Developmental Biology (Bio 445)
Lecture Guide
(pages 63-71
NOTE: We will also cover
some material in Wolpert, Chap 8 (up to Neurulation). We may
not get into this at all until Wednesday.
But please preview that chapter also.
Third week of Development.
__________________
is the process by which the ____________________ embryonic disc is converted into the
_________________________________.
Gastrulation is the beginning of
______________________________________.
During
this period, the embryo is referred to as a _____________________.
_____
important processes occur during this period.
1.
________________________________
2.
________________________________
3.
________________________________
Primitive
Streak
-
This structure appears as _________________________ of the embryo.
-
It is formed by ______________________ and ______________________ of ___________________________cells
to the ___________________ plane of the embryonic disc.
The primitive streak _________________________caudally.
_______________________
– forms at the caudal end of the primitive streak.
The
________________________ forms within the primitive streak and is
continuous with a small depression , the __________________________.
The
formation of the primitive streak define the embryos
_________________ ________________________ axis.
Cells
on the deep surface of the primitive streak form a
__________________________________________________________ called
____________________________________ or mesoblast. These cells form a layer known as the
_______________________________________________.
______________________ – epiblast
cells which have displaced the hypoblast.
_____________________
- formed from the remaining cells of the epiblast.
Cells
from the ______________________ give rise to all three germ layers in the
embryo.
The
primitive streak normally degenerates by ___________________________ .
NOTOCHORD
The
notochord:
1.
defines the ___________________________ and gives it some
rigidity.
2.
serves as the basis for development of the
_________________ ______________________ (bones of the head and vertebral
column)
3.
indicates the future site of the
______________________________ .
___________________________
- formed from the cranial migration of ____________________ from the primitive
_______________________ which forms a cellular cord. This grows cranially between the
__________________ and _____________________________ until it reaches the
_______________ ____________________.
____________________________ - the lumen within the notochordal process.
The
prechordal plate halts the advancement of the notochordal process because its
firmly attached to the _________________________ to form the
_______________________________________________ (future site of the mouth).
_____________________ - future site of the _______________. The germ layers are also fused here. This prevents ___________________________
from migrating beyond this point.
The
notochord is the primary inductor in the early embryo.
The
notochord induces the overlying ectoderm to thicken and form the
_______________________________________.
Remnants
of the notochord can be seen as the ___________________________ of each
intervertebral disc.
The
_________________ is a small diverticulum from the caudal
wall of the _____________________________ projecting into the connecting stalk. Its function is less critical in humans than
in reptiles in birds. However, is does
play a role in the ___________________ and development of the __________________________ .
Figure
1.
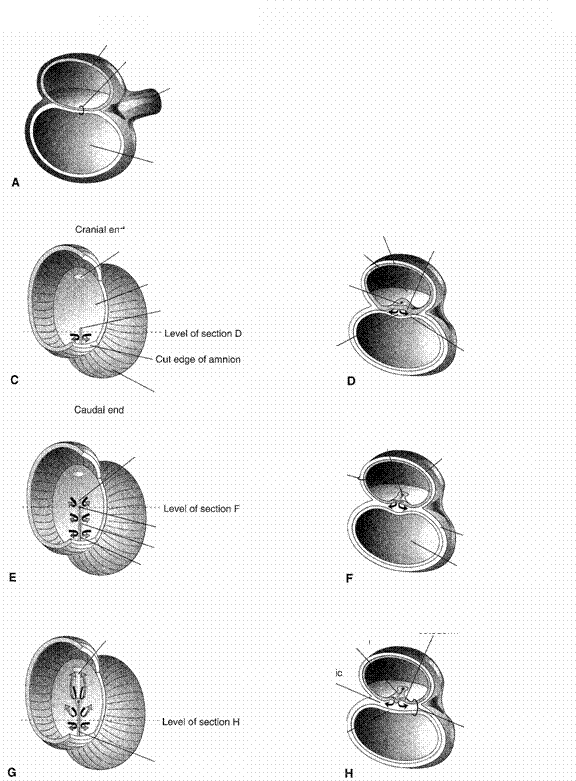
Figure
2.
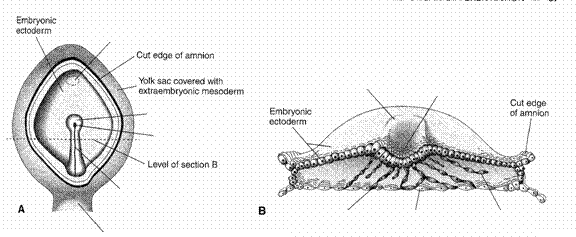
Figure 3
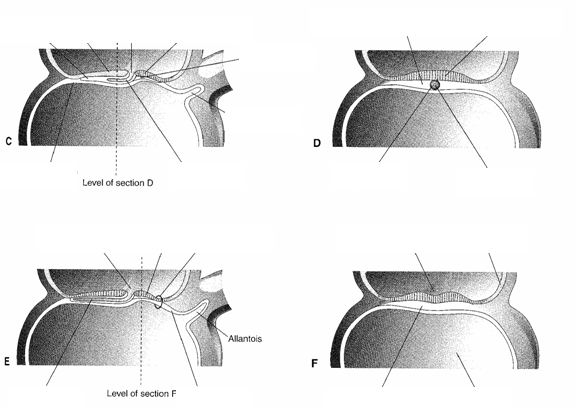
Figure 4
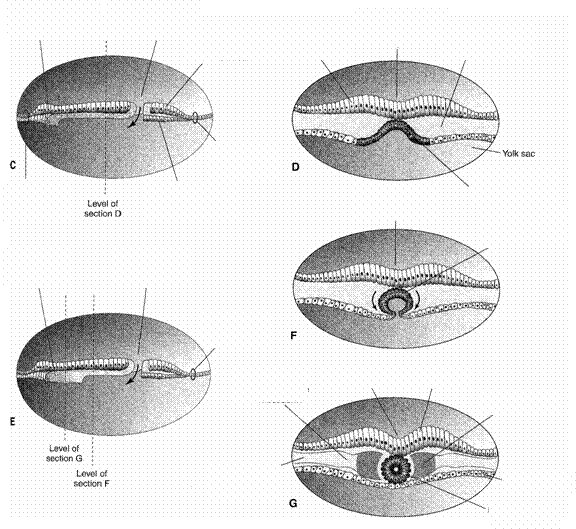
Figure 5 