The International School of Panama
IB Chemistry HL Notes - Bonding
• A chemical bond is a strong attracting force between atoms or ions in a compound. It’s a strong electronic interaction.
• Why do atoms form bonds?
• Because the formation of the bond results in a decrease of their potential energy making the system more stable.
• What electrons are involved in the formation of bonds?
• The electrons in the valence shell, that is valence electrons.
The type of bond formed depends on the attraction for electrons the atoms involved have. This attraction is called Electronegativity.

Why is it important to know the type of bond?
• Because the properties of substances depend mainly on the types of bonds they have…
|
IONIC |
COVALENT |
METALLIC |
|
One metal and one non metal |
Two non metals |
Atoms of the same metal |
|
High difference in electronegativities (usually > 1.7) |
Little or no difference in electronegativities |
No difference in electronegativities |
|
One atomwith high electronegativity and the other low |
Both atoms have high electronegativity |
The atoms of the metal have low electronegativity |
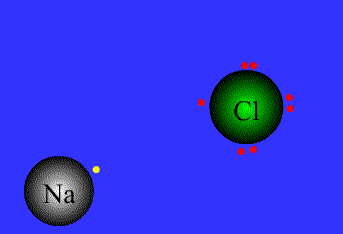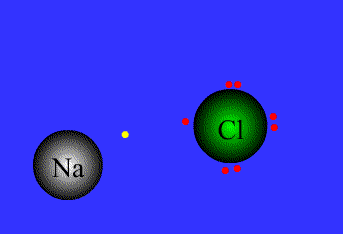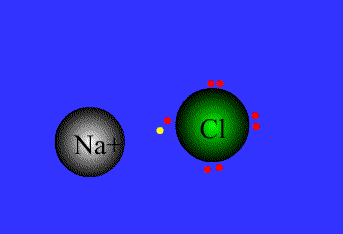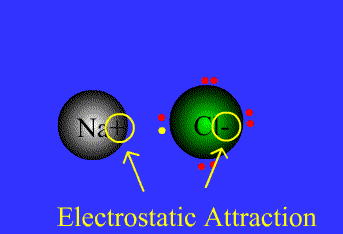
• Ionic Bond: A chemical bond formed by electrostatic attraction between a cation (positive ion) and an anion (negative ion).
• How does the ionic bond form?
Example
Na = 1s22s22p63s1 By level (or shell): 2 8 1
Cl = 1s22s22p63s23p5 By level (or shell): 2 8 7
Na has a single electron in the outer level, so it needs to get rid of the outer electron.
Cl has 7e in the outer level, so it needs to get an extra electron to complete the octect.
Chlorine has high electronegativity (3.5), Na has low electronegativity (0.9)…Therefore when they are close to each other one electron is transferred from Na to Cl, and both acquire a stable configuration with the outer level complete..both get more stable, both are happier…Let´s see the process
http://207.10.97.102/chemzone/lessons/03bonding/mleebonding/ionic_bonds.htm
Covalent bond
• Covalent: Bond formed when electrons are shared by two atoms.
• How does the covalent bond form?
Example
Cl = 1s22s22p63s23p5 By level (or shell): 2 8 7
Cl = 1s22s22p63s23p5 By level (or shell): 2 8 7
Cl has 7e in the outer level, so it needs to get an extra electron to complete the octet.
Chlorine has high electronegativity (3.5). When two chlorine atoms approach each other both nuclei attract the outer electrons equally so they share a pair of electrons acquiring both a configuration with the outer level complete. Both get more stable, both are happier…Let’s see the process
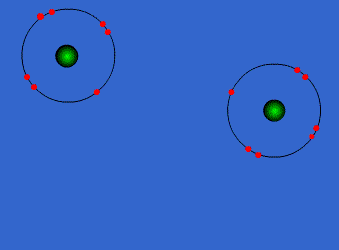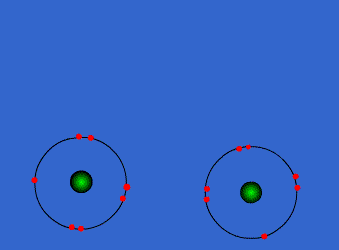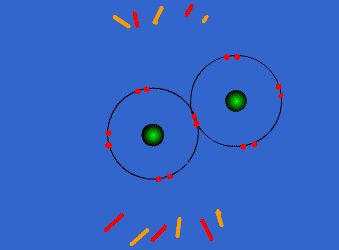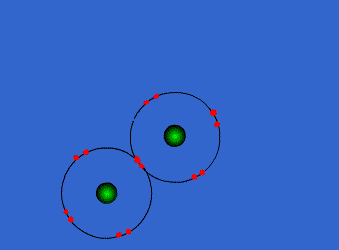
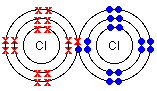
http://www.chemguide.co.uk/atoms/bonding/covalent.html
http://207.10.97.102/chemzone/lessons/03bonding/mleebonding/covalent_bonds.htm
Chlorine and other halogens diatomic molecules:

http://www.chem.ufl.edu/~chm2040/Notes/Chapter_11/covalent.html
Metallic Bond
• Metallic Bond : All the positive nuclei of the metals attract the delocalized outer electrons forming a lattice of positive ions surrounded by a sea of electrons. (electron sea model)
• Why does a metallic bond form?
Example
Na= 1s22s22p63s1 By level (or shell): 2 8 1
Fe= 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6 By level (or shell): 2 14 2
Metals have always few electrons in the outer level.
Metals have low electronegativity, but when several atoms of the metal are together all nuclei attract the outer electrons. This non directional attraction between all nuclei and the outer electrons holds the atoms strongly attached to each other but at the same time allows these outer electrons move freely. This is known as the electron sea model.

http://207.10.97.102/chemzone/lessons/03bonding/mleebonding/metallicbonding.htm
The Lewis electron dot structure of molecules and ions
o Usually the element that appears only once in the molecule is the central atom.
o Fluorine and Hydrogen are always terminal elements (never central)
o Also remember the following tendency in the number of bonds formed by the atoms of the following elements:
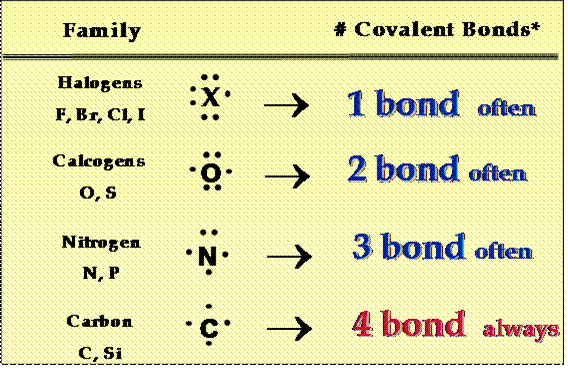
http://www.miramar.sdccd.cc.ca.us/faculty/fgarces/ChemComon/Tutorial/Lewis/LewisTutorial.pdf
· Octet rule: most atoms form stable compounds when they have 8 electrons around (the octet is complete) attaining a noble gas configuration.
· Hydrogen follows the duet rule, that is it forms stable compounds when it has 2 electrons around (attaining He configuration).