_______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________
Page 10
FLYING BC - January 2002
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
periodical laboratory investigations can identify pilots at risk of and experiencing early or pre-diabetic states.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS OF DIABETES USUALLY DEVELOP LATE
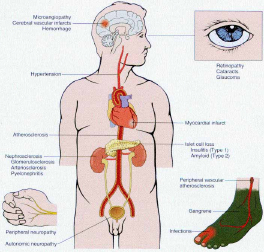
When diabetes is fully manifest, symptoms include excessive thirst, increased urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and weight loss. In women with diabetes, vaginal yeast infections are common. Fungal infections may occur under the breasts or in the groin. Severe gum problems, worsening vision, itching, impotence, and unusual sensations, such as tingling or burning, in the extremities may also be signs of Type 2 diabetes. However, most of these symptoms and signs actually develop long after the disease begins and complications are already developed.
WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES?
There are a number of complications of diabetes that are particularly hazardous for pilots. These include macrovascular complications such as heart attack and stroke, microvascular complications such as blindness and gangrene, and neurological complications such as peripheral neuropathies (loss of sensation balance and coordination).
VASCULAR COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES
Diabetes injures large and small
blood vessels throughout the body. More than 60 per cent of diabetics die of heart attacks and a further 25 per cent die of strokes. A recent study revealed that diabetics without heart disease at the beginning of a seven-year study had the same risk of heart attack as patients who already had heart disease.
DIABETES ACCELERATES THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEART DISEASE
The problem with diabetes goes further than mere hyperglycemia: diabetes is known to adversely affect blood cholesterol and triglycerides, increase blood clotting and elevate blood pressure. Diabetics with high cortisol levels, a stress hormone, are known to have a higher risk of stroke due to the interplay between diabetes and hypertension.
NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES
Approximately 50 per cent of diabetics develop neuropathy after 25 years. Neuropathy is caused by abnormalities developing in nervous tissues as a result of abnormal glucose metabolism. Typically, the nerves in the distal extremities are affected first, causing a "stocking and glove" distribution of numbness and loss of pain sensation. As a result, injuries and infections that normally would alert a patient's attention and response through the experience of pain continue to develop and worsen before a diabetic patient takes notice, often too late. In addition, healing of a burnt or injured extremity is complicated by poor blood supply to the extremity.
SEVERAL DIABETIC COMPLICATIONS CONSPIRE TO PRODUCE SERIOUS DISEASE
Eventually, the combination of neuropathy, vasculopathy and repetitive injury or infection results in gangrene and amputation of the extremity.
Extensive evidence points to the efficacy of early identification, treatment and prevention of diabetic complications through advanced team-based diabetic clinic management strategies. But prevention remains the most effective way to prevent complications.
EYE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES
Diabetic eye complications are the leading cause of blindness in people less than 75-years-old and include diabetic retinopathy, cataracts and glaucoma. Initially, diabetic retinopathy is caused by microvascular changes resulting in small hemorrhages into the retina, the light sensitive area of the eye. Eventually, repeated damage results in new blood vessel formation as a compensatory response and vision becomes seriously compromised when large hemorrhages or retinal detachments occur as a result.
Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness in people less than 75-years-old.
KIDNEY DISEASE AND OTHER DIABETIC COMPLICATIONS
Kidney disease is a very serious complication of diabetes. The risk for this complication is compounded by the presence of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and problems in the urinary tract. Symptoms include swelling in the feet and ankles, fatigue, and pale skin colour. Many diabetics eventually require dialysis or kidney transplantation.
The Diabetic Pilot: Prevention and Management - Part 1


