The Transistor
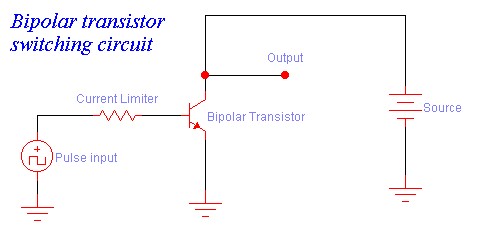
The transistor is a semiconductor that is used to control and anplify electrical pulses and current. It is made up of either a postive negative postive junctions(pnp) or negative postive negative junctions(npn). This technology was develop from the simple postive negative junction(pn) connection which is known as the diode. There are many different types of transistor that are used today but for this robot there are only two. One is the known as a bipolar transistor and the other is the field-effect transistor. The bioplor transistor has three basic connections associated with its type which are the base(B), the collector(C), and the emitter(E). The label are the same for both pnp and npn. The bipolar transistor works as a switch when it is configured to turn on and off when an electrical pulse is input to the base(see the bipolar switch diagram at bottom of page). This happens due to the electrons of the collector moving through the base to the emitter and then to ground. If this is a little hard for you to grasp, think of it as a switch in your home. The potential current is there but is not at work and when you(electrical pulse) turn the switch(transistor) the light come on(transistor allows current to flow through it to ground).The field-effect transistor has similar operation structure but is a little different. This has a gate(G), source(S) and a drain(D) which act like the base the emittre and the collector. This has some advantages over the bipolar due to its high input resistance which results in more stability in output gain and current. Note the gain is a factor of the output divided by the input ans it has no units.
Here are some schematic diagrams of different transistors