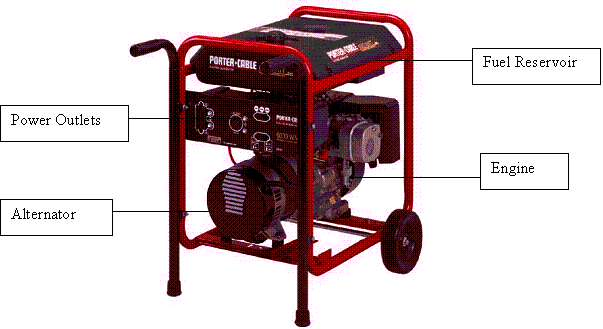
The portable electric power generator (figure 1)
provides a convenient electrical power source.
Our generation became quite dependent on the convenience of electrical
power outlets in our daily activities.
The portable electric power generator supplements our demands for
electrical power sources when the main electrical power source is not
available. The portable electric power
generator converts energy from an engine that operates on gasoline fuel to
conventional electrical power outlets. The
portable electric power generator process consists of three parts; combusting gasoline
fuel to operate the engine, using the rotation from the engine to turn the
alternator; and converting the rotational power into electricity.
Source
Amazon.com. 2003. Porter-Cable BS600 – W. 22 July.
Internet: http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/B00005AUFF/ww2links-20/002-0269740-1152024
Gasoline fuel provides an energy source to run most
of today’s engines. Gasoline fuel
combusts very easily. Igniting gasoline
fuel causes a great amount of pressure and heat. Compressing gasoline fuel then igniting it results in an
explosion, which produces pressure. The
pressure produces power to run the portable electric power generator.
The engine, in the portable power generator, burns
the gasoline fuel inside its combustion chambers, creating a spinning force
through the engine’s drive shaft. The
engine’s drive shaft connects to the alternator unit, consequently spinning its
main shaft that operates the alternator.
The alternator resembles an electric motor (figure 2)
in its operation. The alternator
creates electrical power for batteries or electrical outlets instead of using
electricity from the battery or an electrical outlet to spin the motor. The alternator converts the spinning of its
armature into electricity by passing the coils around the armature through the
magnetic field around the field magnets.
As the coils cross the magnetic field of each magnet, electricity runs
through the coils providing an electrical source to the power outlets to charge
a battery, run an air conditioner, or light a lamp.
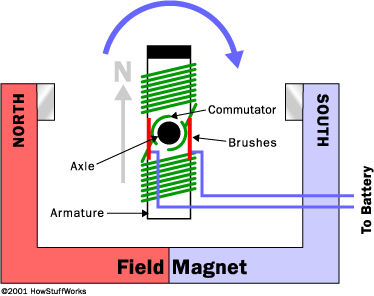 Figure 2
Figure 2
Source
Brain, Marshall. 2003. How Stuff Works: How Electric Motors
Work. July 22. Internet:
http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/motor1.htm
English
200 Technical Communication
Summer
2003