|
Collisions and Impulse
Introduction
 When
collisions occur, the objects deform. They apply force on each
other. The force changes rapidly from 0 to a maximum force and also drops
off quickly. The graph to the left illustrates the change in force vs
time. Usually, The time interval, /\t, is very small and distinct. When
collisions occur, the objects deform. They apply force on each
other. The force changes rapidly from 0 to a maximum force and also drops
off quickly. The graph to the left illustrates the change in force vs
time. Usually, The time interval, /\t, is very small and distinct.
/\p
F = ----
Newton's Second Law of Motion
/\t
F /\t = /\p
F /\t = Impulse
We use F instead of 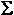 F because it is the
brief force of contact that is applied to both objects. Because the Force
is constantly changing, we use the average force of contact. F because it is the
brief force of contact that is applied to both objects. Because the Force
is constantly changing, we use the average force of contact.
Table of Contents
Problems
| 1. |
Mary, 55.0 kg, is in a bumper car, 540. kg,
and is hit from behind by Amit. They were in contact for 0.35
s. If she was moving 4.25 m/s before the collision, what was the
average force of the collision that increased her speed by 1.15 m/s.
|
| 2. |
A golf club applies an average force of 115
N on a 50.0 g golf ball resting on a tee giving the ball an initial
velocity of 155 m/s. How long was the golf club in contact with the
ball?
|
| 3. |
A tennis racket is used to clear trash off
the tennis court. If the racket applies an average force of 80.0 N
for 0.0450 s on a rock giving the rock an initial velocity of 100.0 km/h,
what is the mass of the rock?
|
| 4. |
William, 105 kg, runs into a 1200. kg
car. He was in contact with the car for 0.55 s and gave the car an
initial velocity of 5.00 km/h. What was the average force applied to
the car? |
Table of Contents
Answers
| 1. |
Mary, 55.0 kg, is in a bumper car, 540. kg,
and is hit from behind by Amit. They were in contact for 0.35
s. If she was moving 4.25 m/s before the collision, what was the
average force of the collision that increased her speed by 1.15 m/s.
|
|
F /\t = /\p = /\mv
/\mv
595 kg x 1.15 m s -1
F = ------- = ----------------------------- = 2.0 x 10 3
N This
is also the force applied by Mary's car on Amit.
/\t
0.35 s
|
|
|
| 2. |
A golf club applies an average force of 115
N on a 50.0 g golf ball resting on a tee giving the ball an initial
velocity of 155 m/s. How long was the golf club in contact with the
ball?
|
|
F /\t = /\p = /\mv
The ball starts off at rest. /\v
= 155 m/s
/\mv
0.0500 kg x 155 m s -1
/\t = ------- = ------------------------------- = 0.0674 s
F
115 kg m s -2
|
|
|
| 3. |
A tennis racket is used to clear trash off
the tennis court. If the racket applies an average force of 80.0 N
for 0.0450 s on a rock giving the rock an initial velocity of 100.0 km/h,
what is the mass of the rock?
|
|
F /\t = /\p = /\mv
100.0
km 1
h 1000 m
----------- x ---------- x ------------ = 27.8 m s -1
The rock starts off at rest. /\v
= 13.9 m/s
h
3600 s 1 km
F /\t
80.0 kg m s -2 x 0.0450 s
m = ------- = ---------------------------------- = 0.129 kg =
129 g
/\v
27.8 m s -1
|
|
|
| 4. |
William, 105 kg, runs into a 1200. kg
car. He was in contact with the car for 0.55 s and gave the car an
initial velocity of 5.00 km/h. What was the average force applied to
the car?
|
|
F /\t = /\p = /\mv
5.00 km 1
h 1000 m
----------- x ---------- x ------------ = 1.39 m s -1
The car starts off at rest. /\v
= 13.9 m/s
h
3600 s 1 km
/\mv
1200. kg x 1.39 m s -1
F = ------- = ----------------------------- = 3.0 x 10 3
N This
is also the force applied to William by the car.
/\t
0.55 s
|
Table of Contents
|