found in the Minas Basin and Gaspereau River
in Nova Scotia, Canada.
Striper
referring to The Striped Bass
Stripper
Guide See
Stripping Guide below
Stripping
Bringing in a fly line with in a series of short or varied pulls so
as to simulate a living insect or bait fish. Often also involves
movements of the rod tip.
|
Stripping guide The stripper or stripping guide is the first guide encountered on the rod nearest the reel on a rod, usually more substantial and larger in diameter than the snake guides nearer the tip. So called because this is the guide that is worked the hardest when you are stripping line in or (even more so) when a fish is stripping line off your reel. Some rods have two stripping guides, with the larger being nearer the reel. |
|
Any
area that causes fish to be concentrated
Structure
Spoon –
Both casting and vertical jigging techniques are used for fishing
these swinging hook heavy metal lures.
Sucker
Fish Suckers are bottom-feeding fish found throughout most
of the United States. Although suckers are not normally targeted by
most anglers the fish is capable of putting up a great fight and is
very fun to catch. Suckers have a fleshy mouth with thick lips that
point downward, allowing the fish to forage for food along the
gravelly and mucky stream and river beds where the fish live. Some
suckers can weigh as much as four or five pounds at lengths of up to
2 feet, making them a formidable fish when hooked on a spinning rod.
Sunfish (Centrarchidae) The sunfishes are a family of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the order Perciformes. The type genus is Centrarchus (consisting solely of the flier, C. macropterus). The family's 27 species includes many fishes familiar to North Americans, including the rock bass, largemouth bass, bluegill, pumpkinseed, and crappies. All are native only to North America.
Family members are distinguished by having at least three anal spines. The dorsal spines are 5–13 in number, but most species have 10–12. The pseudobranch is small and concealed. Sizes of most are in the 8 to 12 inch range. However, some are much smaller, with the blackbanded sunfish at just 3 inches in length, while the largemouth bass is reported to reach almost 3 1/2 ft in extreme cases.
Most
sunfishes are valued for sports fishing, and have been introduced in
many areas outside their original ranges, sometimes becoming invasive species.
Surface
Lure also known as top water lures,
poppers and stickbaits. They
float and resemble prey that is on top of the water. They can make a
popping sound from a concave-cut head, a burbling sound from
"side fins" or scoops or a buzzing commotion from one or
several propellers. A few have only whatever motion the fisherman
applies through the rod itself, though if skillfully used, they can
be very effective.
Surf
Fishing Rod
Surf
fishing rods resemble spinning rods with much larger proportions.
Generally between 10 to 14 feet in length, surf fishing rods need to
be larger and more robust in order for the user to get the bait
out beyond where ocean surf breaks. The shallow water and low
visibility of surf break zones means that fish tend to congregate
just beyond this area. Some people can use surf rods to cast
six ounces of lead weight and bait hundreds of feet, and casting
competitions are sometimes held on dry land.
Surgeon's
knot A common and strong knot for tying tippet material to the
leader or one segment of tippet material to another. A surgeon's knot
is stronger than a blood knot, especially for connection materials of
unlike size and material. The blood knot has the advantage of being
smoother and less likely to catch algae or cause tangles.
Sweet
Jigging:
Same as ripping
sides
Swim
Bait Soft plastic lure that resembles
a baitfish.
Normally a life-size copy of a bluegill, shad, or trout.
Example: Castaic lure
Swimming
Lures Sinking-type artificial
baits designed to resemble a swimming baitfish.
Such plugs vibrate and/or wobble during retrieve; some have built-in rattles.
Also called lipless crankbaits
Swivel
Lets
a line spin without twisting it up.
|
A
strong connection between the mainline and the leader to eliminate
line twist. Made from brass or A small device with two or more eyes (rings) a central swiveling part. |
|
They are used between a lure or leader and line to prevent line twist. Otherwise, line twist can occur when a revolving lure twists line to cause tangles.
Swivel
Winker click here
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Tackle see Fishing Tackle
![]() What
your last catch did to you as you reeled him in, but just before he
wrestled free and jumped back overboard
What
your last catch did to you as you reeled him in, but just before he
wrestled free and jumped back overboard
Tackle Box
A
box or bag with special compartments and features to hold terminal
tackle, lures,
hooks, and other fishing
gear.

