
Genotype- The genetic makeup of an organism.
Phenotype- The expressed traits of an orangism.
Wild type- Individuals with the normal phenotype. The budgie wild type is the normal green.
Allele-
Homozygous-
Heterozygous-
Hybrid-
Modes of inheritance-
Dominant-
Recessive allele- In a heterozygous cell, the allele that is completely masked in the phenotype.
Incomplete Dominance- A type of inheritance in which hybrids have an appearance that is intermediate between the phenotypes of the parental varieties. (between genes which are alleles of one another)
Co-Dominant-
Sex-linked- Sex-linked genes are a bit harder to understand than the above terms. Basic Coloration- Ground Color-
Blue series / Green series-
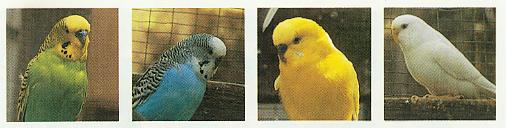
There are two different color series of budgies, green and blue. Green budgies appear green because they produce yellow pigments on top of thier blue coloration. Blue budgies do not produce this yellow coloring, so everywhere that is yellow on a green budgie, will appear white on a blue budgie. I speak about most color mutations in terms of the blue series because all my birds are blue series birds. For Green Series just replaced "Blue" with "Green" and "White" with "Yellow".
Dark Factors-
A bird can have either:
(Example- A bird could have BB as it's genotype)
(Example- The bird with the B gene appears green.)
My Sex-linked Explanation
Feather cross section
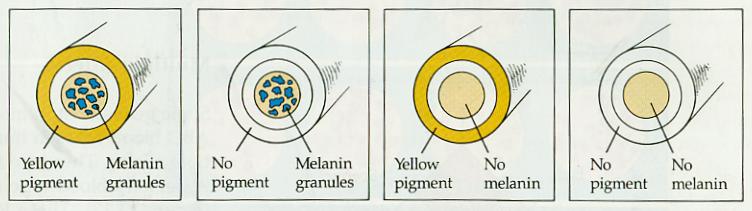
Blue melanin and Yellow pigments combine on the right to produce a Green appearing feather. With no Yellow pigments the feather appears Blue. With no Blue melanin the feather appears yellow. With neither Yellow pigment nor Blue melanin the feather appears white.
In this right, Dark Factors create three distinguishable shades for each color series.
The Green Series consists of:
 Light Green (NO DrkF)
Light Green (NO DrkF)
 Dark Green (1 DrkF)
Dark Green (1 DrkF)
 Olive Green (2 DrkF)
Olive Green (2 DrkF)
 Sky Blue (NO DrkF)
Sky Blue (NO DrkF)
 Cobalt (1 DrkF)
Cobalt (1 DrkF)
 Mauve (2 DrkF)
Mauve (2 DrkF)