|
Vector vs Scalar Measurements
Introduction
| Vector |
Magnitude and Direction. Includes but not limited to velocity,
displacement, force, and momentum. Generally written as boldface or with an
arrow over the symbol. Positive and negative directions must be specified
by the person working the problem.
|
| Scalar |
Only Magnitude. Includes but not
limited to speed, time,
temperature, and energy. Generally written as normal print. |
| Velocity |
Magnitude and direction (VECTOR)
|
| Speed |
Magnitude only (SCALAR)
|
| Displacement |
Change in position including distance and
direction.
|
| Distance |
Change in position without giving a
direction. |
Displacement
Distance
Average Velocity = ----------------------
Average Speed = -------------------
time elapsed
time elapsed
Coordinate axes can be used to set direction.
Calculate the average velocity and average speed of a car that travels 60
km east and then 80 km west in 1 hour.
| East is Positive and
West is Negative
Displacement = +60 km - 80
km = - 20 km
Distance = 60 km + 80 km =
140 km
Displacement - 20 km
Average velocity = -------------------- = -----------
elapsed
time
1 h
Average velocity = - 20 km/h
= 20 km/h West
Distance
140 km
Average speed = ------------------ = -------------
= 140 km/h
elapsed time 1
h |
Pick a Reference
Frame for Vector Measurements.
If you did this in a
car, you would end up 20 km West of your original position.
The total
displacement is the distance and direction from the original point.
The total distance
is how far the car traveled. The odometer would show 140 km
after 1 hour. |
Calculate the average velocity and average speed of a car that travels 160
km north and 40 km south in 1 hour.
| North is Positive and
South is Negative
Displacement = +160 km - 40
km = + 120 km
Distance = 160 km + 40 km =
200 km
Displacement +120 km
Average velocity = -------------------- = -------------
elapsed
time
1 h
Average velocity = + 120
km/h = 120 km/h North
Distance
200 km
Average speed = ------------------ = -------------
= 200 km/h
elapsed time 1
h
|
Pick a Reference
Frame for Vector Measurements.
If you did this in a
car, you would end up 120 km North of your original position.
The total
displacement is the distance and direction from the original point.
The total distance
is how far the car traveled. The odometer would show 200 km
after 1 hour. |
The discrepancy between velocity and speed is only true for average values
and not for instantaneous values.
Displacement = /\x = x2 - x1
/\x
Average Velocity = ------
/\t
Instantaneous Velocity Average velocity over
an indefinitely short time interval.
For one-dimension motion
lim
/\x
v = -----
/\t ->0 /\t
Velocity will be instantaneous unless specified by stating average
velocity or using 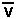
Magnitude of instantaneous velocity and instantaneous speed must be equal.
Table of Contents
Scalar
vs Vector Problems
Calculate the average velocity
and average speed for each of the following:
|
| 1. |
200. meters West, 50. meters East, and 150.
meters West in 3.00 minutes.
|
| 2. |
500. km North, 150. km South, and 100. km
North in 6.00 hours.
|
| 4. |
Two complete times around a 400. meter track
in 2.00 minutes |
Table of Contents
Scalar vs
Vector Answers
Calculate the average velocity
and average speed for each of the following:
|
| 1. |
200. meters West, 50. meters
East, and 150. meters West in 3.00 minutes.
|
|
West
is positive and East is negative.
Displacement = +200. m - 50. m + 150. m = 300.
m
Distance = 200. m + 50. m + 150. m
= 400. m
300. meters
average velocity = ------------------ = 100. m/min
3.00 min
400. meters
average speed = ----------------- = 133 m/min
3.00 min |
Pick a Reference
Frame for Vector Measurements.
If you walked, you would end up
300. m West of your original position.
The total
displacement is the distance and direction from the original point.
The total distance
is how far you walked in 3.00 minutes. |
|
|
|
| 2. |
500. km North, 150. km South,
and 100. km North in 6.00 hours.
|
|
North
is positive and South is negative.
Displacement = + 500. km - 150. km +
100. km
Displacement = 450. km
Distance = 500. km + 150. km + 100. km = 750.
km
450. km
average velocity = -------------- = 75.0 km/h
6.00 h
750. km
average speed = -------------- = 125 km/h
6.00 h |
Pick a Reference
Frame for Vector Measurements.
If you did this in a
car, you would end up 450. km North of your original position.
The total
displacement is the distance and direction from the original point.
The total distance
is how far the car traveled. The odometer would show 750. km
after 1 hour. |
|
|
|
| 4. |
Two complete times around a 400.
meter track in 2.00 minutes
|
|
Forward
from the starting position is + and
backwards from the starting position is negative.
Displacement is 0. m because you end up
at
your starting position.
Distance = 400. m + 400. m
average velocity = 0. m/min
800. meters
average speed = ------------------ = 400. m/min
2.00 minutes |
Pick a Reference
Frame for Vector Measurements.
If you twice around
the track, you would end up at your original position.
The total
displacement is the distance and direction from the original point.
The total distance
is how you ran which is 800. m. |
Table of Contents
|