

|
Light is a form of energy. It is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Visible light consists of seven frequencies or colours of light. These are Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and violet..Visible light has a wavelength/m of 7.5 x 10-7 and a frequency/hz of 4 x 1014. Violet light has the shortest wavelength, and red light has the longest wavelength. The wavelength of a wave is the distance between one crest and the next, The frequency of a wave is the number of waves which pass a point in one second. Light is a transverse wave, similar to a water wave. Unlike sound waves that need a medium to travel through, light can travel in empty spaces, and in a vacuum, unlike sound. Although light is a wave, it can also act as a stream of particles, travelling in straight lines and in a beam. Light is very similar to sound, in as much as they both have a speed (light is very much faster than sound - see table below), and that speed is effected by the medium they are passing through. The speed of light is based upon it's speed in a vacuum, thus avoiding any distortions caused by a medium such as moisture in the air etc. This speed is normally referred to as 300,000km per second (186,000 miles per second). The exact speed is 299,792,458 metres per second.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The speed of light through the universe
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Based on this table, it it correct to say that the nearest star is 4.3 light years from the sun. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reflection Light reflects off a reflective surface with the angle of deflection being equal to the angle of the beam of light, or i = r where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of reflection.. Try this little experiment - (ask your mum/dad first, I don't want them shouting hey! Fizzy you'll have to come round and re-decorate) - Measure 1 metre up a wall and stick on a piece of 'BlueTack' to mark the spot, then place a mirror so the centre is 1 metre away from the wall. Again measure 1 metre away from the centre of the mirror, then using your measure, hold a torch 1 metre heigh and point it at the centre of the mirror (this beam is called the incident ray), Bingo! you will see the spot of light illuminate the bluetack (this beam is called the reflected ray). You are now a junior scientist. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
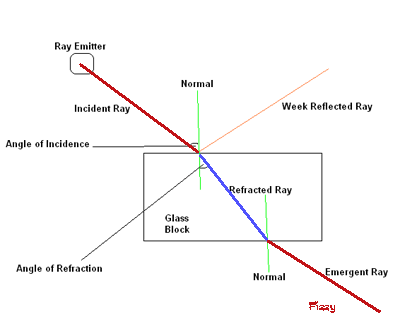
Refraction When a ray of light travels at an angle from air into a clear material such as glass or water, it changes direction. This is called refraction. My sketch below shows how the rays are refracted (bent) when they travel from air into a glass block. |
 |
|
|
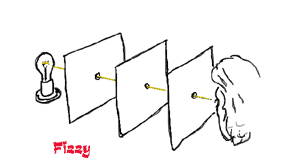
| Light travels in straight lines. To prove this fact, you can carry out a simple experiment as shown in my sketch below. Just cut out three pieces of card and pierce a hole in the centre of each one. Then using a table light or some other light source, place the cards between the light and yourself. |
 |
|
You will find that the holes in the cards have to be precisely lined up before you can see the light, proving that light only moves in straight lines.
|
|
Most objects are only seen because of the light being reflected from them to our eyes. Objects are selective in the coloured light they reflect. A blue object will only reflect blue light, a red object reflects only red light, and so on. If you were to illuminate a red object with a blue light, that object would appear to be black because the blue light would be absorbed as the object can only reflect and not transmit light. However, fluorescent objects do have the ability to emit light in different colours. They will absorb the blue light, and emit red orange and green light. This colour absorbtion make illuminating paintings in art galleries a specialist subject, if the true colours are to be seen by the visitor. Artists studios have massive windows, to allow the maximum of natural light to enter, light and colour being the most important elements to an artist.
|
|
Perceiving Light Although small in size, the eye is a very complex organ. The eye
is approximately 1 inch (2.54 cm) wide, 1 inch deep and 0.9 inches
(2.3 cm) tall.
|
 |
|
The retina contains a chemical called rhodopsin, or "visual purple." This is the chemical that converts light into electrical impulses that the brain interprets as vision. The retinal nerve fibers collect at the back of the eye and form the optic nerve, which conducts the electrical impulses to the brain.
|
 |
|
"God
said let E=+MV2-Ze21 and there WAS Light"
|
![]()
|
Office
|
Quiz
|
![]()