ALL About Intermolecular Forces
Polar Bonds
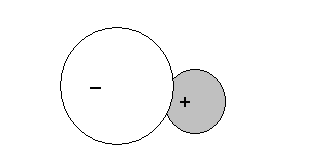
In a covalent bond between two different atoms, one atom has a greater attraction for electrons than the other atom. The atoms with a greater attraction will then pull the electrons of the covalent bonds closer to it, thus, causing the atoms to have slight charges acquired. The atom with the stronger attraction will have a negative charge wheares the other will have a positive charge. An unequal sharing of electrons causes the covalent bond to be polarised.
*A molecule is polarised only when 1. its bonds are polarised
2 . The molecule is not symmetrical
Polar molecules are held together by dipole-dipole forces in the liquid and solid state. These forces are permanent.
They are weaker than covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
Intermolecular Forces- It occurs between seperate molecules.Boiling Point and Melting Point is usually depend on how strong the Intermolecular Forces.Take note this kind of force occur outside the molecules(The word “Inter suggested it”).Whereas Intramolecules forces, its the attraction forces that occurs inside of the Molecules.
The different Kinds of Intermolecular forces
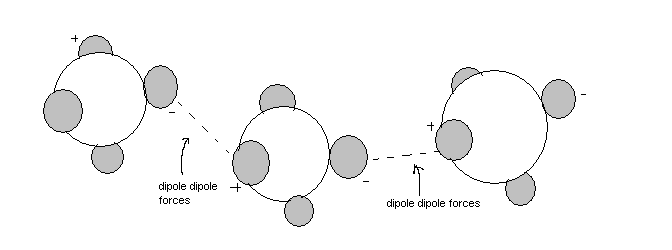
Temporary dipole dipole forces
Temporary dipole dipole forces. It is due to the random movement of electrons around atoms.
The induced dipoles attract one another, producing a weak force, only when other forces are absent.*The strength is proportional to the mass of the atoms and molecules.As bigger the mass of the atom and molecules, the more the electron present. Therefore, the attraction between the two atom or molecules of temporary dipole dipole force will Increase as the mass increase.
Permanent dipole dipole forces
It is due to a differences in electronegativities which result in permanent change in polarity.The little change in the polarity cause a weak permanent dipole dipole force which hold the molecules together.The greater differences in the electronegativites, the stronger the Permanet dipole dipole forces.
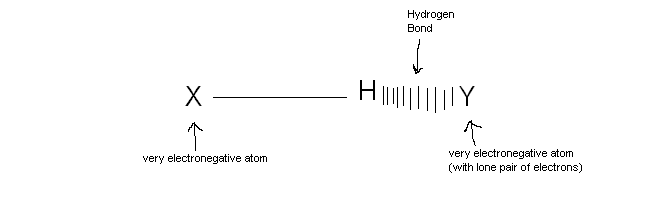
Hydrogen Bonds
When a hydogen atom is covalently attached to very electronegative atom, the hydrogen atom can form a " hydrogen bond " with another very electronegative atom, which has a lone pair. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent and ionic bonds but stronger than ordinary dipole-dipole attractions.
Properties of Hydrogen Bonding
+Soluble in water
+Unusually high boiling points
+Anomalous relative molecular masses
-unexpected molecular masses due to joining of molecules by hydrogen bonds
- Gaseous Hydrogen flurodie has a larger apparent relative molecular mass than expected because the molecules are joined in twos or threes, in the gaseous state by hydrogen bonding.
Criteria For Hydrogen to exist
Hydrogen have to present.
The very electronegativity atoms has to be F or O or N
Generally, Hydrogen bond is stronger than Permanent dipole dipole than induced dipole dipole
Hydrogen Bonding > Permanent dipole dipole > Induced dipole dipole