Tag
end End of fishing line
Tailing
Loop The result of an error in the casting technique.
Tailing loops usually result when the rod tip following a concave
path, such as it will do if the caster "jerks" the rod
forward at the end of the backcast.
Jerking the rod forward from the backcast applies power improperly
and at the wrong time. The rod tip, in turn, dips sharply into
a convex path. Since the line goes where the rod tip goes, the
line is sure to follow the same concave path forming the tailing
loop. The evidence of a tailing loop is a simple unwanted
overhand knot somewhere in the forward part of the tippet.
Sometimes called a "wind knot," the knot is anything but
the result of the wind. When you begin to notice these little
teeny-tiny knots, look for an error in the mechanics of your cast.
Tail
Spinners Compact, lead-bodied lures with one or two
spinner blades attached to the tail, and a treble hook suspended from
the body; designed to resemble a wounded shad; effective on schooling bass.
Tailwater
The downstream section of a river or stream found below a large
man-made dam. The most famous and productive tailwaters are from
bottom-discharge dams, making the water relatively cold and constant
in temperature.
Area
below a reservoir.
Taper
1.
The varying diameter of a fly line over its length.
2.
An area in a body of water that slopes toward deeper depths
Ten
to Two The casting motion whereby the position of the rod
tip is compared to the hands of a clock.
Terminal Tackle
A
general term for describing bobbers, sinkers, hooks, rigs, snaps,
swivels and other gear used at the end of a line.
Terrestrials
Insect species whose life cycle occurs on land, such as beetles and grasshoppers.
Test
Most
fishing line is made of nylon and is called "monofilament,"
or mono for short. It comes on spools of various lengths that are
called "tests." Usually, a four-pound test line will hold
up a fish weighing four pounds without breaking. The larger the test
of the line, the thicker the diameter it is and the more it will
hold. For your basic rig, try to find a piece of four-pound or
six-pound test line that is eight to ten feet long.
Texas
Rig The method of securing a hook to a soft-plastic bait -
worm, lizard, crawfish, by burying the hook point into the body of
the lure

Thermocline
Depth of lake where the lowest level of useable oxygen and cooler
water temperatures meet. Bass will rarely be found below this level.
Thi
Bead See Knot Protector Bead
Thirty
second rule After 30 seconds out of the water, trout have
little chance of surviving if released.
Thorax
the part of an artificial fly
or real insect that relates to the "shoulders and chest" of
a fly.
Three-way
swivel Three rings on this swivel, usually of a brass
color. The hook line is perhaps 2 feet long, attached to one of the
three rings. That keeps it away from the main line and weight. If a
current is running and the bait is spinning, the ring turns and the
line won't kink up
Tide
The rise and falling of the surface of the ocean.
Tighten
the Drag When you tighten the drag on your reel it makes
the line harder for the fish to pull out and makes them get tired
faster. But you have to be careful not to make it too tight or the
fish can pull so hard your line breaks.
Tinsel
A metallic filament used in fly tying to provide flash and color.
Tippet
a.) a short length of gut, nylon, or the like, for tying an artificial fly to the leader.
b.) a branch of the shaft of a bird feather, serving as the tail of an artificial fly.
Tippet The terminal segment of monofilament tied on the end of a leader and connected to the fly.
Tippet is a specific gauge monofilament line that is attached to the end of the leader, to which you tie the fly. The tippet is usually the smallest gauge line on your rig and is virtually invisible to the fish. Tippet is also very flexible and allows your fly to float or swim more naturally.
Tied to the leader, it protects the leader length and condition. This is the line that is cut when flies are switched.

Tip
section The top section of a fly rod, smallest in diameter and
furthest from the rod grip.
Is
also The Help Guides found throughout this Site
![]()
Tiptop
Line guide or Eyelet at top of a fishing rod.
Toe
the bottom of a slope or creek bank.
Topwater
Jerkbait Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more
detailed information here
Top
Water Popper
A
lure that floats and
is designed to be used to create some degree of disturbance on the
surface during retrieve.
Trailer
Hook The
extra hook, or cheater hook added to a single-hook lure, such as a spinnerbait.
Trailing
Shuck A section of synthetic yarn tied to the back of a fly to
imitate a case being shed from an emerging insect.
Transducer
A device that converts electrical energy to sound energy, or the
reverse. Typically associated with depth finders or fish finders.
