PROGRAM
50
C++
K.
Dzwonkiewicz
The Monte Carlo Method
Monte
Carlo methods are computer models that involve some chance or probabilistic
behavior. (Monte Carlo is the famous
gambling resort in Monaco.)
Suppose we have a figure on the x-y plane and we want to
estimate its area. In previous programs
we used inscribed or circumscribed rectangles or trapezoids. The Monte Carlo method also finds area but by
using probability and ratio or percent.
Consider the following
figure…
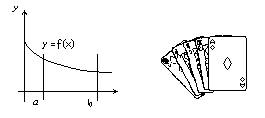
Suppose the figure lies
within some known rectangle. The area
of interest lies between two x values
a £ x £ b. For any random
x value within the area of consideration, we will match a random y value also
within the rectangle, the point will fall either above the curve or on it or
below.
If we choose an interval… a
£ x £
b and also, 0 £ y £ f(a) (see figure above). The bounded area below the curve is called the definite integral
of the function f(x) on the interval [a,b]
The Monte Carlo method is
to throw many random points uniformly distributed over the rectangle that
contains our area of interest. Some
points will land inside the figure and some will land outside. The fraction of all points that land inside
should be approximately equal to the ratio of the figure to the area of the
rectangle.
Randomize 10,000 points
counting how many are on or below the curve.
Multiply the ratio of on and below divided by 10000.0 (or use percent)
times the area of the rectangle. This
will give an approximation of the area under the curve for the interval
considered.
HINTS: We must get a
floating-point number for our random.
This of course can be done by asking interval start and end, then put a
multiple ( by 100) inside the random.
Once you get the random value divide by 100 and use this value for x
(same process for y)
cin>>startval;
// 0 is input
cin>>endval;
// 10 is input
x=(random
(endval*100-startval*100)+startval)/10.0;
// better check this!
(This will generate decimals within 0.00-10.00)
The area
of the rectangle will be the highest point on the curve times the width (to get
the max value of f(x); find the first derivative… set it to zero and solve for
the needed x value that when put into the original expression will result in
rectangle height)
Use the equation… f(x)= -x2
+10x +24, restrict your x values to be in range [0,10].
Approximate area is… 406.666666666666
