Canada
Dates when provinces and territories joinded the Confederation
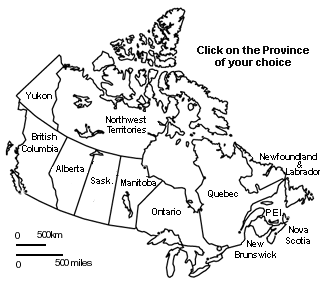
Provinces:
British Columbia
Alberta
Saskatchwan
Manitoba
Ontario
Quebec
New Bruinswick
Prince Edward Island
Nova Scotia
New Foundland
Territories:
Yukon
Northwest Territories
Nunavut
Major Cities
*Captial
**Capital City of Canada
B.C.
*Victoria
Vancouver
AB.
*Edmonton
Calgary
SASK.
*Regina
Saskatoon
MAN.
*Winnipeg
ONT.
*Toronto
**Ottawa
Que.
*Quebec City
Montreal
N.B.
*Fredriction
P.E.I.
*Charlotte Town
N.S.
*Halifax
Sydney
N.F.
*St. John
1867-
Ontario
Quebec
Nova Scotia
New Brunswick
1870-
Manitoba
Northwest Territories
1871-
British Columbia
1873-
Prince Edward Island
1898-
Yukon Territory
1905-
Alberta
Saskatchewan
1949-
Newfoundland
1999-
Nunavut
Aboriginal People
Aboriginal peoples developed a special relationship
with nature, since they depended on it for survival.
Those who lived on Canada's coasts depended on fishing
and hunting. Those who lived in central and eastern
Canada hunted and grew vegetable crops.
The Constitution Act of 1982 recognizes three main
groups of Aboriginal peoples in Canada: the First
Nations, the Inuit and the Métis. Today, there are
more than 50 different languages spoken by Aboriginal
peoples, most of which are spoken only in Canada.
The Aboriginal population is growing almost twice as
fast as the rest of the population in Canada.
Aboriginal peoples make up about three percent of all
Canadians, or roughly 790,000 people. About 69 percent
are First Nations, 26 percent are Métis and five
percent are Inuit.
First Nations
First Nations youth in traditional clothing
The term "First Nations" has been used since the 1970s
instead of "Indian." First Nations describes all
Aboriginal people in Canada who are not Inuit or
Métis. Different First Nations communities have
different languages, cultures and traditions,
depending largely on where they are located.
First Nations people living in eastern North America
invented bark canoes to travel on rivers and lakes.
Some First Nations people lived on the plains, and
moved with the buffalo herds, which they hunted for
food, clothing and tools. They made lightweight, solid
homes that were easy to move. These homes,
called "tepees," were made of poles arranged in a cone
shape and covered with animal skins.
Inuit
Inuit are Aboriginal people who live in Canada's
North, which includes Nunavut, the Northwest
Territories, Northern Quebec and Labrador. They have a
close connection with the land and all the plants and
animals that share it. They adjusted to the cold
northern weather and lived by hunting seals, whales,
caribou and polar bears. Some Inuit people still hunt
for food and clothing.
Métis
Many early French fur traders and some English traders
married First Nations women. Their descendants are
called the Métis people. The Métis, who developed
their own distinct culture on the Prairies, played an
important role in the fur trade.
Today, the majority of Métis people live in the
western regions of Canada.
The British and Canadian governments made many
agreements, or treaties, with the Aboriginal peoples
between 1701 and 1923. These treaties granted the
Aboriginal peoples certain rights and benefits in
exchange for giving up their title to the land. Each
treaty is unique and is seen as a solemn promise.
Aboriginal groups and the Canadian government are
still negotiating new agreements for land and other
rights. These modern agreements are known as land
The Canadian government continues to negotiate with
Aboriginal peoples so that they can regain control
over decisions that affect them and manage their own
affairs. This is known as self-government. Canada is
also working with them to improve their economic
situation and general quality of life.
Aboriginal peoples have unique histories, cultures and
languages. They continue to play an active role in
Canadian society.
Canada's Economy
Resource industries, including fishing, farming, mining, and forestry, have always played an important role in the economy of the Atlantic region.
The Atlantic fishery is the oldest industry in the region. Protecting the fish stocks and prventing overfishing is now a vital issue in the Atlantic provinces.
Today, most manufacturing in the Atlantic region involves processing timber,fish,and agricultural crops.
In Prince Edward Island, New Bruinswick,and Nova Scotia, agricultural crops such as potatoes and fruit are sold fresh or frozen food products in Canada and to other countries. New Bruinswick and Nova Scotia have extensice forests that allow them to produce valuable products like pulp, lumber,and paper. Forest products are the most valuable manufacturing industry in New Bruinswick. Newfoundland, traditionally dependent on the fishing industry, is develpoing its otehr natural resources such as oil,nickel,cobalt, and copper.
Service industries are also very important to the Atlantic economy and the majority of people have jobs delievering these services. As in the rest of Canada, more people work in government,banking, and finacial and personal services than in traditional resource indurstries.
The Atlantic Ocean is also important as a tourist resource in the region. The spectacular scenery and the beutiful coastlines and beaches attract thousands of tourists to the Atlantic provinces each year, creating many service industry jobs.
 Return to home..
Return to home..