There are a few different variations of the Cosine Law that we can use. They are:
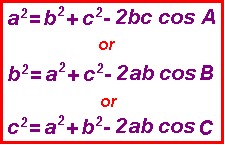
When Can I Use the Cosine Law?
One of the following conditions must be met:
a) two sides and a contained angle are known, or
b) all three sides are known
NOTE: A contained angle is the angle between the two given sides of the triangle
For the mathematical proof of the Cosine Law, see page 562 of the text.
Example 1: Find the missing side in the following triangle.

c² = a² + b² -2ab Cos C
c² = 5² + 7² - 2(5)(7) Cos 43°
c² = 25 + 49 - 51.1947
c² = 22.8052
c = 4.8
Therefore, Side C is 4.8 units long.
Example 2: Find Angle A in the following triangle.
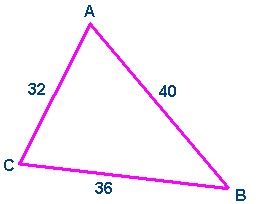
a² = b² + c² - 2bc Cos A
36² = 32² + 40² - 2(32)(40) Cos A
1296 = 1024 + 1600 - 2560 Cos A
Collect like terms
- 1328 = - 2560 Cos A
Divide both sides by - 2560
0.51875 = Cos A
A = Cos -¹(0.51875)
A = 58.8°
Therefore, correct to the nearest degree, angle A measures 59°.
Practice Questions
Page 566, #2,3b,6,7,16,18