Programming algorithms vary for every applications.
Factors such as speed of execution, code size, efficiency, scalability,
and others are just examples of it. A programmer normally justifies
all the factors to come up with an application software.
Programming Loops
Loops in programming are alway present in every software program. A
computer software normally have more than one loops of routine often
know as the main routine. A routine is a set of procedures that is being
repeated over and over.
Example;
|
main
call procedure1
call procedure2
call procedure3
....
goto main
|
|
| |
Fig 1
|
| But most
of the time we have more than one loop of program wherein the
procedures contains also loops of processess inside. The loops
inside a process is often a conditional loop, wherein to
exit a given loop, a condition must be satisfied. This is an example
of a multiloop program. loop2 can be terminated if x and
y are equal. If x and y are not equal, loop3 will be processed
next. |
 |
| |
Fig 2.
|
| An example of a Loop
within a loop. |
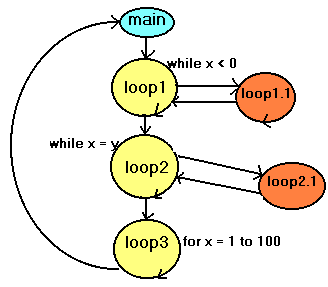 |
| |
Fig. 3
|
Loops are potential hazards in programming;
Conditions inside the loop must always be considered
in order for the proper exiting of the loops. In microcontroller application
design, an assumption that variable will not change is a wrong thing
to do. Voltage fluctuations, spikes or droops, can influence the values
of the variables inside the microcontrollers and can turn a conditional
loop into an infinite loop. The program will stall or hang-up if the
loop cannot be terminated, since the other processes cannot be executed.
If Loop1 hangs-up, Loop2 and Loop3 will not be executed anymore.
Fig. 1 illustrates an
example of a single loop application wherein only one loop is existing
which is the Main Program Loop. Fig. 1 is much more robust
compared to Fig. 2 and Fig.3. , since the procedures
does not contain any loops inside.
Translating Multiple Loops to Single Loop program.
Translation from multi-loop program to single loop
program is a better solution to robustness of the microcontroller
application. The more the loops, the more possibility for hazards.
The lesser the loops, the lesser the hazards. Not most program can
be applicable for convertion from multi-loop to single loop but at
least lessening the number of loops inside the program will lessen
the chances for system failures. An example below shows a multi-loop
psuedo code program to single loop program.