 The Java Platform The Java Platform Java Runtime Environment Java Runtime Environment Data Types Data Types Control Statemets Control Statemets Methods Methods Arrays Arrays Classes and Objects Classes and Objects Inheritance Inheritance Constructor Constructor Interface Interface Packages & Access Modifiers Packages & Access Modifiers Java Collections Framework Java Collections Framework  What are Collections What are Collections  The Java Collections Framework The Java Collections Framework  Benefits Benefits  Collection hierarchy Collection hierarchy 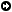 The Collection Interface The Collection Interface  Types of Collection Types of Collection  Iterators Iterators  Using Set Using Set  Using Map Using Map  Example Example | The Collection InterfaceA Collection represents a group of objects, known as its elements. Some Collection implementations allow duplicate elements and others do not. Some are ordered and others unordered. public interface Collection {
// Basic Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object element);
boolean add(Object element); // Optional
boolean remove(Object element); // Optional
Iterator iterator();
// Bulk Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection c);
boolean addAll(Collection c); // Optional
boolean removeAll(Collection c); // Optional
boolean retainAll(Collection c); // Optional
void clear(); // Optional
// Array Operations
Object[] toArray();
Object[] toArray(Object a[]);
} |