Introduction
Background Theory
As the world improves and moves ahead in technology, it makes human life easier. As it is in human nature, they go for everything to make their life more luxurious and soon become a necessity. The Power Line Appliance Controller is not only a luxury design but is also a means of facilitating the disabled.
A power line appliance controller becomes an integral part in everyday life, to make it easier and simpler.
Persons who are more than likely to use the power line appliance controller are:
· Disabled – persons who may be crippled in someway e.g. being restricted to a wheel chair, they can turn on/off a device with just a press of a key on the keyboard
· Employees - households who may be at work all day and be extremely tired at the day’s end, when they get hone they can turn on / off any device e.g. microwave, television set, from one location
· Relaxed - persons who just like to relax and have tasks done for them prior to them getting to the devices e.g. having the microwave or coffee maker turned and the coffee or food maybe made before getting to the devices, or persons who just like to laze around.
Based on the above reasons, it proves that the power line appliance controller would indeed be a luxurious necessity in humans’ lives. Hence, this product would be a highly marketable one and there are no reasons why the design should not be implemented.
Purpose
The purpose of this report, is to explain, one version, our version, of how the Power Line Appliance Controller is constructed, its basic operation and how it is implemented. At the end of this report, you, the audience, should be able to build your own Power Line Appliance Controller, at a affordable cost.
Scope
The Power Line Appliance Controller is sub-divided in the following segments for simplicity:
· Software
- Program
· Hardware
- Transmitter
- Extended Parallel Port
- 555 Timer
- JK Flip Flop
- Multiplexer
- Filter (Coupling Transformer)
- Power Supply
- Power Line
- Receiver
- Operational Amplifier
- Tone Detector
- Debouncer Circuit
- JK Flip Flop
Basic Operation
The user enters a menu driven program that allows him/her to choose which appliance(s) he/she would like to turn on/off. The user enters this option via the keyboard. Depending on the selection made a signal is sent out via the parallel port. The 555 timer generates a frequency which goes to a counter. The counter breaks down the input frequency into 4 distinct frequencies. These 4 frequencies are sent to the multiplexer and together with the signal from the parallel port, one frequency is chosen. The chosen signal is transferred over the same power line. The power line has its own voltage and frequency generated, therefore, there needed to be a method in place to differentiate the user’s signal and the power line’s signal. This is where the filter circuit comes in to play. At the receiver end, the signal is regenerated and is sent to each receiver. The tone decoder in each receiver is set to accept a specific frequency, which determines which appliance is to be turned on/off. This signal is then transferred to a D Flip Flop which is responsible for turning on/off the appliance. One signal is used to toggle the input to the appliance.
See Figure 1 for the Basic Operation the Power Line Appliance Controller
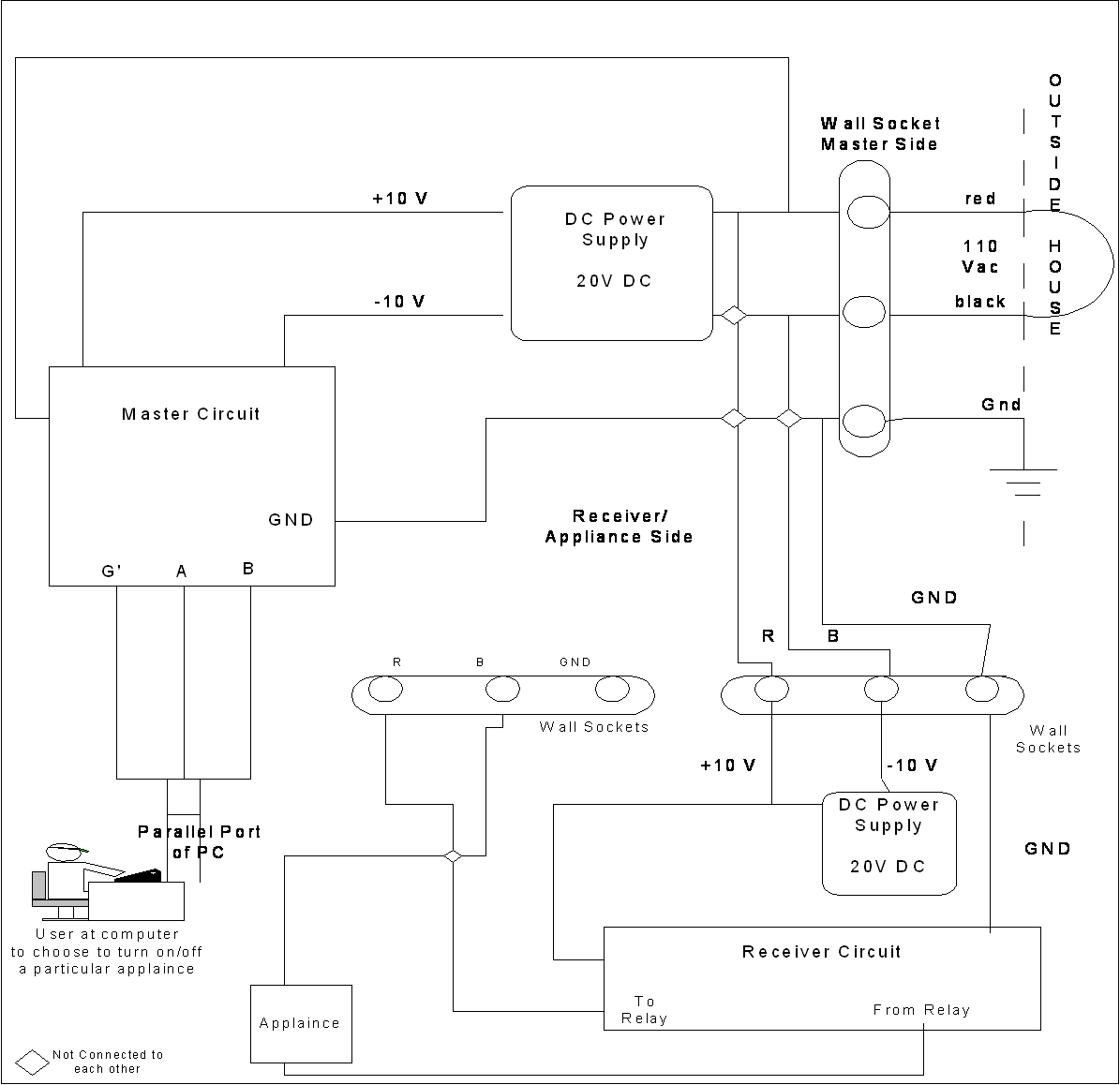
Figure 1 – Basic Operation of the Power Line Appliance Controller