**HOME**
-
Neuron: nerve cell that conducts nerve impulses
-
Sensory neuron (afferent neuron): carries impulses to the central
nervous system
-
Interneuron: carries impulses within the central nervous system
-
Motor neuron (efferent neuron): carries impulses from the central
nervous system to effectors
-
Dendrite: projection of cytoplasm that carries impulses toward the cell
body
-
Axon: extension of cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the
cell body
-
Myelin sheath: insulated covering over the axon of a nerve cell;
composed of Schwann cells
-
Nodes of Ranvier: regularly occurring gaps between sections of myelin
sheath along the axon where nerve cells are transmitted
-
Neurilemma: delicate membrane that surrounds the axon of some nerve
cells
-
Reflex arc: neural circuit that travels through the spinal cord;
provides a framework for a reflex action
-
Nerves conduct electrochemical impulses from the dendrites along the
axon to the end plates of the neuron.
-
Active transport and diffusion of sodium and potassium ions establish a
polarized membrane.
-
An action potential is caused by the inflow of sodium ions.
-
Nerve cells exhibit an all-or-none response.
-
Neurotransmitters allow the nerve message to move across synapses.
-
Meninges: protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
-
Cerebrospinal fluid: circulates between the innermost and middles
membranes of the brain and spinal cord; acts as a transport medium and shock
absorber
-
Olfactory lobes: areas of the brain that detect smell
-
Cerebrum: the largest and most highly developed part of the human brain;
stores sensory information and initiates voluntary motor activities
-
Cerebral cortex: the outer lining of the cerebral hemispheres
-
Corpus callosum: a nerve tract that joins the two cerebral hemispheres
-
Cerebellum: the region of the brain that acts as a relay station by
sending nerve messages between the cerebellum and the medulla
-
Medulla oblongata: the region of the hindbrain that joins the spinal
cord to the cerebellum; the site of autonomic nerve control
-
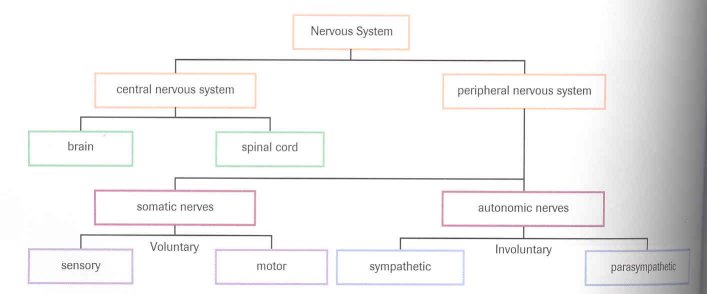
The autonomic nervous system is a motor system.
-
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for stress; the
parasympathetic system returns the body to a resting states.
-
The neurotransmitters released from the sympathetic system are
acetylcholine and norepinephrine; the parasympathetic system releases only
acetylcholine.
-
Endorphins and enkephalins are natural painkillers produced by the body.
**HOME**