Radio Wave (Properties of Waves)
The radio system uses propagation of electromagnetic waves through space, to send information. Being an electromagnetic wave, the radio frequency (r.f.) wave has the same properties as visible light. The r.f. wave is, however, of a much lower frequency and so longer wavelength. The shorter waves in the electromagnetic spectrum have the highest frequency and the longer waves the lowest.
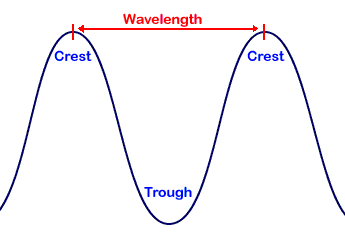
A wave can be thought as a vibrating disturbance by which energy is transmitted. Waves are characterized by their length and height and by the number of waves that pass through a certain point in one second. Wavelength is the distance between identical points on successive waves. Frequency, or number of cycles per second, is given the unit of the hertz (Hz), named after the German radio pioneer Heinrich Hertz. Radio waves range from a few kilohertz to several gigahertz. Amplitude is the vertical distance from the midline of a wave to the peak or trough. wavelength is usually expressed in units of meters, centimeters, or nanometers, and frequency is measured in hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz = 1 cycle
In a vacuum, all electromagnetic waves travel at a uniform speed of about 300,000 km (about 186,000 miles per second).
Radio waves are used in many other applications such as television, telephone transmission, radar, navigational systems and space communications. The table below shows various radio wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum.
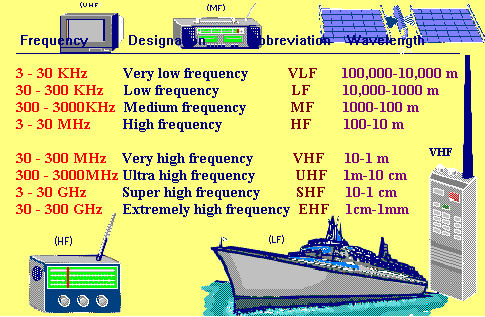
Radio waves, television waves, and microwaves are all types of electromagnetic waves. An electromagnetic wave has an electric field component and a magnetic field component. these two components have the same wavelength and frequency and the same speed, but they travel in mutually perpendicular planes. They only differ from each other in wavelength. Wavelength is the distance between one wave crest to the next. Waves in the electromagnetic spectrum vary in size from very long radio waves the size of buildings, to very short gamma-rays smaller than the size of the nucleus of an atom.