Vertical Spring Deviations
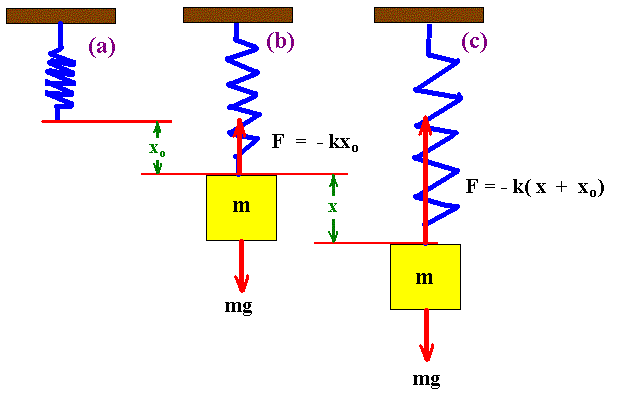
When a mass is hung from a vertical spring, the spring
stretches because 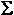 F = 0 = mg - kxo.
Solving for xo. F = 0 = mg - kxo.
Solving for xo.
mg
xo =
------
k
If the spring is now stretched a distance downward of
x, F = mg -k ( x + xo ).
Substitute blue area above.
mg
F = mg - k ( x +
-----
) = mg - kx - mg = - kx
k
This shows that Hooke's Law is valid for Vertical as well as Horizontal
springs. The displacement x must be measured from the new equilibrium
position after the mass has been added.
Energy is also valid for vertical springs. Measuring PE from the
equilibrium position of the original spring
PE = 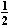 kxo2
- mgxo
Includes both elastic and gravitational PE. kxo2
- mgxo
Includes both elastic and gravitational PE.
When the spring is stretched an additional x
PE = 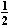 k(
x + xo) 2 - mg ( x + xo
)
Now find the difference between the two PE's. k(
x + xo) 2 - mg ( x + xo
)
Now find the difference between the two PE's.
mg
xo =
------ Remember to use this relationship
and expand the polynomial.
k
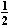 k( x + xo) 2
- mg ( x + xo ) - k( x + xo) 2
- mg ( x + xo ) - 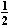 kxo2
+ mgxo = kxo2
+ mgxo = 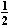 kx2
+ kxxo - mgx kx2
+ kxxo - mgx
mg
= 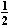 kx2 + kx (
----- ) - mgx kx2 + kx (
----- ) - mgx
k
= 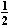 kx2 kx2
This the PE of an oscillating system can be measured from the
new equilibrium position after the mass has been added.
|