Topic 4: Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Why do atoms form bonds?
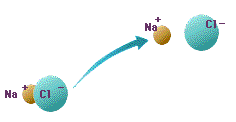
Ion is connected in order to gain the energy of an insufficiency towards being stabilized, since the balance of the electricity of plus or minus has collapsed and energy is not stabilized.
How do ionic and covalent bonds compare?
Ion is equivalent to the ion of electric character contrary to the electricity which the ion itself has, and is connected. A covalent bond is connected by sharing an electron mutually.
How do you name salts
Nomenclature is the system of naming ions. A monatomic ion can be named using the element's name followed by the word "ion." An anion, however, is written with the element's name with the ending dropped and the suffix "-ide" added followed by "ion." For ions with other charges, the element's name with the roman numeral of the positive charge followed by "ion." For example, Cu2+ = Copper(II) ion. This does not apply for atoms that always form atoms with the same charge, such as Mg2+ (Magnesium ion).
Binary compounds, which are made of two atoms, can be named using the cation's name and the anion's name. For example, a compound composed of the cesium ion (Ce+) and a chloride ion (Cl-) is called Cesium Chloride.
What is a polyatomic ion?
The substance which they gather and constitutes an ion is called a polyatomic ion. Hydroxide ion (OH-) nitric acid ion (NO3-) sulfuric acid ion (SO42-) are examples of polyatomic ions. Paranthesis are used to show there are more than one polyatomic ion when writing ion formulas. For example, Ca(H2PO4)2.
There are some rules when naming polyatomic ions. The cation is listed first, then the anion. Ions with larger numbers of oxygen atoms ends with -ate, while ions with smaller number of oxygen atoms ends with -ite.
How are molecules specified?
The minimum unit is defined as one molecule by the substance which consists of a covalent bond and combination of a hydrogen bond, etc. An example of a covalent bond is acetic acid (CH3COOH), etc.
Molecules can be specified by the Lewis structure, a diagram showing the arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms in a molecule. This is a diagram of the Lewis structure:

Main menu
Topic 3: Periodicity
Topic 5: Chemical Equations
Credits and Links