Transom
The thick fiberglass wall of a boat on which the outboard motor is bolted.
Treble Hook Three
hooks made together; built into one.
Some states make double and treble hooks illegal and also regulate the number of hooks that can be attached to one line. Get familiar with your State Fishing Laws by clicking here
Triangle
taper A special taper profile to a fly line designed by Lee
Wulff, with 40 feet of continuous taper, with a thin
running line. Particularly useful for roll casts
Tributary
A creek, stream, or river that feeds a larger stream or river or lake.
Any watercourse that flows into a body of water, including tributaries to a tributary.
Triggering
Employment of any lure-retrieval technique or other fishing strategy
that causes a fish to strike.
Troll
Refers to the revolving motion of the bait
or lures.
Trolling
Trolling
is simply dragging a lure, bait, or a bait-and-lure combination
through the water, using a boat rather than casting and retrieving to
provide movement., Many of the lures used for casting also work for trolling.
This fishing method is used to cover a lot of water and to find fish.
Trolling Lure
A fishing lure used
while trolling.
Trolling Motor
A small, quiet, outboard motor.
Trolling Spoon
A large spoon that is trailed, or trolled, behind a
|
boat to catch fish. |
|
Trout
Any of several species of fish in Salmonidae, closely related to
salmon, and distinguished by spawning more than once.
Trout
Unlimited Non-profit organization dedicated to the protection
and improvement of trout fisheries, with an emphasis towards wild trout.
Tube Bait
See Tube Lure below
|
Tube Lure Soft plastic lures that are hollow inside the body. The end of the lure is like a soft skirt with tentacles. Used on light lead head jigs and with a slip sinker. |
|
Turbidity
the cloudiness (or clarity) of a water sample. If a great amount of
suspended sediments (such as soil particles) are present in the
water, the sample will be very turbid. Water clarity is important in
that it helps keep the water temperature cool, indicates very little
erosion in upstream areas, and is important for fish and insect
reproduction cycles.
Turn In regards to knot tieing. A turn occurs when you pass the tag end completely around the standing line.
Sometimes
called a wrap.
Tyee: Chinook
over 30 pounds
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]

These
are used in fishing "ultra-light" with small, very thin
rods (usually 4 to 5 feet long and as thick as a pencil). These rods
usually carry 2 to 6 pound test fishing line and throw bait
no larger then 1/8th of an ounce. Originally produced to bring more
excitement to crappie fishing, ultra-light fishing is now catching on
with trout fishers as well.
Undercut
Banks
Wherever
strong current flows against an earthen bank, the area beneath the
water may become eroded. This creates a submerged, cavelike overhang
in which trout may hold without worrying about predators. Undercut
banks are also created by man, these so-called "Lunker
Structures" are placed in the stream to provide additional cover
for trout in areas where undercuts do not occur naturally. In all
cases, these stream features will hold fish. Presenting a fly to
these fish, however, can be quite a challenge. Depending on the
current, it may be possible to drift a nymph beneath an undercut, but
more often than not this is an exercise in futility. Creeping up on
the same bank and dapping your fly over the edge works occasionally,
and during a hatch, a dry fly may be drifted against the bank to
elicit strikes from the trout concealed beneath the undercut.
Upland
zone the area adjacent to a creek that extends away
from the wetter riparian corridor.
Upriver
Something that is moving up-river is moving towards the source of a river,
from a point down the river. Something that is up-river is towards
the source of a river.
USCG
U.S.C.G.
United States Coast Guard
USGS
U.S.G.S.
United States Geological Survey.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Variant
A dry fly variety wound hackles that are much larger than normally
recommended. It is tied generally the as conventional patterns.
Ventral
Fin The fin on the anterior or lower surface of the fish-
opposite the back.

Vessel
Every type of watercraft or boat capable of being used as a means of
transportation on water except devices that are propelled entirely by
kicking fins and the floater sits in the water, such as inner tubes
(motor vehicle type), float tubes (belly boats), air mattresses and
sailboards when used without mechanical propulsion by an individual.
Contact your local warden for more information.
Vise
A tool used by fly tiers to hold the hook secure as thread, feathers
and fur are attached and the fly is being constructed. Usually the
most expensive and the single most important purchase for a fly tier.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]

Wacky
worm Rigging method for straight body worm, where the hook
goes through the middle of the worm and is left exposed.
