GSM radio aspects
-:
In GSM the uplink (mobile-to-base) frequency
band is 890-915 MHz and the corresponding downlink (base-to-mobile)
band is 935-960 MHz , resulting in a 45 MHZ spacing for duplex
operation. The GSM uses time division multiple access (TDMA) and
frequency division multiple access (FDMA) , whereby the available
25 MHz spectrum is partitions into 124 carriers ( carrier spacing
= 200KHz ) , and each carrier in turn is divided into 8 time
slots ( radio channels ). Each user transmits periodically in
every eighth time slot in an uplink radio carrier & receives
a corresponding time slot on the downlink carrier. Thus several
conversations can takes place simultaneously at the same pair of
tansmit/receive radio frequencies. The radio parameters for GSM
are summerised in the following table :
Radio parameters and characteristics for GSM
System Parameter |
Value (GSM) |
Multiple Access |
TDMA/FDMA/FDD |
Uplink frequency (mobile-to-base) |
890-915 MHz |
Downlink frequency (base-to-mobile) |
935-960 MHz |
Channel Bandwidth |
200KHz |
Number of channels |
124 |
Channels/carrier |
8 (full rate), 16 (half rate) |
Frame duration |
4.6 ms |
Interleaving duration |
40 ms |
Modulation |
GMSK |
Speech coding method |
RPE-LTE convolution |
Speech coder bit rate |
13 kb/s (full rate) |
Associated control channel |
Extrea frame |
Handoff scheme |
Mobile-assisted |
Mobile station power levels |
0.8, 2, 5, 8 W |
In the GSM system a digitized speech is passed at 64 Kb/s
through a speech coder ( transcoder ) , which compresses the
64 Kb/s PCM(pulse code modulated ) speech to a 13 Kb/s data rate.
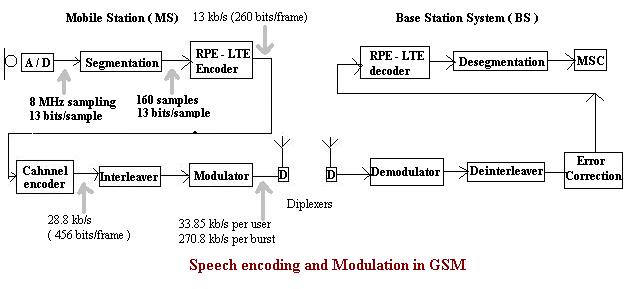
The transcoder models the vocal tract of user and generate a set of filter parameters that are used to represent a segment of speech ( 20 ms long ) , and only the filter parameters and impulse input to the filter are transmitted on the radio interface.The speech coding improves the spectral efficiency of the radio interface thereby increasing a traffic capacity of the system (more users over a limited bandwidth ).