Date Functions
Dates in Excel are actually stored as values, making it easy to do calculations with dates when all you are doing is adding or subtracting number of days. For the other things you might want to do with dates, there are a variety of functions available to help. Here are a few you might find useful.
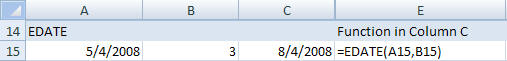
- EDATE*
- The EDATE function will add a number of months to a date.
Syntax: EDATE(start date, months)
Start date should be a valid Excel date format.
Months is the number of months to add to the start date.
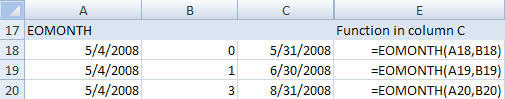
- EOMONTH*
- Gives the end of month date for a date plus a given number of months.
Syntax: EOMONTH(start date, months)
Start date should be a valid Excel date format.
Months is the number of months to add to the start date.
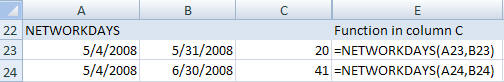
- NETWORKDAYS*
- Returns the number of full workdays between two dates.
Syntax: NETWORKDAYS(start date, end date, holidays)
Start and end dates should be valid Excel date format.
Holiday is an optional range of cells containing dates to exclude from work days.
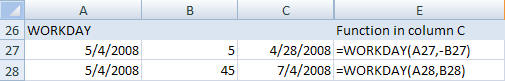
- WORKDAY*
- Returns a date that is the given number of working days before or
after a date.
Syntax: WORKDAY(start date, days, holidays)
Start and end dates should be valid Excel date format.
Holiday is an optional range of cells containing dates to exclude from work days.
*These functions are not available in Excel 2003 unless you have the Analysis ToolPak functions available: Tools > Add-Ins > Analysis ToolPak must be checked.
- DAY
- Returns the day of a date, a number between 1 and 31.
Syntax: DAY(valid date) - MONTH
- Returns the month from a date, a number between 1 and 12.
Syntax: MONTH(valid date) - YEAR
- Returns the year of a date, a number between 1900 and 9999.
Syntax: YEAR(valid date) - TODAY
- Returns the current date.
Syntax: =TODAY() 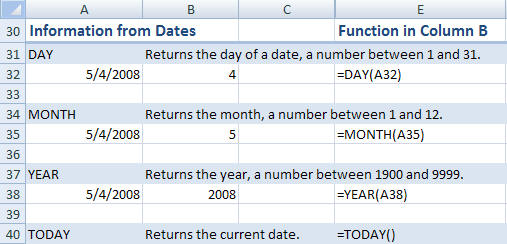
Download the sample workbook functionsamples.xls or for 2007 users functionsamples07.xls.