Looks stupid but works well on spawning fish
Wade
Fish To wade through the water after fish. The lack of
boating mobility is made up for by the contemplative nature of being
partially submerged in the elements.
Catching one fish wading is worth 5 or more from a boat, because you've really earned it.
Wader
belt An adjustable belt cinched near the top of chest waders to
keep out water, particularly recommended as a precaution to the
waders filling up with water in the event of a fall.
Waders
Footed trousers that are constructed of latex, neoprene, Gortex or
other waterproof material so as to keep anglers
dry. Currently waders come in stocking foot or booted form and can be
found in three lengths: hip waders, waist-high waders and chest waders.
Wading
To transverse a river or stream on foot; most commonly done in
shallower waterways.
Wading
boots
Wading
shoes Hiking-like boots worn with stocking foot waders,
generally having felt soles and a more comfortable fit than the boot
portions of boot foot waders.
Wading
staff A walking stick especially adapted to provide stability to
a wading fly angler
when moving through fast or deep water. Some wading staffs are
foldable and can be kept in a fishing vest pocket until needed.
Walk
The Dog Retrieve
method used for fishing topwater lures. Accomplished by twitching
the rod tip downward several times. See how to perform
this technique here
Walleye
A
kind of fish that gives a big fight. Good to eat.
Watermelon
Refers to a hook with a large opening or gap between the shank and
point. This enables the angler
to hook a bigger percentage of fish.
Watershed
the land area that water flows across or through on its way to a
creek, river, bay, or ocean.
Weedguard
A piece of stiff monofilament or light wire attached from the top of
the hook and extending in front of the hook point and bend to the
hook eye. If properly attached, a weedguard reduces the likelihood of
a fly picking up weeds, yet it does not deter the hooking of a fish.
Weedguards are especially popular for underwater warm water flies. See
Weedless Hook
Weedless
usually referring to a hook. Keeps weeds from snagging, letting you
fish vegetation a lot easier. Their name is misleading as they're not
100 percent weedless, but are better than a bare hook for fishing weeds.
Weedless
Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed
information here
Weedless Spoon
– Wobbling spoons made with
a fixed hook and guard for fishing weeds.
![]()
Weedless Spoon
Weekend
Warrior They
dress the part and flock to the rivers in their new waders and Sage
rods on the weekends to 'escape' from the everyday stresses of a
crappy office job, usually get skunked.
Weight
Forward A fly line designed with more weight towards the
front of the line to assist in casting
and loading the rod.
Most of its weight in the first thirty feet of line. The large section of this type of line is called the line belly, with a long tapering of the line toward the front and a short tapering of it back to a thinner running line.
Wet Fly
An
artificial bait
that looks like a fly and sinks.
A wet fly resembles an insect under the water surface. Wet flies can imitate aquatic insects, drowned insects, or the larval stages of aquatic insects swimming to the surface to hatch. Wet flies are traditionally tied with a tail, body, wings, and soft hackle.
Wet fly technique
A wet fly is traditionally fished in a down and across swing.
Wharf
Structure built along the shore of navigable waters so ships may lie
alongside to receive and discharge cargo and passengers.
Whip
Finish
Whip
finisher
Whip
Finishing Tool A tool used in tying flies that helps
the fly tier lay down a smooth and compact head of the fly.
White
Bass (Morone chrysops) The white bass or sand
bass is a freshwater fish of the temperate bass family Moronidae. It
is the state fish of Oklahoma.
Whitefish (white
fish, demersal fish) a fisheries term
referring to several species of oceanic deep water finfish,
particularly cod (Gadus morhua), whiting (Merluccius bilinearis),
and haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus), but also hake (Urophycis),
pollock (Pollachius), or others.
Unlike oily fish, white fish contain oils only in their liver, rather than in the gut and can therefore be gutted as soon as they are caught, on board the ship.
White fish are divided into round fish which live near the sea bed (cod, coley) and flatfish such as plaice which live on the sea bed.
Whitefish
is sometimes eaten straight but often used reconstituted for
fishsticks, gefilte fish, lutefisk, surimi (imitation crabmeat),
etc.
It
is most widely known as the fish in fish and chips.
