Tim Allison: A Virtual Portfolio
Evaluation -- Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's taxonomy was examined this term as a method of determining the level of abstraction on assessment questions. It is a useful system in that it has potential to guide a teacher in the setting of test questions. Using it to analyze a test which I had given to my 11U Chemistry class on placement was a helpful exercise. By assigning a level of abstraction to each question, multiplying by the value of the question, and dividing by the total score of the test, it can be determined (roughly) how demanding the test is of the students. This number, for my test, came out to be about 3.5. The test was demanding of the students, but was, I believe, reasonably so. The class average was approximately 70%; a mark which satisfied both myself and my associate teacher. Bloom's taxonomy can be found below, along with the test in question. Levels ("competences") which were assigned to each question, using Bloom's taxonomy, are written next to or below the question, in red.
Bloom's Taxonomy:
| Competence | Skills demonstrated |
| 1. Knowledge | -observation/recall of information -knowledge of facts/ideas -mastery of subject matter -questions contain such words as: list, define, describe, identify, label, etc. |
| 2. Comprehension | -understanding of information/meaning -using knowledge in a new context -ordering/inferring/predicting -questions contain such words as: summarize, contrast, predict, estimate, discuss, etc. |
| 3. Application | -use of information, methods, concepts, or
theories in new situations -using required skills or knowledge to solve problems -questions contain such words as: demonstrate, calculate, illustrate, solve, classify, relate, etc. |
| 4. Analysis | -pattern recognition -identification/organization of components -questions contain such words as: analyze, order, explain, arrange, etc. |
| 5. Synthesis | -generalization from knowledge -drawing knowledge from several areas together -predicting and drawing conclusions -questions contain such words as: combine, create, design, what if, formulate, generalize, etc. |
| 6. Evaluation | -assess differences and values of various
theories/ideas -make choices based on reason -verify value of evidence/recognize subjectivity -questions contain such words as: assess, rank, measure, recommend, convince, judge, explain, summarize, etc. |
The Test in Question
11U Chemistry
Solutions and Solubility – Unit Test
December 15, 2003
Name:____________________
Part I: Multiple choice /12
The following equation applies to questions 1-3:
|
K2CO3(aq) +
BaCl2(aq) > 2KCl(aq) + BaCO3(s) |
|
| 1. Which compound is insoluble in
water? a) Potassium Carbonate (K2CO3) is
insoluble in H2O |
2. Potassium Chloride is: a) a
precipitate |
| Comprehension | Comprehension |
| 3. Barium Carbonate is: a) a
precipitate |
4. Liquids which dissolve in one
another are said to be: a) alloys |
| Comprehension | Knowledge |
| 5. A solution is said to be
saturated when: a) more solute can be dissolved |
6. H2SO4 (sulfuric
acid) is an acid because: a) it gives up H+ ions |
| Knowledge | Comprehension |
| 7. Ammonia (NH3) is a
base because: a) it gives up H+ ions |
8. Human blood has a pH of 7.4. It
is: a) acidic |
| Comprehension | Comprehension |
