Seismic Waves - shock waves from an earthquake
Types of seismic Waves
|
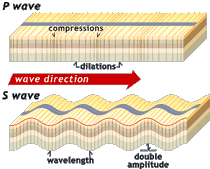
P waves
- travel by back and forth movement of rock
particles. S waves - travel
by up and down movement of rock
L waves - when
P and s waves arrive at the earth's
|
Rock density determines
the speed at which a wave travels. The more
dense the rock, the faster
the speed of the seismic wave.
Different densities of
rock cause speed changes.
Different densities of
rock will also change the angle of a seismic wave. This is -
refraction
- the bending of a (seismic) wave.
Andrija Mohorovicic found
the boundary between the crust and the mantle.
How ?
At 30 to 35 km, seismic
waves speeded up. He inferred that that meant the
rocks got more dense
and were probably different in their makeup. This
boundary between the
mantle and the core is called the MOHO.
There is a zone a certain
distance from an earthquake where no waves
can be detected.
This is the shadow zone caused by the earth's core.
Meteorites are made of
iron and nickel. The theory is that since meteorites
are probably the remains
of planets that have broken apart (most likely
their cores), then
earth's core is probably made of nickel and iron too.
Links
Project
Moholehttp://www.nas.edu/history/mohole/
Project
Mohole Pictures http://www.nas.edu/history/mohole/mohole_gallery.html
Build
a simple seismograph
See
a picture of a seismographhttp://www.exploratorium.edu/faultline/earthquakescience/eqscience5.html
See
seismograph information