Developmental Biology (Bio 445)
Lecture Guide
(pages 72-82 Moore)
NOTE: We will also cover
some material in Wolpert, Chap 8 (up to Neurulation). We may not get into this at all until Wednesday. But please preview that chapter also.
3-4
weeks of Development.
….finishing
off the notochord….
The
floor of the notochordal process AND the underlying endoderm degenerate leaving
the flattened, grooved ____________________
The
floor of the notochordal process AND the underlying endoderm degenerate leaving
the flattened, grooved ____________________.
Notochordal
cell proliferation causes an _________________ of the notochordal
plate and the formation of the rod-shaped ___________.
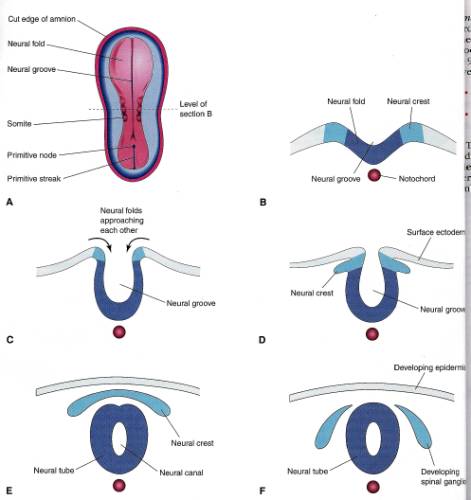
Neurulation
Neurulation is the formation of the ___________________.
The processes involved
in neurulation are completed at the end of week 4.
During neurulation, the
embryo may be referred to as ____________.
The notochord induces
the overlying ectoderm to thicken and form the neural plate.
The ectoderm of the
neural plate gives rise to the (______________) CNS.
Location:
cranial to the _____________________
dorsal to the ______________________
The neural plate extends
as far as the _________________membrane.




Invagination of the
neural plate forms the ________________ bounded on either side by
the _____________________
The cranial _____________
become prominent and are the first indications of ____________________________.
By the end of the 3rd
week, the neural folds have moved together and fused into the ___________________.
Neural Crest Cell
Formation
As the neural tube
closes, ______________ along the “crest” of the neural folds,
lose their ____________ to the surrounding epithelial cells.
These ________________
migrate to first form a flattened layer between the ____________ and the
overlying ectoderm called, collectively, the “_______________”.
These cells continue to
migrate _______________ into right and left masses on either side
of the _______________ where they will eventually form __________________.
neural crest cells give rise to:
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
Somite Formation
On each side of the
notochord/neural tube, the mesoderm _________________________into a column of
tissue called the _____________________________.
Adjacent to the paraxial
mesoderm is the _______________________
Finally, the most
lateral aspect of the mesoderm thins and is called the _________________________


Near the end of the 3rd
week, the paraxial mesoderm becomes paired, cubed bodies of mesoderm called the
_______________________
They develop __________________
and give rise to:
Most of the ___________________________ (and
musculature)
Intraembryonic coelom
The beginnings of the
embryonic body cavity are first seen as isolated _______________
in the ___________________________.
These spaces soon
coalesce to form the single horseshoe-shaped cavity, the ____________________________.
the ___________________
divides the lateral mesoderm into 2 layers:
_______________ (parietal) – continuous with mesoderm covering the amnion
________________(visceral) – continuous with mesoderm covering the yolk sac
additional terminology:
the somatic mesoderm +
ectoderm = _______________________
the splanchnic mesoderm
+ endoderm = _____________________


Chorionic Villi
Development
____________________are projections of ________________ cells into the syncytiotrophoblast.
_____________chorionic villi form when the core of the chorionic villus becomes filled with ________________________.
____________ chorionic villi form when ________________ fill the core of the chorionic villus.
__________________________ are formed from the fusing together of all the _________________________.
The chorionic villi profilerate and form a layer, the ______________ ___________________, which surrounds the ____________ sac and attaches it to the ___________________.
____________________ – chorionic
villi that extend through the shell and anchor themselves into the endometrium.
____________________– extend
laterally and are the major site of interchange between maternal blood and the
embryo.