Topic 8: Gases and Condensation
What are the characteristics of gases?
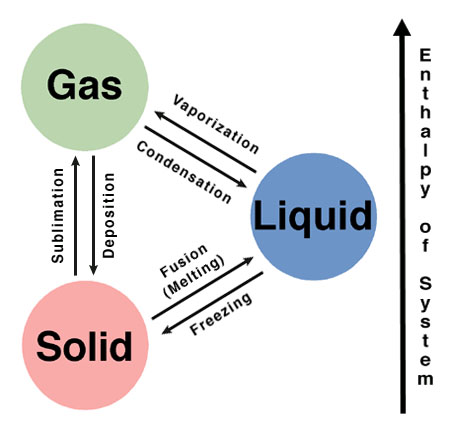 Gases can be compressed and when they are it changes the phase of it into liquid or solid. It all depends how much is the gas compressed to change it into liquid or solid. It is about the same amount of mol of gas it takes to fill three different amounts of area.
For gas 1mol of oxygen to occupies 22,400ml of space to make it a gas. Solid is 1mol of aluminum occupies 10ml of space to make it a solid.
Gases can be compressed and when they are it changes the phase of it into liquid or solid. It all depends how much is the gas compressed to change it into liquid or solid. It is about the same amount of mol of gas it takes to fill three different amounts of area.
For gas 1mol of oxygen to occupies 22,400ml of space to make it a gas. Solid is 1mol of aluminum occupies 10ml of space to make it a solid.
What behaviors are described by the gas laws?
The symbols p, v, t, and n define the mathematical expressions known as the gas laws. P is pressure exerted by the particles. V is the volume occupied by the particles. T is the temperature in Kelvinfs of the particles. N is the number of moles of the particles. When gas is heated its particles move faster and push with more force against the area of the space around the gas. For example when a balloon is inflated at room temperature the walls expand until the pressure inside and outside are equal.
What conditions will cause a gas to condense?
To make a prediction of the condition for gas are based on the kinetic molecular theory. Able to use mathematical models relatively close to reality under most of the conditions is one way to predict its conditions. The boiling point is more correctly defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals to the external or atmospheric pressure. What represents the temperature and pressure at which water vapors and ice are in equilibrium.
Main menu
Topic 7: Causes of Change
Topic 9: Solutions
Credits and Links
 Gases can be compressed and when they are it changes the phase of it into liquid or solid. It all depends how much is the gas compressed to change it into liquid or solid. It is about the same amount of mol of gas it takes to fill three different amounts of area.
For gas 1mol of oxygen to occupies 22,400ml of space to make it a gas. Solid is 1mol of aluminum occupies 10ml of space to make it a solid.
Gases can be compressed and when they are it changes the phase of it into liquid or solid. It all depends how much is the gas compressed to change it into liquid or solid. It is about the same amount of mol of gas it takes to fill three different amounts of area.
For gas 1mol of oxygen to occupies 22,400ml of space to make it a gas. Solid is 1mol of aluminum occupies 10ml of space to make it a solid.