These are the steps in aerobic respiration
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway which occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and during which glucose is oxidized anaerobically to form pyruvic acid.
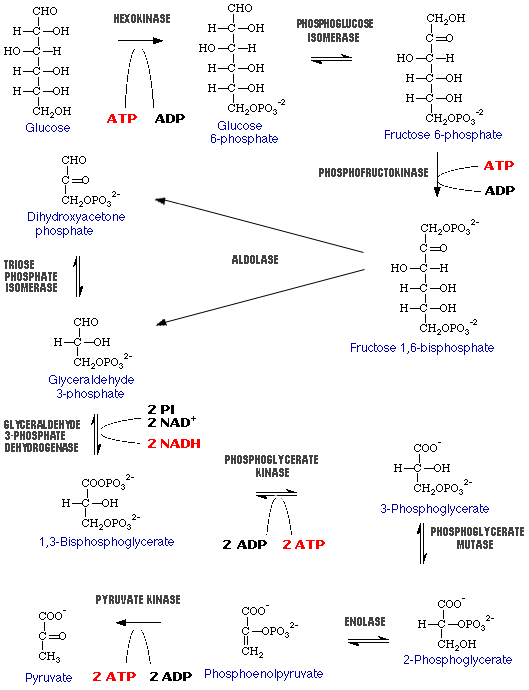 Glycolysis Pathway
Glycolysis Pathway
Kreb Cycle
Krebs cycle is a chemical cycle involving eight steps that completes the metabolic breakdown of glucose molecules to carbon dioxide; occurs wihin the mitochondrion; the second major stage in cellular respiration. Also called citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle.
 Kreb Cycle
Kreb Cycle
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactrions of the electron transport chain. It has two components, the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Electron Transport Chain
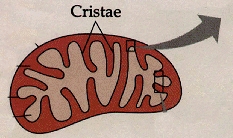
This represents the electron transport chain. Electrons moves down a chain of proteins and electon acceptors down to oxygen because each step is inscreasingly more electonegative. By doing this it creates a protein gradient across the membrane in the mitochondria so that H+ can produce ATP in chemiosmosis. This takes place in the cristae of the mitochondria.
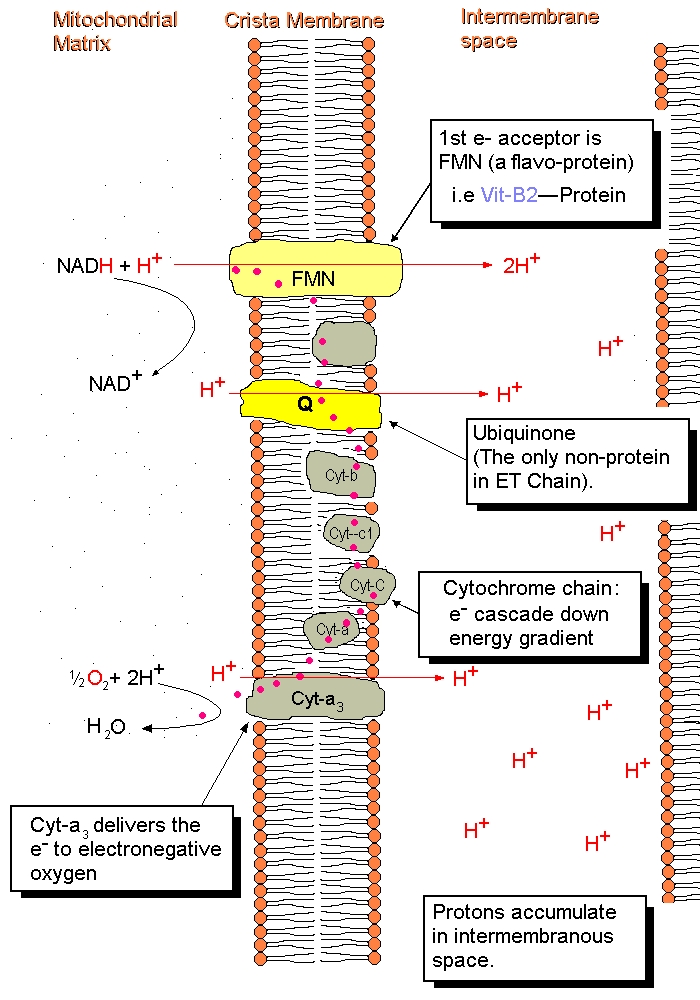 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the ability of certain membranes to use chemical energy to pump hydrogen ions and then harness the energy stored in the H+ gradient to drive cellular work, including ATP synthesis. A chemiosmotic gradient is the combined electrostatic and osmotic concentration gradient generated by the electron- transport chains of mitochondria; the energy in this gradient is used, for the most part, to synthesize ATP.
ATP synthase makes ATP as the H+ ions move from one side of the membrane to the other and the ATP synthase spins like a turbine to produce ATP.
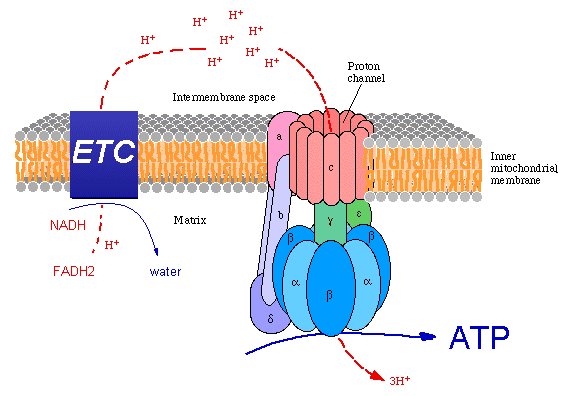
 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration takes place when the body needs ATP but it does not have enough oxygen to use aerobic respiration. Of the above processes, only glycolysis does not need oxygen so only glycolysis can produce ATP in the absense of aerobic respiration. Without oxygen the body must rely on fermintation to provide energy to the body
Fermintation
Fermentation is the anaerobic production of alcohol, lactic acid or similar compounds from carbohydrate resulting from glycolysis.
Humans ferment lactic acid in muscles where oxygen becomes depleted, resulting in localized anaerobic conditions. This lactic acid causes the muscle stiffness couch-potatoes feel after beginning exercise programs. The stiffness goes away after a few days since the cessation of strenuous activity allows aerobic conditions to return to the muscle, and the lactic acid can be converted into ATP via the normal aerobic respiration pathways.
 Cellular Fermentation
Cellular Fermentation
This is a link to a page which animates respiration as well as some other links
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Animation Aerobic Respiration Cellular Respiration Overview Lots of good stuff
