Project management is the process by which a proposed project is developed within a rigorous framework. The subset of project management that this lecture will focus on is 'project scheduling', that is the process by which the various activities that need to be undertaken during a projects lifetime should be scheduled. There are a range of activity management tools that are commercially available.
Project scheduling is concerned with the techniques that can be employed to manage the activities that need to be undertaken during the development of a project.
Scheduling is carried out in advance of the project commencing and involves:
Once the project is underway control needs to be exerted to ensure that the plan continues to represent the best prediction of what will occur in the future:
Effective project planning will help to ensure that the systems are delivered:
Two project scheduling techniques will be presented, the Milestone Chart (or Gantt Chart) and the Activity Network.
Milestones mark significant events in the life of a project, usually critical activities which must be achieved on time to avoid delay in the project.
Milestones should be truely significant and be reasonable in terms of deadlines (avoid using intermediate stages).
Examples include:
A Gantt chart is a horizontal bar or line chart which will commonly include the following features:
Project management tools incorporating Gantt Charts include PRINCE [CCTA, 1990], MacProject and Microsoft Project.
Example of a Gantt Chart:

Figure 1: Example of a Gantt Chart
Which tasks is ahead of schedule ? Which task is behind schedule ?
Alternative Gantt Chart incorporating features commonly present in automated tools:

Figure 2: Example of a Gantt Chart showing Project Management Tool Features
Gantt charts produced in this form are:
There are no widely accepted standards for Gantt charts. Automated tools are available which produce Gantt charts directly from activity networks or from a full definition of the tasks.
Automated tools have features which assist the planning function including:
Now try to create a Gantt chart from the information presented in the Gantt Chart tutorial.
The foundation of the approach came from the Special Projects Office of the US Navy in 1958. It developed a technique for evaluating the performance of large development projects, which became known as PERT - Project Evaluation and Review Technique. Other variations of the same approach are known as the critical path method (CPM) or critical path analysis (CPA).
The heart of any PERT chart is a network of tasks needed to complete a project, showing the order in which the tasks need to be completed and the dependencies between them. This is represented graphically:

Figure 3: Example of an Activity Network
The diagram consists of a number of circles, representing events within the development lifecycle, such as the start or completion of a task, and lines, which represent the tasks themselves. Each task is additionally labelled by its time duration. Thus the task between events 4 & 5 is planned to take 3 time units. The primary benefit is the identification of the critical path.
The critical path = total time for activities on this path is greater than any other path through the network (delay in any task on the critical path leads to a delay in the project).
Tasks on the critical path therefore need to be monitored carefully.
The technique can be broken down into 3 stages:
1. Planning:
2. Scheduling:
3. Analysis:
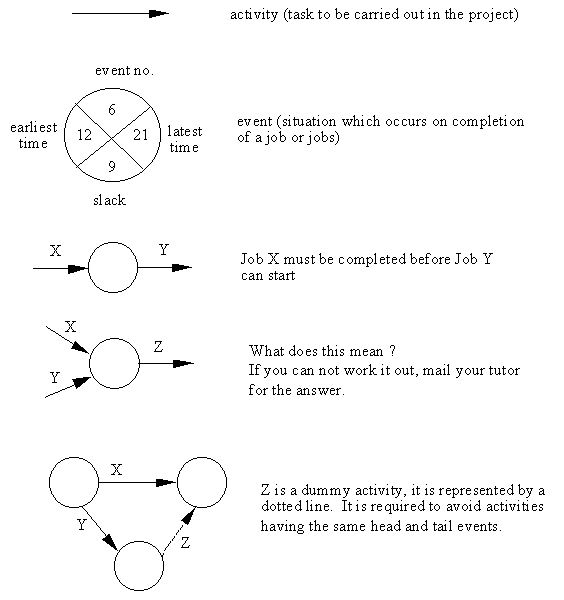
Figure 4: Symbols Used in Activity Networks
List of activities for the network:
Task Location Dependent On Duration
A - 3
B - 6
C - 3
D A 5
E C 2
F B, D, E 6
G A 9
Calculation of Earliest Time:
Use the instructions presented in section 3.2 and the the following diagram ..
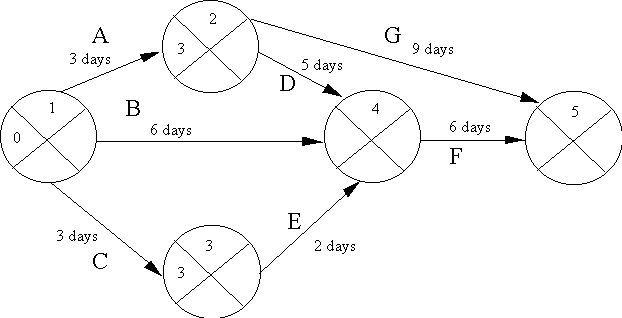
Figure 5: Calculation of Earliest Start Time
What is the earliest time for event 4 ? If you are unsure, the answer is explained here.
What is the earliest time for event 5 ? If you are unsure, the answer is explained here.
Calculation of Latest Time:
Use the instructions presented in section 3.2 and the the following diagram ..
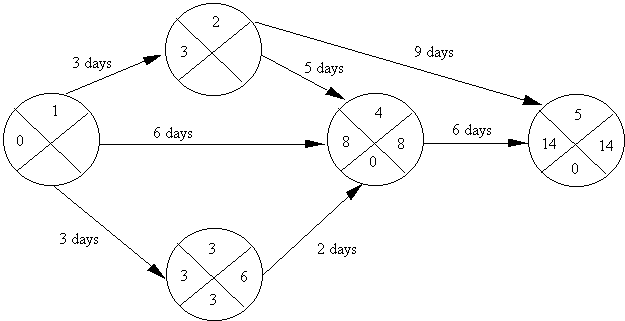
Figure 6: Calculation of Latest Start Time
What is the latest time for event 2 ? If you are unsure, the answer is explained here.
What is the latest time of event 1 ? If you are unsure, the answer is explained here.
Drawing the Critical Path:

Figure 7: Drawing the Critical Path
Analysis of the network allows the 'float' to be calculated, this is essentially the amount of time an action can be delayed without delaying the overall project.
Activities on the critical path must be monitored very carefully. Now try the Activity Network tutorial.