|
Radioactive Decay
Introduction
Radioisotopes spontaneously change the number of protons, and/or number of
neutrons, or spontaneously release energy. They may be naturally occurring or
man made.
Natural Radioisotopes Carbon-14, Potassium-38, Uranium-235, Uranium-238, and Radon-222
Alpha Decay  |
The nucleus ejects a particle that contains 2 protons and 2 neutrons. The mass
number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2.
---->  + +
|
Beta Decay
 |
n ---> p + e- The neutron changes into a
proton and an electron. The e- is the beta particle - a high speed, high energy
particle that leaves the nucleus. The mass number stays the same and the atomic
number increases by one.
--->  +
+
|
Gamma Radiation  |
This type of decay follows an earlier nuclear reaction. Although the number of
protons, neutrons, and electrons stays the same; there is a very small decrease
in the mass of each particle. This mass is converted into energy in the form of
gamma rays.
--->  +
+
|
Positron Decay  |
p --->
n + e+ The proton changes into a neutron and a positron. The positron
particle is the anti-particle of the electron. When it hits an electron, they
are both annihilated releasing a characteristic amount of energy as photons. The
mass number stays the same and the atomic number decreases by one.
--->  +
+
|
|
Electron Capture |
p + e- --->
n An electron falls into the nucleus and combines with a proton to form a
neutron. The electron must lose energy in the process. It has the same effect as
positron decay although the process is different. The mass number stays the same
and the atomic number decreases by one.
+  --->
--->
|
Conserve
Mass Number & Atomic Number
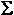 Mass of Numbers Reactants =
Mass of Numbers Reactants = 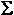 Mass of Numbers Products
Mass of Numbers Products
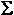 Atomic Numbers Reactants =
Atomic Numbers Reactants = 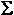 Atomic Number Products
Atomic Number Products
|
Finding
the Product Process
|
| 1. |
Find the Mass Number and Atomic Number of
the beginning isotope.
|
| 2. |
Use the type of decay to place the
appropriate particle in the equation.
|
| 3. |
Find the Total of Mass Numbers present on
the Reactant Side, left side, and the Product Side, right side.
|
| 4. |
Calculate the missing Mass Number and place
it on the appropriate side to Conserve Mass Number.
|
| 5. |
Find the Total Atomic Numbers present of the
Reactant Side and the Product Side.
|
| 6. |
Calculate the missing Atomic Number and
place it on the appropriate side to Conserve Atomic Number.
|
| 7. |
Look up the Atomic Number on the Periodic
Chart to determine the element. |
Uranium-238  decay
decay
 ---> --->  + _____
+ _____
Sum Mass Number Reactants =
238
Sum Mass Number Products = 4 + ____
Sum Atomic Number Reactants =
92
Sum Atomic Number Products = 2 + ___
Missing particle must have a Mass Number of 234 and an Atomic Number of
90. The Atomic Number identifies the element to be thorium.
 ---> --->  +
+ 
Table of Contents
Radioactive
Decay Problems
| 1. |
Find the products of
the following decays:
|
|
a. |
praseodymium-134 --->  |
e. |
gadolinium-146 ---> electron capture |
|
b. |
rubidium-106 ---> |
f. |
actinium-224 --->  |
|
c. |
protactinium-228 ---> |
g. |
mercury-193 --->  |
|
d. |
radium-226 ---> |
h. |
tin-121 ---> 
|
| 2. |
Determine the type
of decay of the following:
|
|
a. |
palladium-111 ---> silver-111 |
|
b. |
erbium-165 ---> holmium-165 |
|
c. |
americium-243 ---> neptunium-239 |
|
d. |
tungsten-187 ---> tungsten-187 |
|
e. |
tantalum-178 ---> hafnium-178 |
|
f. |
actinium-223 ---> francium-219 |
|
g. |
lead-214 ---> bismuth-214 |
|
h. |
cadmium-105 ---> silver-105 |
Table of Contents
Radioactive
Decay Answers
Table of Contents
|