| 9. Fresh milk has a pH of 6.7. It
is: a) acidic |
10. Covalent compounds may be
soluble in water if they are: a) non-polar |
| Comprehension | Knowledge |
| 11. The difference between a strong
acid and a weak acid is that: a) A strong acid has bigger muscles than
a weak acid. |
12. Hydronium ions (H3O+)are
present in pure water at a concentration of: a) 0M
|
| Knowledge | Knowledge |
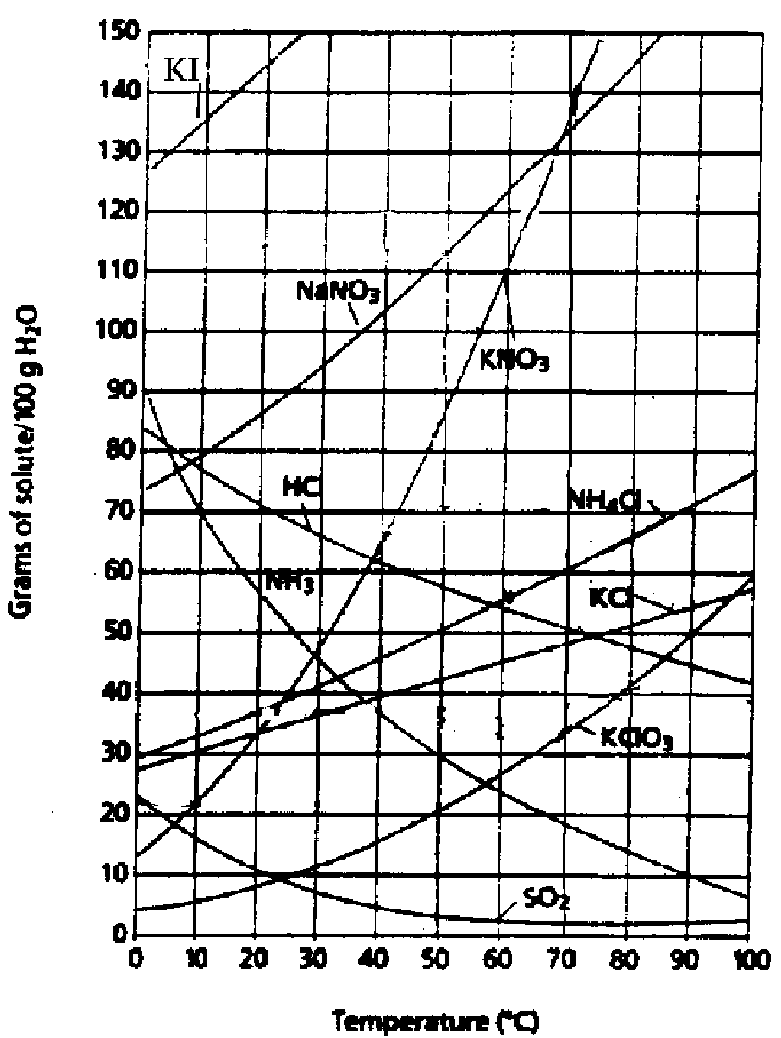
This graph goes with Part II of the test (next page).
Part II: Solubility /10
Choose two compounds from the solubility curve (previous page) to answer all of the questions in this section:
Compound i)_______________ Compound ii)_______________
1. What is the solubility (g/100g of H2O) of each compound at (4 marks): (Analysis)
| a) 50°C: i) |
ii) |
| b) 0°C: i) |
ii) |
2. If 45g of your compounds are dissolved in water at 30°C, will the solution be unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated? (2 marks) (Analysis)
i) _______________________ ii) ______________________
3. Saturated solutions of each of your compounds at 70°C are cooled to 30°C. What will happen in each of the solutions? (4 marks) (Synthesis)
i)
ii)
Part III: Concentrations and pH /18
1. Choose 2 of the following 3 questions. Please show your work (3 marks each): (Application)
a) Plumbing solder is currently contains 200 ppm of lead. This has led to concerns about lead contaminating drinking water. If 132 grams of solder are used on the plumbing in the construction of a house, how much lead (i.e., how many grams) does this represent?
b) The amalgam used to make dental fillings contains 0.389g of mercury, 0.270g of silver; 0.069g of tin; 0.046g of copper; and 0.004g of zinc. Find the mass% of zinc in the amalgam.
c) The maximum acceptable concentration of nitrates in Ontario drinking water is 10 ppm. A sample of drinking water contains 0.0008g of nitrates in 100g of water. Is this above or below the maximum acceptable limit?
2. Choose 2 of the following 4 questions. Please show your work (6 marks each): (Application)
a) An aqueous solution of HCl contains 182.3g/L of HCl. 100 mL of this solution are diluted to 2.00L with water. What is the concentration of HCl in the solution that was just made? What is the pH?
HCl > H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
b) You want to make 1.25L of 0.05M HNO3. All that you have available is 141.75g/L HNO3. How much of this solution will need to be diluted with water to make the solution you want? What will be the pH of the solution you make?
HNO3 > H+(aq) + NO3-(aq)
c) An aqueous solution of KOH contains 123.4g/L of KOH. 10 mL of this solution are diluted to 2.50L with water. What is the concentration of NaOH in the solution that was just made? What is the pH?
KOH >K+(aq) + OH-(aq)
d) You want to make 1.50L of 5.0 x 10-3M NaOH. All that you have available is 2.0M NaOH. How much of this solution will need to be diluted with water to make the solution you want? What will be the pH of the solution you make?
NaOH > Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)
***BONUS: On the solubility curves, why do the solubilities of ammonia, hydrogen chloride, and sulfur dioxide decrease with increasing temperature, whereas the solubilities of the other compounds increase? (Knowledge)