Wide
Gap Hook Refers to a hook with a large opening or gap
between the shank and point. This enables the angler
to hook a bigger percentage of fish.
Willowleaf
A blade design used on spinnerbaits that resembles a half moon.
Winding
Wraps of thread that are used to attach the stripping guides and
snake guides on the fly rod blank.
Wind
knots In the process of casting, especially for beginners, loops
form particularly in the leader and tippet. The formation of such
loops is made worse by casting in the wind and hence when they become
knots in the leader or tippet they are called wind knots.
The telltale result of a tailing loop
|
|
|

|
The typical build of a wobbler consists of:
|
Woody
Debris Logs, branches, even whole trees sometimes
end up in trout streams. These features block the current and provide
shelter for fish. Swinging a streamer from upstream is one
presentation that works in these instances. Woody debris, when
combined with another feature, such as deep water or the tongue of a
pool, is a trout magnet.
Worm Hook A name and shape of a fish hook. See more detailed information here
Wulff Dry Flies See Royal Wulff Dry Flies
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
X
diameter A system to indicate the diameter of leader and tippet
material, with 0X (zero-X) representing the largest diameter (.011
inches) and 8X (.003 inches) representing a small, light diameter.
Commonly used values are 1X (.010), 2X (.009), 3X (.008), 4X (.007),
5X (.006), 6X (.005). The strength of these monofilament diameters
varies with the kind of material.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Yolk
Sac In embryos and early fish larvae, a bag-like ventral
extension of the gut containing nutritive materials. It nourishes the
growing fish until it is able to feed itself.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
![]()
Zara Pooch Brand name of topwater lure.
Zara
Puppy Brand
name of topwater lure.
Zara
Spook Brand
name of topwater lure.
Zebco
Zebco, headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma was acquired by the W. C.
Bradley Co. in 2001. Zebco is a designer and marketer of branded
fishing tackle in North America. The brands marketed by this division
include Zebco, Rhino, Quantum, Lew’s, Martin, and Cajun Line.
Zebra
Mussel
An exotic mussel that has infested U.S. water and threatens our
fisheries. Looks like zebra stripe little clams, and they attach to
boats, trailers, docks, etc.
Use
care when boating in areas with this creature.
Inspect
your boat and trailer prior to launching in another body of water.
Zinger
A retractable string clip used to connect tools to ones fly vest.
Zipperlip:
Secret fishing hole.
Zipper
Worm New style of plastic worm that features a flat body
with ridges that look similar to a zipper on clothing.
Very popular on the west coast.
Z-Lon
Trade name for a synthetic yarn used in making carpeting. Can be
used for many purposes in fly tying such as nymph bodies, spent
wings, and trailing shucks.
Zooplankton
Small aquatic animals that are suspended or swimming in water.
Z-ray A brand name of heavy spoon typically used in trout fishing.
Zug Bug A type of wet fly or fly pattern commonly used by fly fishers in lakes.
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
This is a Stand Alone Page. There is no where to link back to.
Simply Close This Window or Visit or Homepage at
FUNdamentals of Fishing
|
It is important that people who
fish follow all fishing rules and regulations. |
Copyright ©  Jon's Images, Inc.
Jon's Images, Inc.
All rights reserved
This website is the composition of many hours of research. Information contained within this site has come from numerous sources such as websites, newspapers, books, and magazines.
No animals were harmed in the making of this site.
If you have any
hints, suggestions, techniques or anything that you would like to
share or have me put onto this web page,
please feel
free to Email
me.
Please direct website comments
or questions to webmaster
DISCLAIMER: PLEASE READ - By printing, downloading, or using you agree to our full terms. If you do not agree to the full terms, do not use the information. We are only publishers of this material, not authors. Information may have errors or be outdated. Some information is from historical sources or represents opinions of the author. It is for research purposes only. The information is "AS IS", "WITH ALL FAULTS". User assumes all risk of use, damage, or injury. You agree that we have no liability for any damages. We are not liable for any consequential, incidental, indirect, or special damages. You indemnify us for claims caused by you.
Please be advised that the content of this site is a source of information only. The FUNdamentals of Fishing Website cannot take responsibility for animal welfare or actions taken as a result of information provided, and if in doubt you should seek the advice of a qualified physician or veterinarian.

I do not suffer from insanity; I enjoy every minute of it!