Bernoulli's Principle
Introduction
| Bernoulli's Principle |
Where the velocity of a fluid is high, the pressure is
low, and where the velocity of a fluid is low the pressure will be high. |
P1 + 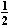  v12
+ v12
+  gy1 =
P2 + gy1 =
P2 + 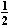  v22
+ v22
+  gy2
Bernoulli's Equation gy2
Bernoulli's Equation
or
P + 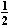  v2
+ v2
+  gy = Constant gy = Constant
 If
we apply this to the example to the left, P is the same because the top and the
spigot are both exposed to atmospheric pressure. Also, as long as
the diameter of the can is much larger than the spigot, v2 will be
approximately zero. If
we apply this to the example to the left, P is the same because the top and the
spigot are both exposed to atmospheric pressure. Also, as long as
the diameter of the can is much larger than the spigot, v2 will be
approximately zero.
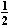  v12
+ v12
+  gy1 = gy1 =  gy2 gy2
or
v1 = ( 2g ( y2
- y1 ) ) 1/2 also called Torricelli's
theorem
This special case was discovered a century earlier.
Another special case exist when there is no appreciable
difference in height.
P1 + 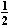  v12
= P2 + v12
= P2 + 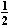  v22 v22
This equation shows why the pressure is high when the
velocity is low and why the pressure is low when the pressure is high.

When a ping pong ball is placed over the opening to a hair
dryer, the ball remains centered at all times even when the hair dryer is
tilted.
Of course, if tilted sufficiently, the ball will drop.
The faster the air travels, the more the dryer can be tilted until the ball
drops.
As the ball moves off center, the pressure will be less
toward the center and more toward the outside. This pushes the ball more
toward the center.
 It
also explains how a wing works. Since the distance traveled across the top
is greater than the distance traveled under the wing, the air must travel faster
over the wing. It
also explains how a wing works. Since the distance traveled across the top
is greater than the distance traveled under the wing, the air must travel faster
over the wing.
Since the air is moving faster it has the lower press.
Since the pressure is less on the top of the wing, the wing has lift.

Bernoulli's principle also explain how a sailboat can sail
into the wind.
The wind speed increases in the narrow space between the two
sails. Thus the atmospheric pressure behind the sail is greater than the
reduced pressure in front of the sail. The mainsail is set an an angle
midway between the wind direction and the keel. The net force on the sail
acts nearly perpendicular to the sail. This would tend to move the boat
sideways. The keel extends vertically downward beneath the water.
The water exerts a force on the keel nearly perpendicular to the keel. The
resultant of these two forces is almost directly forward.

A venturi tube is essentially a pipe with a narrow
constriction. A carburetor is an example of a venturi tube. As the
air speeds up as it enters the constriction, the pressure decreases. This
sucks the gasoline from the reservoir and puts it in the gaseous phase.
This makes it burn better in the cylinder.
Modern cars use fuel injectors which use a pump to push the
gasoline through an opening designed to separate it into a mist. The
smaller the gasoline droplets, the better it burns.

The chimney to the right also works partially because of
Bernoulli's Principle. As wind passes over the narrow opening at the top,
the lower pressure sucks the smoke up the chimney. It also rises because
hot air is less dense than cold air.
Table of Contents
Problems
| 1. |
What is the lift due to Bernoulli's
Principle on a wing of 70.0 m2 area if the air passes over the
top and bottom surfaces at speeds of 340. m/s and 290. m/s
respectively?
|
| 2. |
A can has an inside diameter of 12.2
cm. (a) How far below the water level do you want make a
0.0500 cm diameter hole to have a velocity of 2.25 m/s?
(b) How far must the water drop for the speed to drop by 1/2?
|
| 3. |
If the wind blows at 200. km/h over your
house during Hurricane Bonnie, what is the net force on the roof if the
area is 288 m2?
|
| 4. |
Wind at 20.0 km/h blows over the 12.0 cm
diameter opening of a chimney. The box where the fuel burns is
1.00 m x 1.50 m. What is the pressure
difference in the chimney? |
Table of Contents
Answers
| 1. |
What is the lift due to Bernoulli's
Principle on a wing of 70.0 m2 area if the air passes over the
top and bottom surfaces at speeds of 340. m/s and 290. m/s
respectively?
|
|
Pb +   vb2
= Pt + vb2
= Pt +   vt2
Solve for Pb - Pt. vt2
Solve for Pb - Pt.
Pb - Pt
=   vt2
- vt2
-   vb2 vb2
Pb - Pt
=  x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 340. m s -1 ) 2
- x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 340. m s -1 ) 2
-  x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 290. m s -1 ) 2 x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 290. m s -1 ) 2
Pb - Pt
= 1.58 x 107 N/m2
Force lift = 1.58 x 107
N/m2 x 70.0 m2 = 1.10 x 10
9 N
|
|
|
| 2. |
A can has an inside diameter of 12.2
cm. (a) How far below the water level do you want make a
0.0500 cm diameter hole to have a velocity of 2.25 m/s?
(b) How far must the water drop for the speed to drop by 1/2?
|
|
(a) v1 = ( 2g ( y2
- y1 ) ) 1/2
Solve for y2 - y1.
0.0500 cm is much smaller than 12.2 cm.
v12
( 2. 25 m s -1 )2
y2 - y1 = -------
= --------------------- = 0.258 m
2g 2 x 9.80 m s
-2
(b)
v12
( 1.13 m s -1 )2
y2 - y1 = -------
= --------------------- = 0.0651 m
2g 2 x 9.80 m s
-2
The water must drop from a difference of 0.258 m to a difference of 0.0651
m.
Thus the water must drop by
0.258 m - 0.0651 m or 0.193 m
|
|
|
| 3. |
If the wind blows at 200. km/h over your
house during Hurricane Bonnie, what is the net force on the roof if the
area is 288 m2?
|
|
200.
km 1
h
1000 m
----------- x ---------- x ------------
= 55.6 m s -1
1
h 3600
s 1 km
Pb +   vb2
= Pt + vb2
= Pt +   vt2
Solve for Pb - Pt. vb
= 0 vt2
Solve for Pb - Pt. vb
= 0
Pb - Pt
=   vt2
- vt2
-   vb2 vb2
Pb - Pt
=  x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 55.6 m s -1 ) 2
- x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 55.6 m s -1 ) 2
-  x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 0 m s -1 )
2 x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 0 m s -1 )
2
Pb - Pt
= 1.55 x 106 N/m2
Force lift = 1.55 x 106
N/m2 x 288 m2 = 4.45 x 10
8 N
|
|
|
| 4. |
Wind at 20.0 km/h blows over the 12.0 cm
diameter opening of a chimney. The box where the fuel burns is
1.00 m x 1.50 m. What is the pressure
difference in the chimney?
|
|
20.0
km 1
h
1000 m
----------- x ---------- x ------------
= 5.56 m s -1
1
h 3600
s 1 km
Pb +   vb2
= Pt + vb2
= Pt +   vt2
Solve for Pb - Pt. vb
= 0 vt2
Solve for Pb - Pt. vb
= 0
Pb - Pt
=   vt2
- vt2
-   vb2 vb2
Pb - Pt
=  x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 5.56 m s -1 ) 2
- x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 5.56 m s -1 ) 2
-  x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 0 m s -1 )
2 x 1.00
x 10 3 kg m -3 x ( 0 m s -1 )
2
Pb - Pt
= 1.55 x 104 N/m2 = 15.5 kPa
|
Table of Contents
|