Breast Cancer...
INTRODUCTION:


Understanding Cancer
Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the organs of the body. Normally, cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When cells grow old, they die, and new cells take their place.
Sometimes this orderly process goes wrong. New cells form when the body does not need them, and old cells do not die when they should. These extra cells can form a mass of tissue called a growth or tumor.
Not all tumors are cancer. Tumors can be benign or malignant:
Benign tumors are not cancer:
Benign tumors are rarely life-threatening.
Usually, benign tumors can be removed, and they seldom grow back.
Cells from benign tumors do not spread to tissues around them or to other parts of the body.
Malignant tumors are cancer:
Malignant tumors generally are more serious than benign tumors. They may be life-threatening.
Malignant tumors often can be removed, but they can grow back.
Cells from malignant tumors can invade and damage nearby tissues and organs. Also, cancer cells can break away from a malignant tumor and enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system. That is how cancer cells spread from the original cancer (primary tumor) to form new tumors in other organs. The spread of cancer is called metastasis.
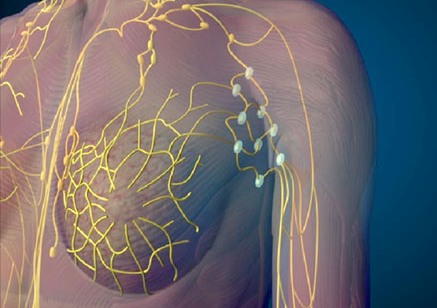
When breast cancer cells enter the lymphatic system, they may be found in lymph nodes near the breast.
The cancer cells also may travel to other organs through the lymphatic system or bloodstream. When cancer spreads (metastasizes), the new tumor has the same kind of abnormal cells and the same name as the primary tumor. For example, if breast cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are breast cancer cells. The disease is metastatic breast cancer, not bone cancer. It is treated as breast cancer, not as bone cancer. Doctors sometimes call the new tumor "distant" or metastatic dise