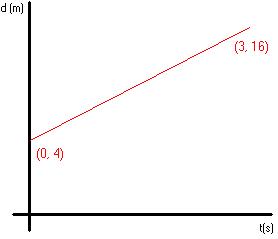
m(slope) = ![]() d/
d/![]() t = (16 - 4)/(3 - 0) = 12/3 = 4 m/s = average
velocity in 0s - 3s.
t = (16 - 4)/(3 - 0) = 12/3 = 4 m/s = average
velocity in 0s - 3s.
Example #2:
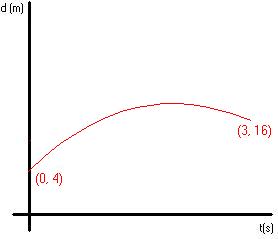
m(slope) = 4 m/s = average velocity
Instantaneous Rate of Change: while average growth
rate is the slope between two given points on a graph, instantaneous growth rate
is at an instant, ie: at a point.
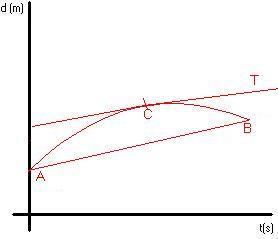
Example: s(t) = -t2 + 9t + 1

Find the instantaneous growth rate (velocity) when:
2. t = 4.5s
3. t = ?, s = 0m
We can't use this equation as shown above. Since we are looking for the
instantaneous rate of change, then the change in both x and y equals 0. To find
an approximation allow the change (![]() x and y) to
approach 0.
x and y) to
approach 0.

Using this method find out what the instantaneous growth rate equals for the other three times indicated. Your final answers should be: 1. mTan approaches 9; 2. mTan approaches 0; 3. s = 0 when t = 9.11 and t = -0.11.
Here's a few helpful links:
Average Rate of
Change
Instantaneous vs. Average rate of change
Rates of Change