SECOND APPROXIMATION OF
A REAL DIODE
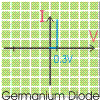
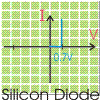
In the second approximation the current starts to flow by the time threshold voltage reaches at 0.7V for Silicon and 0.3V for Germanium. As show in the graph Maximum current starts flowing at 0.7V and 0.3V respectively.


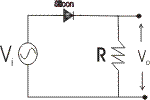
The equivalent circuit of a Real Diode is shown above the Germanium type is series with a 0.3V DC source and the Silicon type is series with 0.7V DC source.
EXAMPLE 1
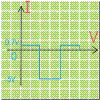
Sketch the output wave shape for the circuit. The generator signal is a sine wave with a 5-volts peak. Use the second approximation of the real diode.
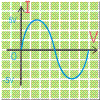
Solution
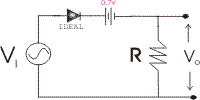
The equivalent circuit of the example. The Silicon diode is replaced with an ideal diode in series with a 0.7V dc source.
During the positive half cycle the diode is ON.
D1 = ON
Applying KVL to circuit.
Vg – Vt – Vr = 0
Voltage across the resistor R is equal to the output voltage Vo the equation becomes
Vr = Vo = Vg – Vt
Vo = 5 – 0.7
Vo = 4.3 Vp
During the negative half cycle the diode is OFF because the current is in opposite direction with the triangle.
D1 = OFF
The voltage output is equal to the current (I) multiply with the resistance (R)
Vo = IR
Since the diode is Off thereby no current will flow across the diode and current (I) is zero across the resistor (R).
Vo = (0)R
Vo therefore is equal to zero.
Vo = 0V.
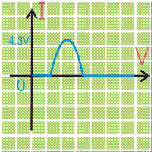
Therefore, during the positive half cycle of the input the output voltage Vo = 4.3V. And during the negative half cycle of the input the output voltage Vo = 0V. The out put waveshape of the example is shown below:
EXAMPLE 2
A silicon diode is used in the positive clipper. Sketch the output waveshape if the input is:
a.) a sine wave with a peak value of 5 volts.
b.) A square wave with a peak value of 5 volts.
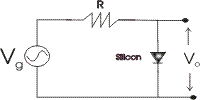
EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT
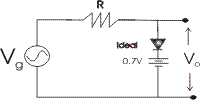
This is the equivalent circuit of the example.
Solution a
During the positive half cycle the diode is On.
D = ON
Since the diode is ON, it is equivalent to a close switch thereby the output voltage Vo is equal to 0.7V.
Vo = 0.7V
During the NEGATIVE half cycle the diode is OFF.
By applying KVL to the circuit the equation becomes:
-Vg – Vr – Vo = 0
Transposing Vo to the left the equation becomes:
Vo = -Vg – Vr
Voltage out (Vo) is equal to negative Vg minus current (I) multiply by the resistance (R).
Vo = -Vg - IR
Since the diode is OFF it is replaced with an open switch, thus, no current will flow across the diode and current across R is equal to zero.
Vo = -Vg – (0)R
Vo = -Vg – 0
Vo = -Vg
Vo = -5V
Therefore the output Voltage (Vo) during positive half cycle is equal to Vo = 0V. And the output voltage (Vo) during the negative half cycle is equal to Vo = -5V
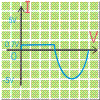
The output wave shape of the solution a of the example.
Solution B
The same solution from the solution A the output waveshape of the solution B is shown below: