|
| Introduction
to the World Wide Web Programming |
Mr. Rodelio P. Barcenas
Computer Engineering Department
Don Bosco Technical College
What is HTML or HyperText MarkUp Language?
HTML is a web document
which contains hyperlinks to other web documents. Unlike a book, this
can be treated as a linear document wherein pages are contained in one
physical location. A web page can contain hundreds of pages which can
be found in different locations around the world. Readers of the web page
can feel that he is just reading a sequence of pages but in reality informations
came from different location.
Some advantages of
HTMLs vs Linear Documents.
- Readers can read
at their own pace
- Easily Update on
documents
- Contains Videos,
Sound and images
Web Servers and
Web Browsers
Here is an illustration
on how the web operates.
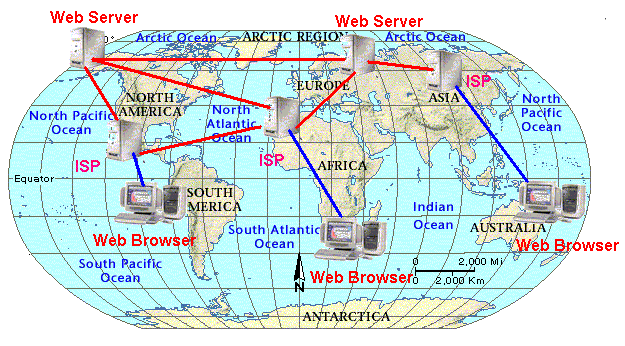
A Web Browser
is the client while the Web Server is the respondent. The web browser
request for files while the http server makes the transaction possible.
You will see at this point a client - server scenario.
Types of Browsers
- MOSAIC (oldest)
- Netscape Communicator/
Navigator
- Microsoft IE
- SUN Hot Java
- Others
Versions of HTML
| Version |
Description |
| HTML
0.0 |
The
Original Version developed by Timothy Berners - Lee and other researchers
at CERN, it has long been replaced
by other versions of HTML |
| HTML
1.0 |
The
first public version of HTML, which included support for inline images
and text controls. Some browsers, most notably the text based LYNX
browser on the UNIX systems, operate at the 1.0 level |
| HTML
2.0 |
The
version supported by all graphical browsers, including Netscape Navigator,
Mosaic and Internet Explorer, It supported interactive form elements
such as option buttons and text boxes. A document written to follow
2.0 specification would be readable by most browsers on the internet. |
| HTML
3.2 |
This
version is also reffered to as HTML+. It includes more support for
creating and formating t ables and expands the options for creating
interactive form elements. It also allows for the creation of complex
mathematical equations. |
 |
 |
|