|
|
|
 The Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem  Objectives: To find the length of one side of a right triangle, given the lengths of the other two sides, and to determine whether a triangle is right, given the lengths of its three sides. Objectives: To find the length of one side of a right triangle, given the lengths of the other two sides, and to determine whether a triangle is right, given the lengths of its three sides.
 The Pythagorean Theorem: If triangle ABC is a right triangle with c the length of the hypotenuse and a and b the lengths of the legs, then c2 = a2 + b2 The Pythagorean Theorem: If triangle ABC is a right triangle with c the length of the hypotenuse and a and b the lengths of the legs, then c2 = a2 + b2
The Greek philosopher Pythagoras discovered the relationship between the hypotenuse and the two legs of a right triangle. right triangle is any triangle with one right angle.
Examples:
a.) A surveyor walked 8m east then 6m north. How far is she from the starting point? 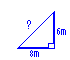 Use the Pythagorean Theorem: c2 = a2 + b2 = 62 + 82 = 36 + 64 = 100 c2 = 10 (the square root of 100) Thus, the surveyor was 10m from her starting point.
b.) Determine whether the triangle with sides 3, 1, and is a right triangle:
|
|
|
|