all info found of wikipedia.org
pictures taken from google image search
|
biology assignments
12/02/07
bibliography
all info found of wikipedia.org pictures taken from google image search
11/30/07
Guard Cells
In plants, a specialized cell on the undersurface of leaves for controlling gas exchange and water loss. Guard cells occur in pairs and are shaped so that a pore, or stomata, exists between them. They can change shape with the result of the pore disappearing. During warm weather, when a plant is in danger of losing excessive water, the guard cells close.
Posted by brega2
at 1:25 PM EST
Updated: 12/02/07 5:52 PM EST Post Comment | Permalink | Share This Post
Sclerenchyma
Plant tissue whose function is to strengthen and support, composed of thick-walled cells that are heavily toughened. Opon maturity the cell inside dies, and only the cell walls remain. Sclerenchyma may be made up of one or two types of cells: sclereids, occurring singly or in small clusters, are often found in the hard shells of fruits and in seed coats, bark, and the stem cortex; fibres, frequently grouped in bundles, are elongated cells, often with pointed ends, associated with the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) of the plant. Some fibres provide useful materials, such as flax from Linum usitatissimum and hemp from Cannabis sativa.
Posted by brega2
at 1:22 PM EST
Updated: 12/02/07 5:53 PM EST Post Comment | Permalink | Share This Post
Collenchyma cells
Collenchyma tissue is composed of elongated cells with unevenly thickened walls. They provide structural support, particularly in growing shoots and leaves. Its growth is strongly affected by stress upon the plant. 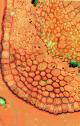
Posted by brega2
at 1:20 PM EST
Updated: 12/02/07 5:55 PM EST Post Comment | Permalink | Share This Post
Parenchyma
Parenchyma cells are thin-walled cells of the ground tissue that make up the bulk of most nonwoody structures. Parenchyma cells in between the epidermis and pericycle in a root or shoot constitute the cortex, and are used for storage of food. Parenchyma cells within the center of the root or shoot constitute the pith. Parenchyma cells in the ovary constitutes the nucellus and are brick-like in formation. Parenchyma cells in the leaf constitute the mesophyll; they are responsible for photosynthesis and they allow for the interchange of gases (info found on wikipeidia.org)
Posted by brega2
at 1:07 PM EST
Updated: 12/02/07 5:47 PM EST Post Comment | Permalink | Share This Post Newer | Latest | Older |
You are not logged in.
Log in
|