The Periodic Table of Elements
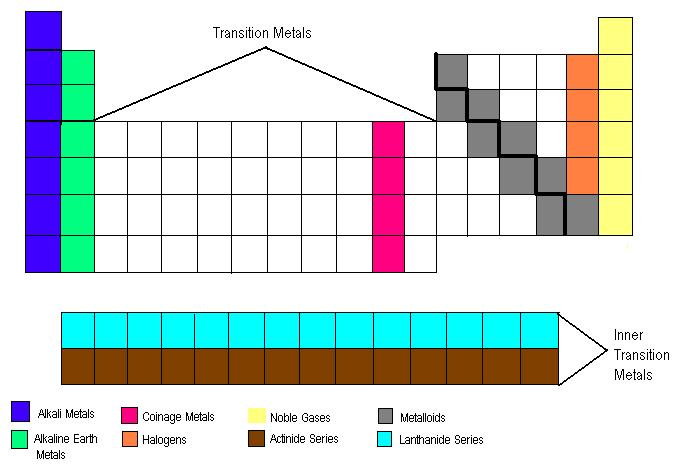 ***Except Aluminum (not considered a metalloid)
***Except Aluminum (not considered a metalloid)

Dalton's Atomic Theory
- All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms (small particles that can no longer be divided and still maintain the properties of that element).
- Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element.
- Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds.
- chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction.
Atoms are made up of subatomic particles:
Atomic Number
- Identifies the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
- Each element has a specific number of protons
- The atom of an element is always neutral, therefore, the number of protons and the number of electrons is the same.
How to find the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom:
Atomic mass - Atomic Number = Number of Neutrons
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
- total mass of each element and the atoms of each of those elements
H2O
2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen
H - 2 x 1.01 = 2.02
O - 1 x 16.0 = 16.0
------
18.02 = amu
Group - vertical column of the periodic table.
Period - horizontal row of the periodic table.
Links
An Element of Interest
Periodic Table of Elements
- Label a blank periodic table with: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, coinage metals, halogens, noble gases, nonmetals, metals, lanthanide series, actinide series, period, group/family
- Calculate the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an element
- Calculate the amu of a compound
- Identify how many atoms of an element are in a compound
- State Dalton's Atomic Theory
- List properties of metals and nonmetals
- Identify the atomic number, atomic mass, symbol, and element name on a small diagram from the periodic table
- Identify the 3 main subatomic particles found in the atom of an element and identify their charge


